A call option grants you the right, but not the obligation, to purchase an underlying asset at a predetermined price before a specific expiration date, offering potential for profit if the asset's value rises. This financial instrument is widely used for speculation, hedging, and leverage in various markets like stocks, commodities, and indices. Discover how call options can enhance your investment strategy by reading the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
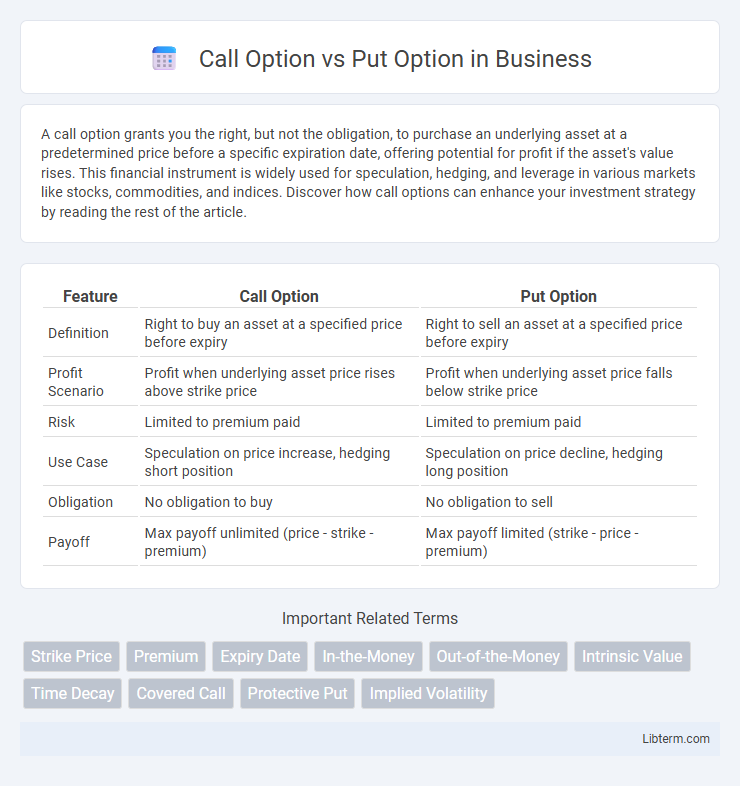
| Feature | Call Option | Put Option |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Right to buy an asset at a specified price before expiry | Right to sell an asset at a specified price before expiry |
| Profit Scenario | Profit when underlying asset price rises above strike price | Profit when underlying asset price falls below strike price |
| Risk | Limited to premium paid | Limited to premium paid |
| Use Case | Speculation on price increase, hedging short position | Speculation on price decline, hedging long position |
| Obligation | No obligation to buy | No obligation to sell |
| Payoff | Max payoff unlimited (price - strike - premium) | Max payoff limited (strike - price - premium) |
Introduction to Options: Call vs Put
Call options give the buyer the right to purchase an underlying asset at a specified strike price before the expiration date, enabling profit from asset price increases. Put options provide the buyer the right to sell the underlying asset at a predetermined strike price, protecting against or profiting from price declines. Both call and put options serve as essential tools for hedging, speculation, and portfolio management in options trading.
What is a Call Option?
A call option is a financial contract that gives the buyer the right, but not the obligation, to purchase an underlying asset at a predetermined price, known as the strike price, within a specified time frame. Investors use call options to speculate on the price increase of assets like stocks, commodities, or indices, allowing leveraged exposure with limited risk to the premium paid. The value of a call option rises as the underlying asset's price exceeds the strike price before expiration, enabling potential profit through exercising the option or selling it in the market.
What is a Put Option?
A put option is a financial contract that gives the holder the right, but not the obligation, to sell a specific amount of an underlying asset at a predetermined price, known as the strike price, within a set expiration period. Investors use put options primarily to hedge against potential declines in the value of assets or to speculate on downward price movements. Unlike call options, which provide buying rights, put options increase in value as the price of the underlying asset decreases.
Key Differences Between Call and Put Options
Call options grant the holder the right to buy an underlying asset at a specified strike price before expiration, while put options grant the right to sell the asset under similar terms. Call options typically benefit from a rise in the asset's price, whereas put options gain value when the asset's price declines. Key differences also include their payoff profiles, with calls offering potential unlimited upside and puts providing a hedge against downward price movements.
How Call Options Work
Call options grant the buyer the right to purchase an underlying asset at a specified strike price before the option's expiration date, enabling potential profit if the asset's market price rises above the strike price. Traders buy call options to leverage upward price movements with limited risk, as the maximum loss equals the premium paid. The value of call options increases as the underlying asset's price rises, influenced by factors such as volatility, time decay, and interest rates.
How Put Options Work
Put options grant the holder the right to sell an underlying asset at a predetermined strike price before or at expiration, providing a means to hedge against market declines or speculate on falling prices. When the asset's market price falls below the strike price, the value of the put option typically increases, allowing the investor to sell at the higher strike price or to profit from selling the option itself. This mechanism makes put options valuable tools for portfolio protection and bearish market strategies in options trading.
Pros and Cons of Call Options
Call options provide investors the potential for significant gains by allowing the purchase of an asset at a predetermined price before expiry, enabling profit from upward price movements with limited initial capital. However, the main drawback of call options is the risk of losing the entire premium paid if the underlying asset's price does not exceed the strike price by expiration. Call options offer leverage and limited risk but require precise timing and market direction prediction to be profitable.
Pros and Cons of Put Options
Put options provide investors with the ability to profit from declining asset prices, serving as an effective hedge against potential losses in a portfolio. The main advantage of put options is that they offer downside protection without requiring the sale of the underlying asset, enabling risk management and strategic flexibility. However, the cons include the premium cost paid for the option, which can erode returns if the market does not move as anticipated, and the limited window of expiration, which can result in total loss of the investment if the put option is not exercised timely.
When to Use Call or Put Options
Call options are ideal when investors anticipate a stock's price will rise, allowing them to buy shares at a predetermined lower strike price and profit from the difference. Put options serve best when expecting a decline in the stock price, giving the right to sell shares at a higher strike price to limit losses or benefit from downward movements. Strategic use depends on market outlook: bullish sentiment favors call options, while bearish or hedging objectives align with put options.
Call vs Put Options: Which Is Right for You?
Call options grant the buyer the right to purchase an asset at a predetermined price before expiration, benefiting from asset price increases. Put options give the buyer the right to sell an asset at a set price, profiting from price declines or hedging against losses. Choosing between call vs put options depends on your market outlook, risk tolerance, and investment strategy.
Call Option Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com