Outstanding shares represent the total number of a company's shares currently held by all its shareholders, including restricted shares owned by insiders. These shares are crucial for calculating key financial metrics such as earnings per share (EPS) and market capitalization. Explore the full article to understand how outstanding shares impact your investment decisions and company valuation.
Table of Comparison
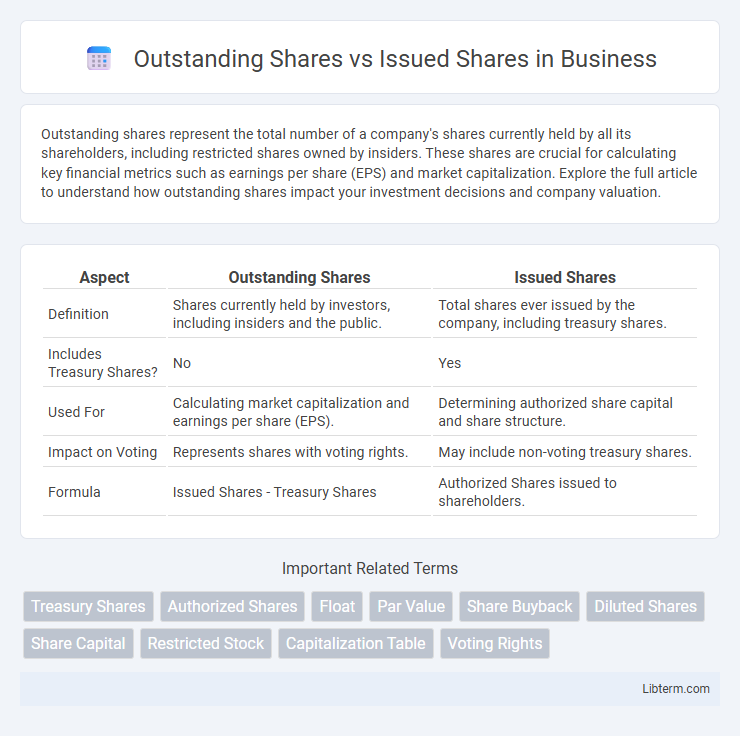
| Aspect | Outstanding Shares | Issued Shares |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Shares currently held by investors, including insiders and the public. | Total shares ever issued by the company, including treasury shares. |
| Includes Treasury Shares? | No | Yes |
| Used For | Calculating market capitalization and earnings per share (EPS). | Determining authorized share capital and share structure. |
| Impact on Voting | Represents shares with voting rights. | May include non-voting treasury shares. |
| Formula | Issued Shares - Treasury Shares | Authorized Shares issued to shareholders. |
Introduction to Outstanding Shares vs Issued Shares
Outstanding shares represent the total number of a company's shares currently held by all shareholders, including insiders but excluding treasury shares. Issued shares encompass all shares that have ever been sold by the company, including both outstanding shares and treasury shares repurchased by the company. Understanding the distinction between outstanding and issued shares is crucial for accurate market capitalization calculation and shareholder equity analysis.
What Are Issued Shares?
Issued shares represent the total number of a company's stock shares that have been allocated and sold to investors, including shares held by insiders and the public. This figure encompasses both outstanding shares currently held by investors and treasury shares that the company has repurchased but not retired. Understanding issued shares is essential for assessing a company's capital structure and shareholder equity.
Understanding Outstanding Shares
Outstanding shares represent the total number of a company's shares currently held by all shareholders, including institutional investors and company insiders, reflecting the actual ownership in the company. These shares exclude treasury shares, which are shares repurchased by the company and held in its treasury. Understanding outstanding shares is crucial for calculating market capitalization, earnings per share (EPS), and determining voting power at shareholder meetings.
Key Differences Between Issued and Outstanding Shares
Issued shares represent the total number of shares a company has sold to investors, including both outstanding shares held by shareholders and shares held in the company's treasury. Outstanding shares refer specifically to the shares currently held by shareholders, excluding treasury stock and shares repurchased by the company. The key difference lies in that issued shares encompass all shares ever distributed, while outstanding shares only count actively held equity that impacts voting rights and earnings per share calculations.
Importance in Corporate Finance
Outstanding shares represent the total shares currently held by shareholders, including insiders and the public, while issued shares encompass all shares ever sold, including those held as treasury stock. Understanding the distinction is crucial in corporate finance for accurate market capitalization calculation, shareholder equity assessment, and earnings per share (EPS) determination. Precise knowledge of outstanding shares aids in evaluating shareholder dilution risk and informs strategic decisions on financing and stock buybacks.
How These Shares Impact Shareholder Equity
Outstanding shares represent the total shares held by investors, excluding treasury shares, directly affecting shareholder equity by determining the ownership proportion and voting power in a company. Issued shares encompass all shares ever distributed by the company, including those held in treasury, influencing the total potential equity base and dilution of shareholder value. The distinction impacts key financial metrics such as earnings per share (EPS) and book value per share, which are critical for assessing shareholder equity and investment decisions.
Effects on Earnings Per Share (EPS)
Outstanding shares directly impact Earnings Per Share (EPS) since EPS is calculated by dividing net earnings by the number of outstanding shares, reflecting the actual shares held by investors. Issued shares include both outstanding shares and treasury shares, which do not affect EPS as they are not part of the float available for trading or earnings distribution. Changes in outstanding shares, through stock buybacks or issuance, alter the EPS by modifying the denominator, thereby influencing investor perceptions of profitability.
Influence on Voting Rights
Outstanding shares represent the total shares currently held by investors, directly determining voting power in corporate decisions. Issued shares include both outstanding shares and treasury shares, but only outstanding shares confer voting rights. The distinction between these share types critically influences shareholder influence, as treasury shares held by the company do not participate in voting.
Common Misconceptions Explained
Outstanding shares represent the total number of shares currently held by all shareholders, including restricted shares held by insiders, while issued shares encompass all shares that the company has ever created and sold, including those repurchased by the company. A common misconception is that issued shares and outstanding shares are always equivalent, but treasury shares (repurchased stock) cause the difference. Understanding this distinction is crucial for accurate market capitalization and shareholder equity calculations.
Conclusion: Why the Distinction Matters
The distinction between outstanding shares and issued shares is crucial for accurate financial analysis and corporate governance. Outstanding shares, which exclude shares repurchased by the company, directly impact earnings per share (EPS) calculations and voting rights distribution, reflecting the actual equity held by investors. Issued shares represent the total shares a company has ever sold, providing a broader view of capital structure but not indicating current ownership or dilution effects.
Outstanding Shares Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com