Direct investment involves acquiring a significant ownership stake in a foreign company or establishing operations abroad, aiming for long-term control and influence. This strategy can enhance global presence, increase market access, and generate substantial returns but requires careful risk assessment and resource commitment. Explore the rest of the article to understand how direct investment can shape your international business success.
Table of Comparison
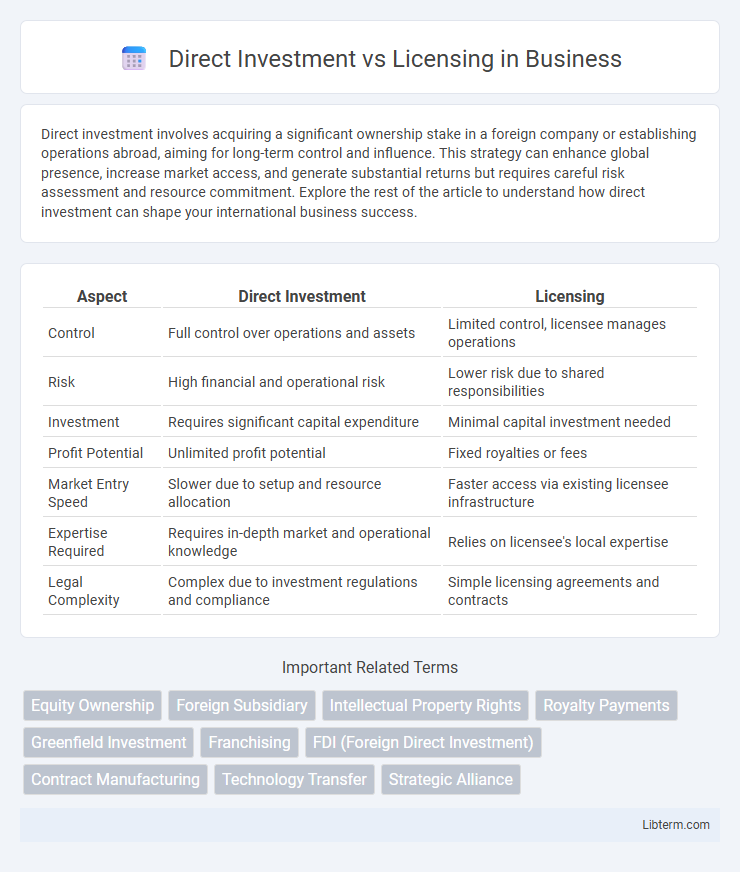
| Aspect | Direct Investment | Licensing |
|---|---|---|
| Control | Full control over operations and assets | Limited control, licensee manages operations |
| Risk | High financial and operational risk | Lower risk due to shared responsibilities |
| Investment | Requires significant capital expenditure | Minimal capital investment needed |
| Profit Potential | Unlimited profit potential | Fixed royalties or fees |
| Market Entry Speed | Slower due to setup and resource allocation | Faster access via existing licensee infrastructure |
| Expertise Required | Requires in-depth market and operational knowledge | Relies on licensee's local expertise |
| Legal Complexity | Complex due to investment regulations and compliance | Simple licensing agreements and contracts |
Introduction to Direct Investment and Licensing
Direct investment involves a company establishing or acquiring physical assets in a foreign country, allowing for full operational control and direct market presence. Licensing permits a firm to grant rights to a foreign entity to produce or sell its products, leveraging local expertise while minimizing risk and capital commitment. Both strategies serve as entry methods into international markets but differ in control, investment level, and risk exposure.
Key Definitions: Direct Investment vs Licensing
Direct investment involves a company committing capital to establish or acquire business operations in a foreign country, gaining full control over assets and management. Licensing permits a company (licensor) to grant another party (licensee) the rights to produce, use, or sell its intellectual property, technology, or products under agreed terms without direct involvement in foreign operations. These key distinctions highlight direct investment's emphasis on ownership and control versus licensing's reliance on contractual agreements for market entry.
Market Entry Strategies: An Overview
Direct investment enables companies to establish full control over foreign operations, facilitating deeper market penetration and long-term presence while bearing higher risks and capital requirements. Licensing allows firms to grant local partners the rights to produce or sell products, offering lower risk and investment but limited control and profit potential. These contrasting market entry strategies depend on factors like resource availability, risk tolerance, and desired level of market involvement.
Advantages of Direct Investment
Direct investment offers greater control over operations, enabling companies to maintain proprietary technology, consistent product quality, and strategic decision-making aligned with corporate goals. It facilitates deeper market penetration and stronger brand presence through full ownership of local facilities, leading to higher long-term profits and competitive advantages. Furthermore, direct investment allows for better responsiveness to market changes and customer preferences, enhancing overall business flexibility and growth potential.
Advantages of Licensing
Licensing offers companies a low-risk entry strategy by allowing them to leverage established local partners' market knowledge and distribution networks, which reduces upfront capital investment and operational expenses. It enables rapid international expansion with minimal legal complexities compared to direct investment, facilitating faster access to foreign markets. Licensing also provides an efficient way to monetize intellectual property, such as patents or trademarks, while retaining control over technology and brand reputation.
Risks and Challenges of Direct Investment
Direct investment involves significant financial exposure and operational risks due to full ownership and control, including market entry barriers, political instability, and currency fluctuations. Companies face challenges in managing local regulations, cultural differences, and supply chain complexities, which can impact profitability and strategic objectives. Unlike licensing, direct investment demands substantial resource commitment and longer timeframes before returns are realized, increasing vulnerability to economic downturns and competitive pressures.
Risks and Challenges of Licensing
Licensing involves granting permission to another company to use intellectual property, which carries risks such as loss of control over technology and potential misuse or misrepresentation of brand. Challenges include difficulty in enforcing contract terms across different jurisdictions, exposure to less reliable partners, and limited ability to adapt quickly to market changes. These risks often result in lower profit margins and potential conflicts that may harm long-term strategic goals.
Factors Influencing the Choice Between Direct Investment and Licensing
Factors influencing the choice between direct investment and licensing include control over intellectual property, resource commitment, and market risk tolerance. Direct investment offers greater control and potential for higher returns but requires significant capital and operational involvement, while licensing involves lower risk and investment yet entails less control and profit sharing. Market conditions, legal environment, and company strategic goals also play crucial roles in determining the optimal entry strategy.
Case Studies: Real-World Examples
Case studies reveal that direct investment offers firms like Tesla control over manufacturing and branding, enabling rapid innovation and market adaptation. Licensing arrangements, exemplified by IKEA's global franchising model, allow companies to expand with lower capital risk while leveraging local expertise. Analysis of these examples highlights trade-offs between resource commitment and market flexibility in international business strategies.
Conclusion: Which Market Entry Mode Is Optimal?
Direct investment offers greater control, higher profit potential, and deeper market presence, making it optimal for firms seeking long-term strategic commitment and competitive advantage. Licensing provides lower risk and requires less capital expenditure, suitable for companies aiming for quick market access with minimal investment. The optimal market entry mode depends on factors like resource availability, market knowledge, risk tolerance, and strategic objectives.
Direct Investment Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com