A joint venture combines resources and expertise from two or more businesses to pursue a specific project or goal, allowing each party to share risks and rewards. This strategic partnership can accelerate growth, enter new markets, and enhance innovation by leveraging complementary strengths. Discover how your business can benefit from joint ventures by exploring the full article on effective collaboration strategies.
Table of Comparison
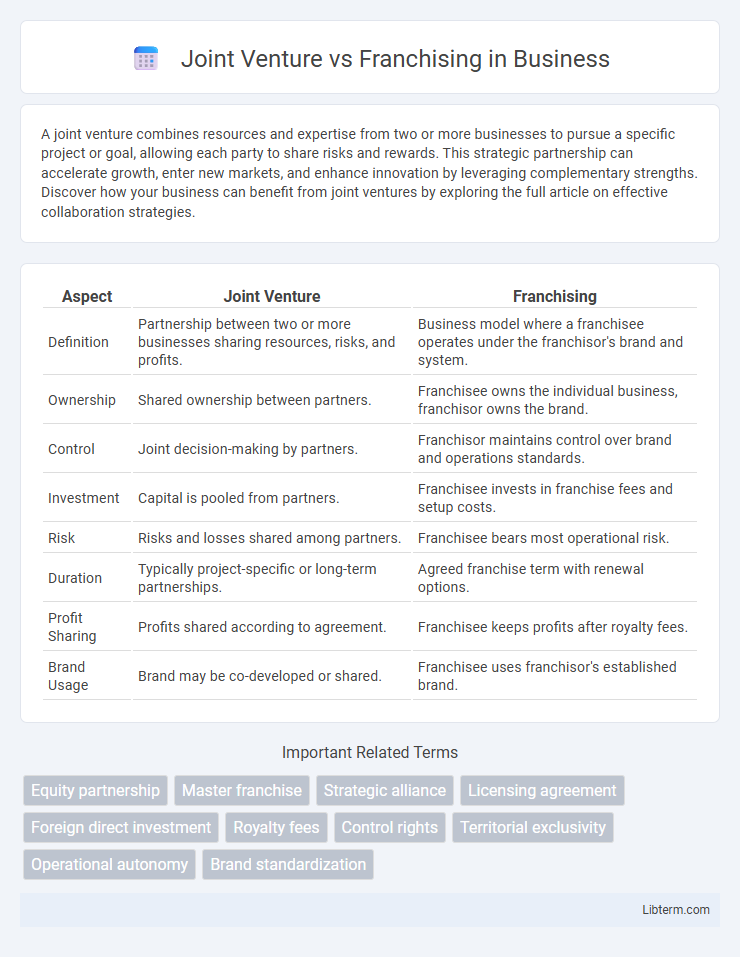
| Aspect | Joint Venture | Franchising |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Partnership between two or more businesses sharing resources, risks, and profits. | Business model where a franchisee operates under the franchisor's brand and system. |
| Ownership | Shared ownership between partners. | Franchisee owns the individual business, franchisor owns the brand. |
| Control | Joint decision-making by partners. | Franchisor maintains control over brand and operations standards. |
| Investment | Capital is pooled from partners. | Franchisee invests in franchise fees and setup costs. |
| Risk | Risks and losses shared among partners. | Franchisee bears most operational risk. |
| Duration | Typically project-specific or long-term partnerships. | Agreed franchise term with renewal options. |
| Profit Sharing | Profits shared according to agreement. | Franchisee keeps profits after royalty fees. |
| Brand Usage | Brand may be co-developed or shared. | Franchisee uses franchisor's established brand. |
Introduction to Joint Venture and Franchising
A joint venture is a strategic partnership where two or more businesses pool resources to achieve a specific objective while remaining independent entities, sharing risks, profits, and management responsibilities. Franchising involves a franchisor granting a franchisee the right to operate a business using its brand, systems, and support in exchange for fees and royalties, enabling rapid market expansion with limited capital investment. Both models facilitate business growth but differ in control, risk distribution, and operational involvement.
Definition and Key Features of Joint Venture
A joint venture is a strategic alliance where two or more parties create a new business entity by pooling resources, sharing risks, and combining expertise to achieve specific objectives. Key features include shared ownership, joint control and decision-making, and mutual contribution of capital, technology, or market access. Unlike franchising, where a franchisee operates under a franchisor's brand and business model, a joint venture involves active collaboration and profit-sharing among partners within a newly formed enterprise.
Definition and Key Features of Franchising
Franchising is a business model where a franchisor grants a franchisee the rights to operate a business using the franchisor's brand, products, and operational methods. Key features include standardized business practices, brand consistency, ongoing support and training from the franchisor, and payment of initial fees plus ongoing royalties by the franchisee. This model allows rapid expansion and reduces financial risk for the franchisor while providing franchisees with a proven business system.
Legal Structure and Ownership Differences
Joint ventures involve creating a new legal entity owned by two or more parties sharing equity, risks, and profits based on agreed terms. Franchising operates under a licensing agreement where the franchisor retains ownership and grants the franchisee rights to use its brand and business model in exchange for fees. Legal implications include joint venture partners sharing liability and decision-making, while franchisees operate independently but must comply with franchisor standards.
Capital Investment and Financial Commitment
Joint ventures require substantial capital investment from all partners, sharing both financial risks and rewards, often involving complex funding arrangements to support business operations. Franchising demands a lower initial financial commitment, typically involving franchise fees and ongoing royalty payments, allowing franchisees to leverage established brand equity with reduced upfront capital. Investors seeking deeper control and equity stakes often prefer joint ventures, whereas franchising suits those prioritizing lower financial exposure and operational support.
Control, Management, and Decision-Making
Joint ventures involve shared control, management, and decision-making between partners, allowing for collaborative strategy and resource pooling. Franchising grants the franchisee operational independence but under strict control and guidelines set by the franchisor, limiting the franchisee's autonomy in management and decisions. Control in joint ventures is mutual with joint accountability, whereas franchising enforces a hierarchical control structure with the franchisor retaining ultimate decision authority.
Risk Sharing and Profit Distribution
Joint ventures enable partners to share risks by pooling resources and responsibilities, with profit distribution typically aligned to each partner's equity share and contribution agreement. Franchising limits the franchisor's risk exposure as the franchisee invests capital and manages operations, while the franchisor earns profits mainly through royalties and fees based on sales performance. In joint ventures, risks and profits are mutually shared, whereas franchising offers a more scalable model with asymmetric risk and income streams.
Branding, Marketing, and Operational Support
Joint ventures allow partners to combine brand equity and share marketing strategies, creating a unified market presence while leveraging local expertise for operational support. Franchising enables rapid brand expansion through standardized marketing campaigns and proven operational systems, ensuring consistency across multiple locations. Both models provide distinct advantages in branding and operational support, with joint ventures fostering collaborative innovation and franchising offering centralized control.
Pros and Cons: Joint Venture vs Franchising
Joint ventures offer shared control and pooled resources, enabling partners to leverage complementary strengths and enter new markets with reduced risk, but they often involve complex management structures and potential conflicts. Franchising allows rapid expansion using franchisees' capital and local market knowledge while maintaining brand control, yet it can result in less operational control and variability in quality. Both models provide strategic growth options but differ in investment risk, control, and partnership dynamics.
Choosing the Right Model: Factors to Consider
Choosing between a joint venture and franchising depends on control preferences, financial investment, and risk tolerance. Joint ventures offer shared ownership and decision-making, suitable for companies seeking collaboration and resource pooling, while franchising provides a scalable model with standardized brand usage and lower capital commitment. Key factors include desired level of operational control, market knowledge, and long-term growth strategies to align the choice with business objectives.
Joint Venture Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com