Open innovation accelerates business growth by leveraging external ideas and technologies alongside internal resources, fostering collaboration beyond traditional boundaries. Companies that embrace open innovation tap into diverse expertise, reducing development costs and speeding up time-to-market for new products. Explore the full article to discover how your organization can implement open innovation strategies effectively.
Table of Comparison
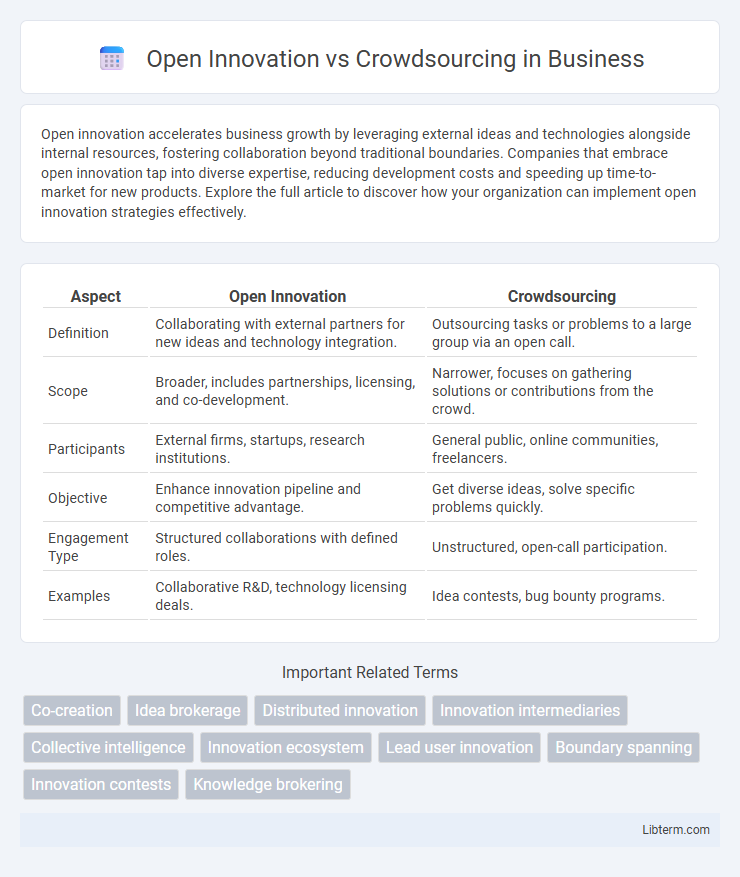
| Aspect | Open Innovation | Crowdsourcing |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Collaborating with external partners for new ideas and technology integration. | Outsourcing tasks or problems to a large group via an open call. |
| Scope | Broader, includes partnerships, licensing, and co-development. | Narrower, focuses on gathering solutions or contributions from the crowd. |
| Participants | External firms, startups, research institutions. | General public, online communities, freelancers. |
| Objective | Enhance innovation pipeline and competitive advantage. | Get diverse ideas, solve specific problems quickly. |
| Engagement Type | Structured collaborations with defined roles. | Unstructured, open-call participation. |
| Examples | Collaborative R&D, technology licensing deals. | Idea contests, bug bounty programs. |
Understanding Open Innovation: A Brief Overview
Open innovation refers to the strategic practice of leveraging external and internal ideas, knowledge, and paths to market to accelerate innovation and create value. It contrasts with traditional closed innovation by encouraging collaboration with partners, startups, universities, and customers to enhance product development and problem-solving. Crowdsourcing is a subset of open innovation that involves sourcing ideas, services, or content from a large, undefined group of people, often via online platforms, to tap into diverse expertise and creativity.
Defining Crowdsourcing: Core Concepts
Crowdsourcing is a distributed problem-solving and production model that leverages the collective intelligence and diverse skills of a large, undefined group of people, often via online platforms. It enables organizations to obtain ideas, services, or funding from a broad crowd, increasing innovation potential beyond internal capabilities. Core concepts include openness, scalability, diversity, and leveraging external contributions to solve complex challenges efficiently.
Key Differences Between Open Innovation and Crowdsourcing
Open Innovation involves leveraging external and internal ideas for comprehensive product development and business growth, while Crowdsourcing specifically taps into a large, undefined group for solving specific problems or generating ideas. Open Innovation integrates strategic partnerships with established entities, emphasizing collaboration throughout the innovation process, whereas Crowdsourcing relies on the power of diverse, often anonymous participants contributing discrete solutions. The scope of Open Innovation is broader, encompassing co-creation and technology sharing, contrasted with Crowdsourcing's targeted approach toward gathering input or solutions from a crowd.
Historical Evolution: From Closed to Open Innovation
The shift from closed innovation, where companies relied solely on internal R&D, to open innovation began in the early 2000s as businesses recognized the value of external ideas and technologies. Crowdsourcing emerged as a specific form of open innovation, enabling companies to tap into global talent pools through digital platforms for problem-solving and idea generation. This evolution reflects a broader trend toward collaborative innovation ecosystems, accelerating product development and enhancing competitive advantage.
Advantages of Open Innovation for Modern Enterprises
Open Innovation enables modern enterprises to accelerate product development by leveraging external knowledge and expertise, reducing time-to-market and innovation costs. This approach fosters collaboration across diverse networks, enhancing creativity and increasing the potential for breakthrough technologies. Companies benefit from shared risks and expanded market opportunities by integrating both internal and external innovation sources.
Crowdsourcing Benefits: Harnessing Collective Intelligence
Crowdsourcing benefits organizations by harnessing collective intelligence to solve complex problems, accelerate innovation, and reduce costs through diverse, real-time input. This approach enables access to a vast pool of global talent and ideas, driving creativity and enhancing product development efficiency. Companies leveraging crowdsourcing enjoy improved decision-making and faster market responsiveness by tapping into a broad spectrum of expertise beyond traditional internal resources.
Applications of Open Innovation Across Industries
Open innovation drives transformative applications across industries by leveraging external and internal ideas for product development, accelerating research, and enhancing competitive advantage. Sectors such as pharmaceuticals utilize open innovation for collaborative drug discovery, while automotive companies adopt it to co-create advanced vehicle technologies with startups and research institutions. This approach fosters agile problem-solving and rapid market adaptation, distinguishing it from crowdsourcing's often narrower focus on gathering ideas or solutions from a large, undefined public pool.
Successful Crowdsourcing Case Studies
Successful crowdsourcing case studies such as Lego Ideas and Threadless demonstrate how companies leverage public creativity to enhance product innovation and market relevance. Lego Ideas allows fans to submit and vote on new set designs, resulting in popular products driven directly by consumer demand, while Threadless empowers artists globally to create and sell T-shirt designs based on community feedback. These examples highlight crowdsourcing's ability to harness diverse expertise and foster engagement, accelerating innovation cycles beyond traditional R&D limitations.
Challenges and Limitations: Open Innovation vs Crowdsourcing
Open Innovation faces challenges such as protecting intellectual property, managing complex collaborations, and aligning diverse stakeholder interests, which can slow decision-making and innovation speed. Crowdsourcing often struggles with quality control, participant motivation, and data security, leading to inconsistent results and potential misuse of information. Both approaches require robust governance frameworks and clear communication strategies to mitigate risks and maximize benefits.
Choosing the Right Model: Strategic Considerations for Businesses
Choosing between Open Innovation and Crowdsourcing depends on a business's strategic goals, resource availability, and desired level of external collaboration. Open Innovation integrates external ideas with internal R&D to drive long-term competitive advantage, while Crowdsourcing leverages a broader, often non-expert community for specific problem-solving or idea generation. Evaluating factors such as intellectual property control, speed of innovation, and scale of engagement ensures the chosen model aligns with organizational priorities and innovation objectives.
Open Innovation Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com