Brand acquisition involves the strategic process of purchasing an existing brand to expand market reach, enhance product offerings, or increase competitive advantage. It requires careful evaluation of brand value, customer loyalty, and market positioning to ensure a successful integration. Explore the rest of this article to learn how your business can benefit from effective brand acquisition strategies.
Table of Comparison
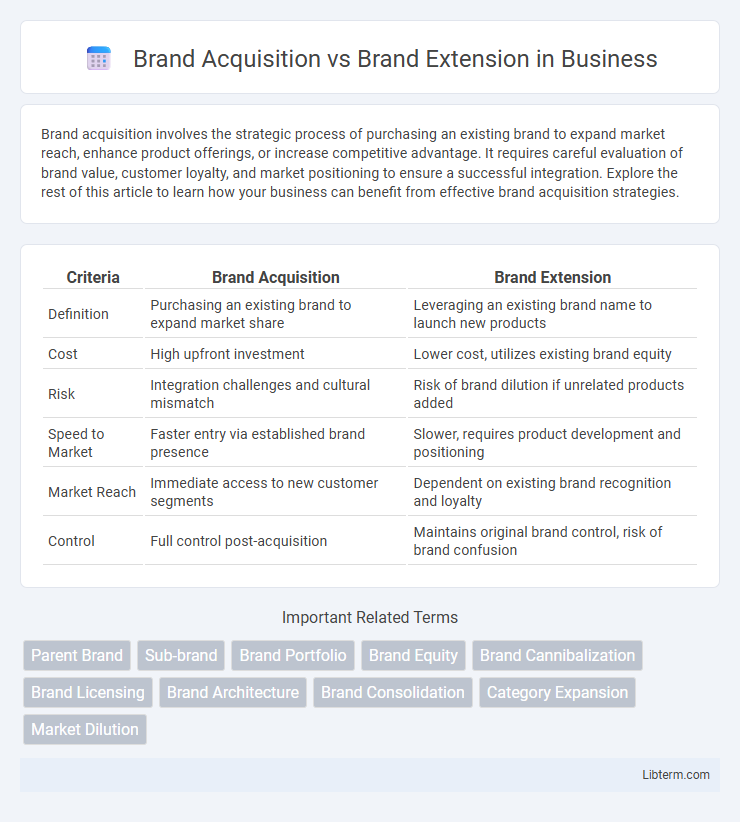
| Criteria | Brand Acquisition | Brand Extension |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Purchasing an existing brand to expand market share | Leveraging an existing brand name to launch new products |
| Cost | High upfront investment | Lower cost, utilizes existing brand equity |
| Risk | Integration challenges and cultural mismatch | Risk of brand dilution if unrelated products added |
| Speed to Market | Faster entry via established brand presence | Slower, requires product development and positioning |
| Market Reach | Immediate access to new customer segments | Dependent on existing brand recognition and loyalty |
| Control | Full control post-acquisition | Maintains original brand control, risk of brand confusion |
Understanding Brand Acquisition
Brand acquisition involves purchasing an existing brand to quickly enter new markets or expand product offerings, leveraging the acquired brand's established customer base and market presence. This strategy allows companies to capitalize on brand loyalty, reduce the risks associated with launching new products, and gain immediate competitive advantages. Understanding brand acquisition requires analyzing the target brand's equity, market position, and compatibility with the acquiring company's portfolio to ensure long-term value creation.
Defining Brand Extension
Brand extension involves leveraging an existing brand's established reputation to introduce new products or product categories, thereby capitalizing on brand equity and consumer trust. This strategy minimizes marketing costs and reduces the risk associated with launching new products by associating them with familiar brand attributes. Unlike brand acquisition, which involves purchasing an entire brand to gain market share, brand extension focuses on organic growth within the current brand's framework.
Key Differences Between Acquisition and Extension
Brand acquisition involves purchasing an existing brand to instantly gain market share, customer base, and brand equity, while brand extension leverages an established brand name to launch new products within or outside the current product category. Acquisitions typically require substantial financial investment, complex integration processes, and risk related to cultural and operational alignment, whereas extensions generally involve lower costs, capitalize on brand recognition, and rely on consumer trust in the original brand. The key difference lies in acquisition expanding the company's portfolio by adding separate brands, whereas extension grows the current brand's presence by introducing related products.
Strategic Objectives of Brand Acquisition
Brand acquisition aims to rapidly increase market share and expand product portfolios by purchasing established brands with loyal customer bases and proven market performance. This strategy enables companies to enter new markets or segments, leverage acquired brand equity, and achieve economies of scale more efficiently than organic growth approaches. Key strategic objectives include enhancing competitive positioning, diversifying risk, and strengthening overall brand portfolio synergies to maximize shareholder value.
Benefits of Pursuing Brand Extension
Brand extension leverages existing brand equity to enter new product categories, reducing marketing costs and consumer trust barriers. It enables faster market acceptance by capitalizing on established brand recognition and loyalty. This strategy supports diversification while maintaining a cohesive brand image, enhancing long-term growth potential.
Risk Factors in Brand Acquisition
Brand acquisition involves purchasing an existing brand, which carries significant risk factors such as high financial investment, potential cultural clashes, and integration challenges that can impact operational efficiency. Market misalignment or overestimation of brand equity may lead to diminished returns and brand dilution. Failure to properly assess these risks can result in loss of customer loyalty and a negative impact on the acquiring company's overall brand portfolio.
Challenges in Implementing Brand Extension
Implementing brand extension poses challenges such as potential brand dilution, where the new product may confuse or weaken the core brand identity. Consumer skepticism can arise if the extension strays too far from the parent brand's established market or values, leading to lower acceptance rates. Market research complexity increases because companies must ensure alignment between the extension and customer expectations to maintain brand equity.
Case Studies: Brand Acquisition Success Stories
Sony's acquisition of Columbia Pictures in 1989 exemplifies brand acquisition success by expanding its entertainment portfolio and leveraging existing industry expertise to enter the film production market. Facebook's purchase of Instagram in 2012 showcases how acquiring a rapidly growing brand can instantly capture new demographics and enhance social media dominance. Similarly, Amazon's acquisition of Whole Foods in 2017 enabled immediate entry into the physical grocery retail sector, combining e-commerce strengths with established brand loyalty.
Notable Examples of Brand Extension
Notable examples of brand extension include Apple expanding from computers to smartphones with the iPhone and Nike branching out from footwear to apparel and accessories. These extensions leverage existing brand equity to enter new markets while maintaining consumer trust. Successful brand extensions enhance revenue streams without the significant costs associated with acquiring new brands.
Choosing the Right Strategy: Acquisition vs Extension
Selecting the appropriate strategy between brand acquisition and brand extension depends on market conditions, resource availability, and long-term business goals. Brand acquisition offers immediate market entry by purchasing established brands with existing customer bases and distribution networks, while brand extension leverages the current brand's equity to introduce new products under a familiar name, minimizing marketing costs. Analyzing factors like brand equity strength, competitive landscape, and operational capacity ensures strategic alignment and maximizes return on investment.
Brand Acquisition Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com