A leveraged buyout (LBO) is a financial transaction where a company is acquired using a significant amount of borrowed money, often secured by the assets of the company being purchased. This strategy allows investors to make large acquisitions without committing a lot of capital upfront, enhancing potential returns while increasing financial risk. Discover how leveraged buyouts work, their advantages and risks, and what they mean for your investment decisions in the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
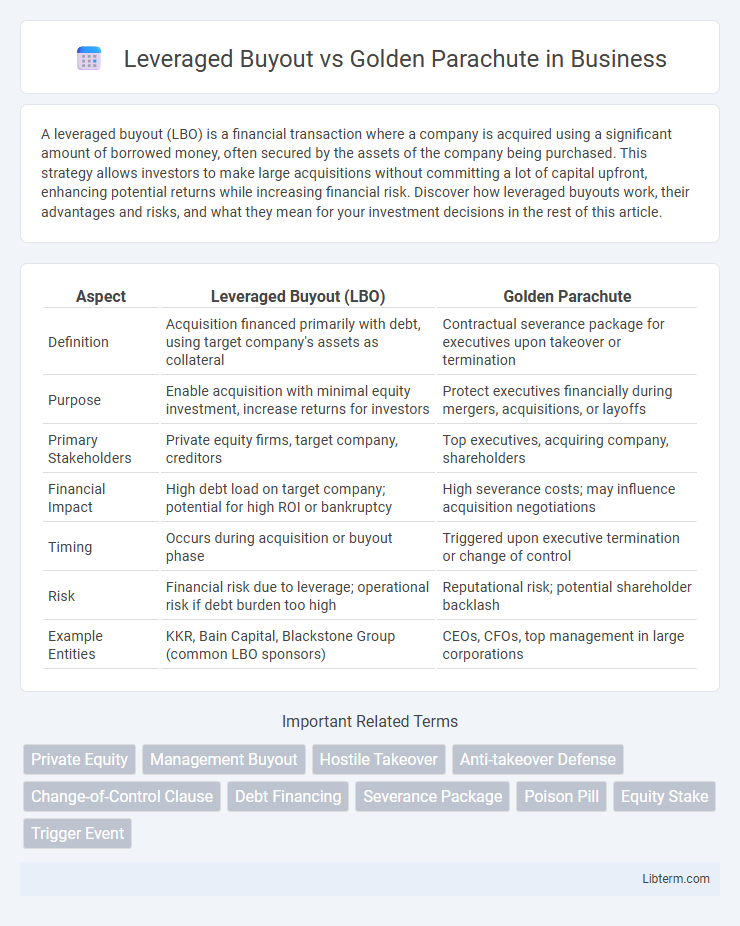
| Aspect | Leveraged Buyout (LBO) | Golden Parachute |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Acquisition financed primarily with debt, using target company's assets as collateral | Contractual severance package for executives upon takeover or termination |
| Purpose | Enable acquisition with minimal equity investment, increase returns for investors | Protect executives financially during mergers, acquisitions, or layoffs |
| Primary Stakeholders | Private equity firms, target company, creditors | Top executives, acquiring company, shareholders |
| Financial Impact | High debt load on target company; potential for high ROI or bankruptcy | High severance costs; may influence acquisition negotiations |
| Timing | Occurs during acquisition or buyout phase | Triggered upon executive termination or change of control |
| Risk | Financial risk due to leverage; operational risk if debt burden too high | Reputational risk; potential shareholder backlash |
| Example Entities | KKR, Bain Capital, Blackstone Group (common LBO sponsors) | CEOs, CFOs, top management in large corporations |
Introduction to Leveraged Buyout and Golden Parachute
Leveraged Buyouts (LBOs) involve acquiring a company primarily through borrowed funds, using the target's assets as collateral to finance the purchase, which enhances potential returns while increasing financial risk. A Golden Parachute refers to substantial severance packages or financial benefits guaranteed to top executives in the event of a merger or takeover, providing protection during ownership changes. Both concepts play critical roles in corporate finance strategies, with LBOs focusing on acquisition tactics and Golden Parachutes addressing executive risk management.
Definition of Leveraged Buyout (LBO)
A Leveraged Buyout (LBO) is a financial transaction in which a company is acquired using a significant amount of borrowed funds, with the assets of the company being purchased often serving as collateral for the loans. This strategy enables buyers to make substantial acquisitions without committing large amounts of capital upfront, relying instead on the target company's cash flow to service the debt. LBOs are commonly employed by private equity firms aiming to improve operational efficiency and generate high returns through strategic management post-acquisition.
Definition of Golden Parachute
A Golden Parachute is a contract clause that guarantees substantial financial benefits to executives if they are terminated following a merger or acquisition, creating a safety net during corporate restructuring. Leveraged Buyouts (LBOs) involve acquiring a company using significant debt, often forcing management changes that can trigger Golden Parachute payouts. The strategic use of Golden Parachutes protects key executives by securing severance packages, stock options, and bonuses, thereby aligning interests during high-stake buyouts.
Key Mechanisms of Leveraged Buyouts
Leveraged buyouts (LBOs) involve acquiring a company primarily using borrowed funds, with the acquired company's assets often serving as collateral for the loans, enabling significant leverage and potential high returns. Key mechanisms include debt financing through bonds or loans, management buy-in or buyout to align incentives, and aggressive cost-cutting or asset sales to improve cash flow and debt servicing. Unlike golden parachutes, which provide executives with lucrative exit packages during takeovers, LBOs focus on restructuring ownership and financial engineering to maximize investment value.
Main Features of Golden Parachutes
Golden parachutes provide key executives with substantial financial compensation and benefits if they are terminated following a merger or acquisition, often including severance pay, stock options, and bonuses. These agreements are designed to protect executives from abrupt job loss and ensure stability during corporate transitions. The main features include triggered payouts upon change of control, predefined compensation packages, and clauses that incentivize executives to support mergers without fear of financial loss.
Advantages of Leveraged Buyouts
Leveraged Buyouts (LBOs) enable private equity firms to acquire companies using significant debt, enhancing potential returns on invested equity and enabling value creation through operational improvements. LBOs provide disciplined financial structuring, aligning management incentives with shareholder interests and driving efficiency in capital allocation. This strategy often leads to substantial equity appreciation and increased control over strategic decisions compared to Golden Parachutes, which primarily offer executive protections without directly enhancing company value.
Benefits and Controversies of Golden Parachutes
Golden parachutes provide executives with substantial financial security during mergers or acquisitions, offering benefits like protection against abrupt termination and ensuring leadership stability. These agreements can attract top talent by safeguarding compensation, yet they often spark controversy due to perceived excessive payouts and misaligned incentives with shareholder interests. Critics argue that golden parachutes may encourage risky corporate behavior and undermine corporate governance by prioritizing executive gain over company performance.
Comparing Financial Implications: LBO vs Golden Parachute
Leveraged Buyouts (LBOs) involve acquiring a company primarily using borrowed funds, increasing debt levels and potentially enhancing equity returns through financial leverage. Golden Parachutes guarantee significant severance payments to executives upon takeover or merger, creating substantial contingent liabilities that can affect company valuation and cash flow. While LBOs impact capital structure and financial risk, golden parachutes primarily influence post-transaction costs and executive compensation expenses.
Impact on Companies and Executives
Leveraged buyouts (LBOs) often place significant financial strain on companies due to the high debt levels incurred, potentially jeopardizing long-term operational stability but offering executives substantial equity gains if the buyout succeeds. Golden parachutes provide executives with guaranteed severance packages during mergers or acquisitions, reducing personal financial risk and sometimes encouraging smoother transitions, yet they may lead to shareholder concerns over excessive executive compensation. Both strategies influence corporate governance by balancing executive incentives with company integrity, impacting stakeholder trust and strategic decision-making.
Leveraged Buyout vs Golden Parachute: Strategic Considerations
Leveraged buyouts (LBOs) involve acquiring a company primarily through borrowed funds, emphasizing debt optimization and operational efficiency to enhance shareholder value. Golden parachutes provide financial protection to executives during mergers or acquisitions, aligning leadership stability with transaction outcomes but potentially increasing corporate costs. Strategic considerations between LBOs and golden parachutes must balance aggressive financial restructuring with executive risk mitigation to ensure long-term organizational resilience.
Leveraged Buyout Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com