Outsourcing allows businesses to reduce operational costs by delegating tasks to external specialists, enhancing efficiency and access to skilled talent. It enables your company to focus on core activities while leveraging global resources for faster project completion and innovation. Discover how strategic outsourcing can transform your business by reading the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
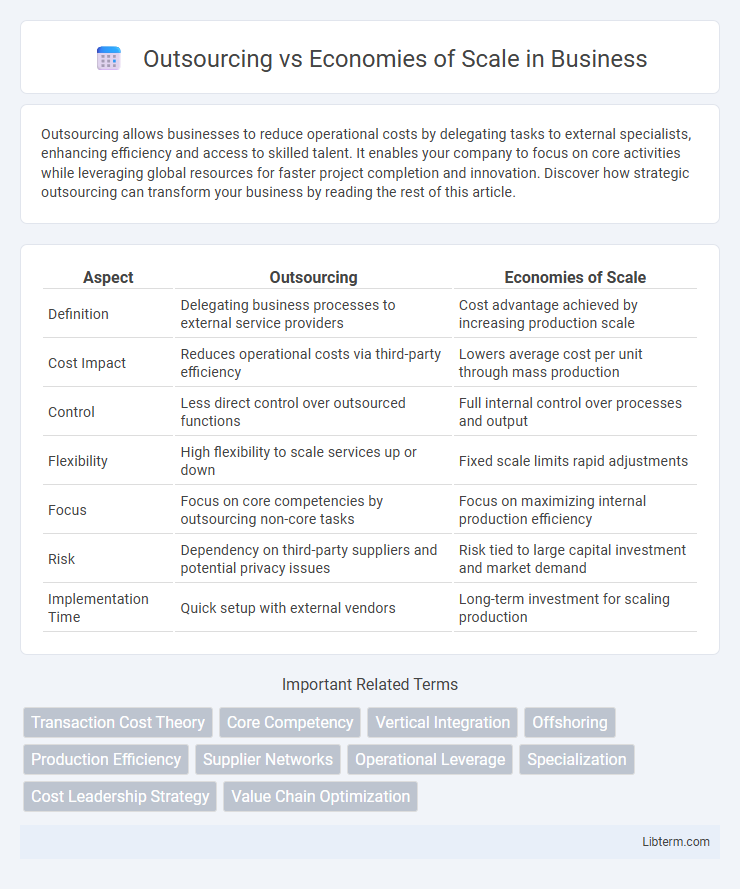
| Aspect | Outsourcing | Economies of Scale |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Delegating business processes to external service providers | Cost advantage achieved by increasing production scale |
| Cost Impact | Reduces operational costs via third-party efficiency | Lowers average cost per unit through mass production |
| Control | Less direct control over outsourced functions | Full internal control over processes and output |
| Flexibility | High flexibility to scale services up or down | Fixed scale limits rapid adjustments |
| Focus | Focus on core competencies by outsourcing non-core tasks | Focus on maximizing internal production efficiency |
| Risk | Dependency on third-party suppliers and potential privacy issues | Risk tied to large capital investment and market demand |
| Implementation Time | Quick setup with external vendors | Long-term investment for scaling production |
Introduction to Outsourcing and Economies of Scale
Outsourcing involves delegating business processes to external providers, enabling companies to reduce operational costs and focus on core activities. Economies of scale refer to cost advantages gained as production output increases, resulting in lower per-unit costs. Understanding the balance between outsourcing and economies of scale helps businesses optimize efficiency and achieve competitive advantage.
Defining Outsourcing in Modern Business
Outsourcing in modern business involves delegating specific operations or services to third-party providers to enhance efficiency and reduce costs. This strategic practice enables companies to focus on core competencies while leveraging specialized external expertise and resources. By contrast, economies of scale refer to cost advantages gained through increased production levels within the company, highlighting different approaches to optimizing operational expenses.
Understanding Economies of Scale
Economies of scale occur when a company reduces its average costs by increasing production volume, achieving cost advantages through bulk purchasing, optimized labor specialization, and improved technology utilization. This concept helps businesses spread fixed costs over more units, enhancing profitability and competitive pricing. Understanding economies of scale is essential to deciding whether to outsource operations or maintain in-house production for maximizing efficiency and cost savings.
Key Differences Between Outsourcing and Economies of Scale
Outsourcing involves delegating specific business processes or functions to external vendors to reduce costs and focus on core competencies, whereas economies of scale refer to cost advantages gained by increasing production volume within a company. Key differences include the reliance on external partners in outsourcing versus internal capacity expansion in economies of scale, and the short-term flexibility outsourcing offers compared to the long-term cost efficiency achieved through scaling operations. Outsourcing often targets specialized services or tasks, while economies of scale benefit mass production and resource utilization across the entire organization.
Benefits of Outsourcing for Business Growth
Outsourcing enables businesses to access specialized skills and cutting-edge technology without heavy upfront investment, driving operational efficiency and accelerating growth. It allows companies to scale operations flexibly, reducing fixed costs and reallocating resources toward core competencies and innovation. By leveraging external expertise, businesses enhance productivity and responsiveness, fostering competitive advantage and market expansion.
Advantages of Achieving Economies of Scale
Achieving economies of scale reduces per-unit costs by increasing production volume, leading to enhanced operational efficiency and greater profit margins. Large-scale operations benefit from bulk purchasing and specialized labor, which decreases input costs and improves product quality. This cost advantage provides businesses with a competitive edge, enabling reinvestment into innovation and market expansion.
When to Choose Outsourcing Over Scaling Internally
Outsourcing is ideal when specialized expertise or cost reductions in non-core activities can be leveraged more efficiently than scaling internal operations, especially for companies lacking infrastructure or facing capacity constraints. Firms benefit from outsourcing when rapid market entry, flexible resource allocation, and risk mitigation outweigh the long-term benefits of economies of scale. Choosing outsourcing over internal scaling becomes critical when fixed costs of expansion are high, and external vendors provide superior technology or process efficiencies.
Risks and Challenges Associated with Both Strategies
Outsourcing poses risks such as loss of control over quality and data security, along with potential communication barriers and dependency on third-party providers. Economies of scale face challenges including significant upfront investment, reduced flexibility, and the risk of diseconomies due to overly complex management structures. Both strategies require careful risk management to balance cost savings with operational efficiency and organizational resilience.
Real-World Examples: Outsourcing vs Economies of Scale
Outsourcing enables companies like Apple to leverage specialized suppliers for components, reducing production costs without heavy capital investment. Economies of scale are exemplified by Walmart, which achieves low per-unit costs by mass purchasing and streamlined logistics across its extensive global network. Real-world decisions often balance outsourcing benefits with achieving scale efficiencies to optimize overall cost structures and competitive advantage.
Conclusion: Selecting the Optimal Strategy for Your Business
Choosing between outsourcing and economies of scale depends on your company's specific needs, cost structure, and long-term goals. Outsourcing offers flexibility and access to specialized expertise, reducing operational expenses, while economies of scale focus on increasing production efficiency to lower unit costs internally. Aligning the strategy with your business model and market demands ensures optimal resource allocation and competitive advantage.
Outsourcing Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com