Disintermediation refers to the elimination of intermediaries in a supply chain or transaction process, allowing direct interaction between producers and consumers. This shift can reduce costs, increase efficiency, and enhance transparency in various industries, especially with the rise of digital platforms. Explore the rest of this article to understand how disintermediation impacts your business and everyday transactions.
Table of Comparison
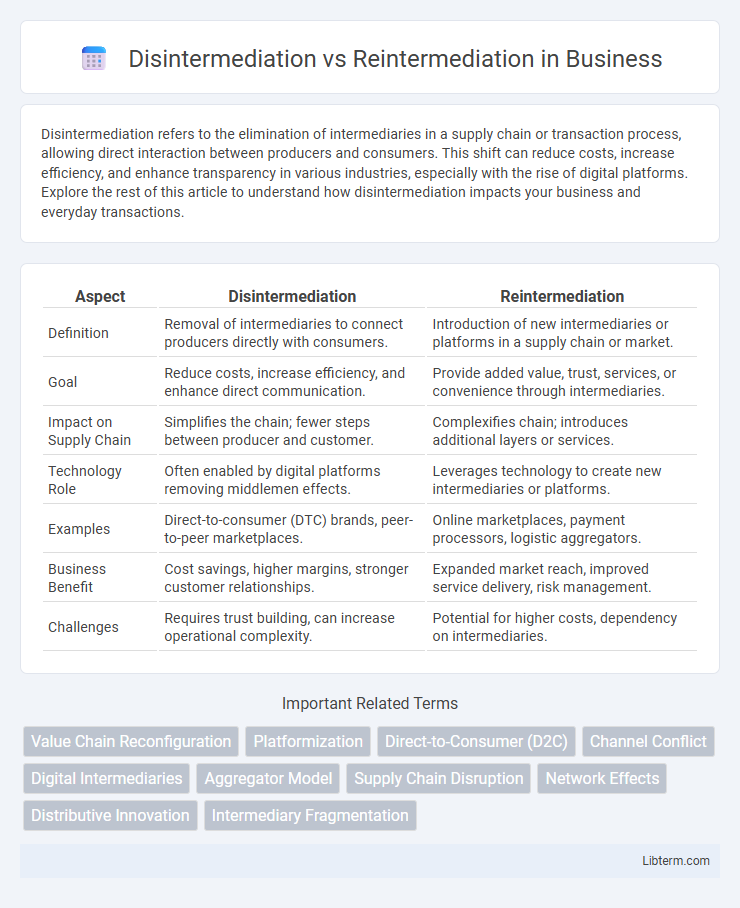
| Aspect | Disintermediation | Reintermediation |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Removal of intermediaries to connect producers directly with consumers. | Introduction of new intermediaries or platforms in a supply chain or market. |
| Goal | Reduce costs, increase efficiency, and enhance direct communication. | Provide added value, trust, services, or convenience through intermediaries. |
| Impact on Supply Chain | Simplifies the chain; fewer steps between producer and customer. | Complexifies chain; introduces additional layers or services. |
| Technology Role | Often enabled by digital platforms removing middlemen effects. | Leverages technology to create new intermediaries or platforms. |
| Examples | Direct-to-consumer (DTC) brands, peer-to-peer marketplaces. | Online marketplaces, payment processors, logistic aggregators. |
| Business Benefit | Cost savings, higher margins, stronger customer relationships. | Expanded market reach, improved service delivery, risk management. |
| Challenges | Requires trust building, can increase operational complexity. | Potential for higher costs, dependency on intermediaries. |
Introduction to Disintermediation and Reintermediation
Disintermediation refers to the removal of intermediaries in a supply chain or distribution channel, allowing producers to directly reach consumers, often enabled by digital platforms that reduce costs and increase efficiency. Reintermediation occurs when new intermediaries emerge to add value or facilitate transactions in digital markets, such as online marketplaces, payment processors, or logistics providers. Understanding these concepts is crucial for businesses adapting to evolving market structures driven by technology and consumer behavior shifts.
Defining Disintermediation: Key Concepts
Disintermediation refers to the process of removing intermediaries from a supply chain or distribution channel, enabling direct interaction between producers and consumers. This concept is driven by advancements in digital technologies that reduce transaction costs and increase market transparency. By eliminating middlemen, businesses can streamline operations, reduce costs, and enhance customer relationships.
Understanding Reintermediation: Fundamentals
Reintermediation involves introducing new intermediaries within a supply chain or business process to enhance efficiency, reduce costs, or improve customer experiences. Companies implement reintermediation by leveraging digital platforms, technology solutions, or specialized services that create added value between producers and consumers. This strategic shift reverses disintermediation, emphasizing optimized intermediaries that streamline transactions and foster stronger market connections.
Historical Context and Evolution
Disintermediation emerged prominently in the late 20th century as digital technologies enabled consumers and businesses to bypass traditional intermediaries such as banks and wholesalers, reducing costs and increasing efficiency. The subsequent rise of e-commerce and direct-to-consumer models in the 1990s intensified the trend, reshaping industries like retail, finance, and media by eliminating layers of middlemen. Reintermediation evolved as new digital platforms, marketplaces, and financial technology firms stepped in, creating novel intermediary roles that leverage data analytics and technology to add value, demonstrating that middlemen adapt rather than disappear in the evolving digital economy.
Drivers of Disintermediation in Modern Markets
Technological advancements such as the rise of digital platforms and blockchain drive disintermediation by enabling direct interactions between producers and consumers, reducing reliance on traditional intermediaries. Consumer demand for transparency, reduced costs, and faster transactions further fuels the shift towards disintermediation. Regulatory changes promoting open access and competitive markets also encourage businesses to bypass established intermediaries.
The Role of Technology in Reintermediation
Technology accelerates reintermediation by enabling new digital platforms and services that create value-added intermediaries between producers and consumers. Advanced data analytics, artificial intelligence, and blockchain improve transparency, personalization, and trust, fostering innovative intermediaries that optimize transaction efficiency. These technological advancements reshape traditional supply chains, introducing virtual marketplaces and fintech solutions that redefine intermediaries' roles in various industries.
Industry Case Studies: Disintermediation vs Reintermediation
Industry case studies in sectors like finance and retail highlight the impact of disintermediation, where companies bypass traditional intermediaries to reduce costs and improve direct customer engagement. Conversely, reintermediation emerges as new digital platforms and service providers create valuable intermediaries that facilitate transactions, enhance user experiences, and enable market expansion. For instance, fintech firms in banking disrupt legacy intermediaries while e-commerce platforms reintroduce new intermediaries through advanced data analytics and personalized services.
Advantages and Challenges of Disintermediation
Disintermediation eliminates intermediaries in supply chains or financial transactions, reducing costs and enhancing direct customer engagement, which can lead to increased transparency and faster service delivery. The advantages include improved profit margins, greater control over the customer experience, and streamlined communication channels. Challenges involve managing increased operational responsibilities, the need for robust technological infrastructure, and potential risks from reduced market reach or expertise traditionally provided by intermediaries.
Benefits and Risks of Reintermediation
Reintermediation introduces new intermediaries leveraging technology platforms to enhance market efficiency, increase transparency, and provide added value through improved services and data analytics. Benefits include risk management, better customer support, and streamlined transaction processes, which foster trust and scalability in digital ecosystems. However, risks involve potential increased costs, slower decision-making, and reduced direct interaction, which can diminish the agility and cost advantages initially gained through disintermediation.
Future Trends and Strategic Implications
Future trends in disintermediation emphasize direct-to-consumer models driven by digital platforms, reducing reliance on traditional intermediaries in sectors like retail and finance. Conversely, reintermediation is gaining traction through advanced technologies such as AI and blockchain, enabling new intermediaries to provide enhanced value with greater transparency and efficiency. Strategically, businesses must balance adopting disintermediation to cut costs while leveraging reintermediation to foster innovation, improve customer experience, and build competitive advantage.
Disintermediation Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com