Variable costs fluctuate in direct proportion to production levels, impacting your overall expenses as output changes. Understanding these costs is essential for managing budgets, pricing strategies, and profitability. Explore the rest of the article to learn how to effectively control variable costs in your business.
Table of Comparison
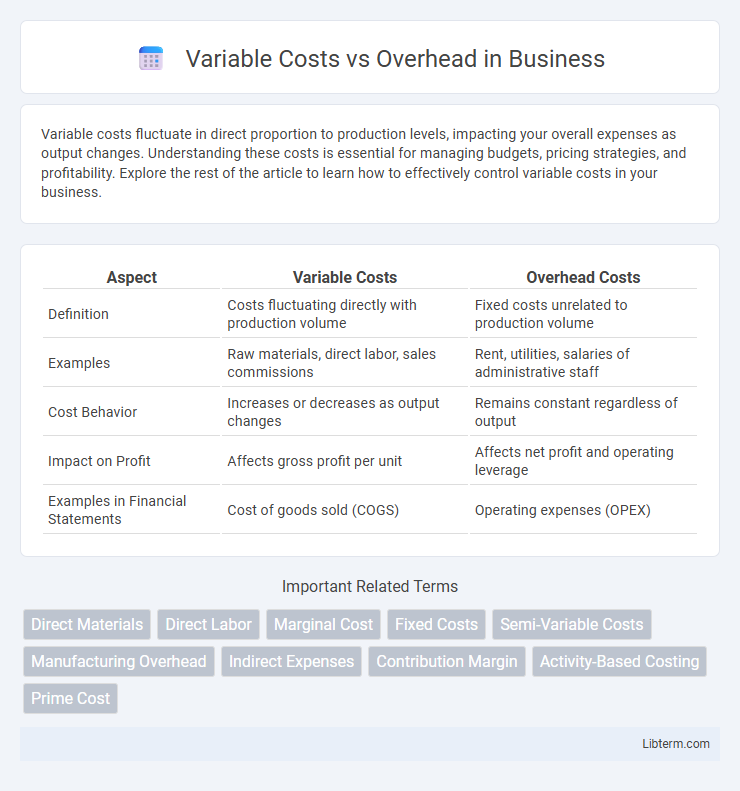
| Aspect | Variable Costs | Overhead Costs |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Costs fluctuating directly with production volume | Fixed costs unrelated to production volume |
| Examples | Raw materials, direct labor, sales commissions | Rent, utilities, salaries of administrative staff |
| Cost Behavior | Increases or decreases as output changes | Remains constant regardless of output |
| Impact on Profit | Affects gross profit per unit | Affects net profit and operating leverage |
| Examples in Financial Statements | Cost of goods sold (COGS) | Operating expenses (OPEX) |
Understanding Variable Costs
Variable costs fluctuate directly with production volume, including expenses like raw materials, direct labor, and utility costs tied to manufacturing output. These costs are essential for managers to monitor because they impact profit margins and pricing strategies as production scales. Unlike fixed overhead costs, which remain constant regardless of output, understanding variable costs enables more accurate budgeting and efficient resource allocation.
Defining Overhead Expenses
Overhead expenses refer to the ongoing indirect costs of operating a business that are not directly tied to producing goods or services, such as rent, utilities, and administrative salaries. These fixed or semi-fixed costs remain relatively constant regardless of production volume, distinguishing them from variable costs that fluctuate with output. Properly identifying and managing overhead expenses is critical for accurate budgeting, cost control, and pricing strategies.
Key Differences Between Variable Costs and Overhead
Variable costs fluctuate directly with production volume, including expenses like raw materials and direct labor, while overhead consists of fixed or semi-fixed expenses such as rent, utilities, and salaries that do not change with output. Variable costs impact unit cost calculations and profitability on a per-product basis, whereas overhead is allocated across total production to assess overall business efficiency. Understanding these distinctions aids in accurate budgeting, cost control, and pricing strategies.
Examples of Variable Costs in Business
Variable costs in business include expenses that fluctuate with production volume, such as raw materials, direct labor, and sales commissions. For instance, a manufacturing company incurs costs for steel and packaging proportional to units produced, while a retail business's inventory purchases vary with sales demand. These costs contrast with overhead, which remains fixed regardless of output levels.
Types of Overhead: Fixed vs. Variable Overheads
Variable costs fluctuate directly with production volume, while overhead encompasses all fixed and variable indirect expenses necessary to run a business. Fixed overhead includes rent, salaries, and insurance, which remain constant regardless of output, whereas variable overhead changes with activity levels, such as utilities and maintenance. Understanding the distinction between fixed and variable overhead is crucial for precise cost control and accurate financial forecasting.
Impact of Variable Costs on Profit Margins
Variable costs directly affect profit margins because they fluctuate with production volume, increasing expenses as output rises, which reduces per-unit profitability if sales prices remain constant. Managing variable costs such as raw materials, direct labor, and packaging is crucial for maintaining healthy profit margins, especially in industries with tight pricing strategies. In contrast, overhead expenses remain fixed regardless of production level, making variable cost control vital for optimizing overall financial performance.
How Overhead Affects Business Operations
Overhead costs, including rent, utilities, and administrative salaries, directly impact a business's operational efficiency and profit margins by representing fixed expenses that must be covered regardless of production volume. Unlike variable costs, which fluctuate with output, overhead remains constant, imposing a baseline financial burden that influences pricing strategies and cash flow management. Effective control and allocation of overhead expenses are crucial for sustaining profitability and enabling strategic decision-making in resource utilization.
Methods to Calculate Variable Costs and Overhead
Variable costs are calculated by multiplying the cost per unit by the number of units produced, using methods such as the high-low method or scatter plot analysis to distinguish variable expenses from fixed costs. Overhead costs are allocated using approaches like activity-based costing (ABC) or traditional absorption costing, which assign indirect expenses based on activities or production volume. Accurate separation of variable costs from overhead enables precise budgeting and cost control in managerial accounting.
Strategies to Control Variable Costs and Overhead
Implementing budget tracking and regular cost analysis effectively controls variable costs by identifying fluctuations tied directly to production output. Streamlining operational processes and leveraging technology minimizes overhead expenses, such as administrative and facility costs, without compromising business functions. Negotiating supplier contracts and optimizing resource allocation further contribute to maintaining a balanced cost structure for sustained financial efficiency.
Optimizing Cost Structure for Business Efficiency
Variable costs fluctuate directly with production volume, including expenses like raw materials and direct labor, while overhead comprises fixed costs such as rent, utilities, and administrative salaries that remain constant regardless of output. Optimizing cost structure for business efficiency involves carefully managing variable costs to align with sales cycles and rigorously controlling overhead to minimize waste without compromising operational capacity. Leveraging data analytics and cost management tools enables businesses to identify cost drivers and implement strategies that balance scalability with financial stability.
Variable Costs Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com