Profit is the financial gain realized when revenue exceeds expenses, serving as a key indicator of business success and sustainability. Maximizing profit involves strategic management of costs, pricing, and market positioning to enhance overall performance. Discover how you can boost your profit margins and drive financial growth by exploring the detailed insights in this article.
Table of Comparison
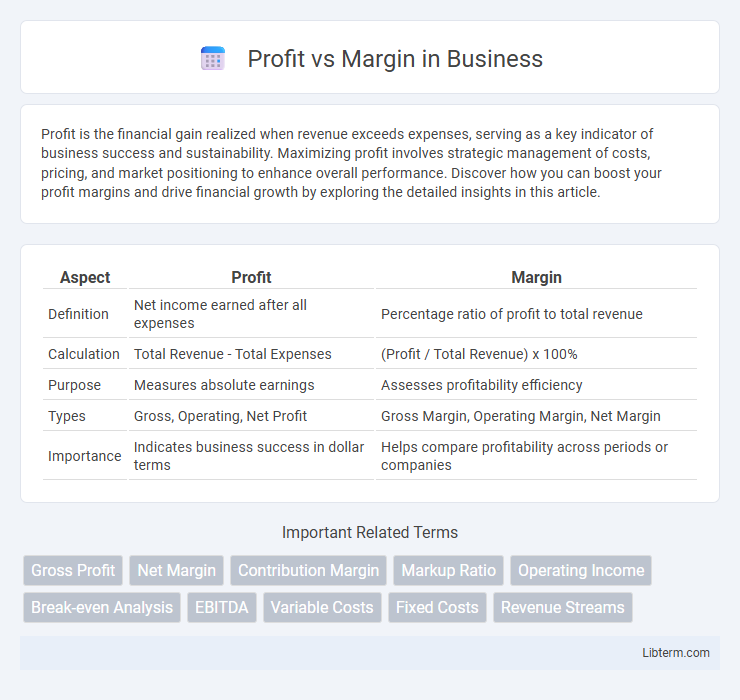
| Aspect | Profit | Margin |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Net income earned after all expenses | Percentage ratio of profit to total revenue |
| Calculation | Total Revenue - Total Expenses | (Profit / Total Revenue) x 100% |
| Purpose | Measures absolute earnings | Assesses profitability efficiency |
| Types | Gross, Operating, Net Profit | Gross Margin, Operating Margin, Net Margin |
| Importance | Indicates business success in dollar terms | Helps compare profitability across periods or companies |
Understanding Profit: Definition and Importance
Profit represents the financial gain realized when revenue exceeds expenses during a specific period, serving as a key indicator of a company's overall financial health. Understanding profit is crucial for businesses to evaluate operational efficiency, make informed investment decisions, and ensure long-term sustainability. Accurate profit analysis allows companies to identify cost-saving opportunities and optimize pricing strategies to maximize returns.
What Is Margin? Explaining the Key Concept
Margin represents the percentage of revenue that remains after covering the cost of goods sold, indicating the profitability of each sale. It is calculated by subtracting the cost of goods sold from total sales and then dividing by total sales, expressed as a percentage. Understanding margin helps businesses evaluate pricing strategies and operational efficiency to maximize profit potential.
Profit vs Margin: Core Differences
Profit represents the absolute financial gain after deducting all expenses from total revenue, while margin indicates the percentage of revenue that remains as profit, reflecting profitability relative to sales. Profit provides a concrete dollar amount showing total earnings, whereas margin offers insight into efficiency and cost control by comparing profit against sales revenue. Understanding the core difference between profit and margin helps businesses evaluate performance using both total income and profit ratio metrics.
Types of Profit: Gross, Operating, and Net
Gross profit represents revenue minus the cost of goods sold, highlighting the efficiency of production and sales processes. Operating profit deducts operating expenses such as wages, rent, and utilities from gross profit, reflecting the profitability of core business operations. Net profit accounts for all expenses, including taxes and interest, showcasing the company's overall financial health and profitability.
Breakdown of Common Margin Types
Gross margin indicates the percentage of revenue remaining after deducting the cost of goods sold, reflecting the efficiency of production and pricing strategies. Operating margin measures the profitability from core business operations by subtracting operating expenses, providing insight into operational efficiency. Net margin represents the overall profitability after all expenses, taxes, and interest, offering a comprehensive view of financial health.
How Profit and Margin Impact Business Decisions
Profit represents the absolute financial gain a business makes after all expenses, while margin measures profitability as a percentage of revenue, highlighting efficiency in cost management. Businesses use profit to assess overall financial health and sustainability, influencing investment and operational strategies. Margin analysis guides pricing, cost control, and competitive positioning to maximize long-term profitability.
Calculating Profit: Essential Formulas
Calculating profit involves subtracting total costs from total revenue, expressed as Profit = Revenue - Costs, where costs include fixed and variable expenses. Gross profit specifically deducts the cost of goods sold (COGS) from revenue, highlighting production efficiency without operational expenses. Understanding profit margins, such as gross margin (Gross Profit / Revenue x 100%) and net margin (Net Profit / Revenue x 100%), helps assess profitability relative to sales and guides financial decision-making.
Margin Calculation: Step-by-Step Guide
Margin calculation involves determining the percentage difference between revenue and cost to assess profitability efficiency. To calculate margin, subtract the cost of goods sold (COGS) from total revenue, then divide the result by total revenue and multiply by 100 to express it as a percentage. This step-by-step method helps businesses evaluate their pricing strategy and operational effectiveness by highlighting how much profit is retained from each dollar of sales.
Common Mistakes: Confusing Profit with Margin
Confusing profit with margin is a common mistake that leads to incorrect financial analysis and business decisions. Profit refers to the absolute amount of money earned after all expenses are deducted, while margin represents the percentage of revenue that remains as profit. Understanding the distinction between gross margin, operating margin, and net profit margin is crucial to accurately assessing a company's financial health and pricing strategies.
Strategies to Improve Both Profit and Margin
Implementing dynamic pricing strategies and reducing variable costs are key methods to boost profit and margin simultaneously. Streamlining operations through automation and negotiating better terms with suppliers can also enhance overall profitability and increase margin percentages. Focusing on high-margin products and cross-selling opportunities maximizes revenue while maintaining cost efficiency.
Profit Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com