Lean Startup focuses on rapid experimentation, customer feedback, and iterative product development to minimize risks and adapt quickly, whereas Traditional Startup often relies on extensive planning, large initial investments, and a fixed business model. By embracing Lean Startup principles, Your business can save resources and increase the chances of finding a product-market fit faster. Explore the full article to discover key differences and how to apply these approaches effectively.
Table of Comparison
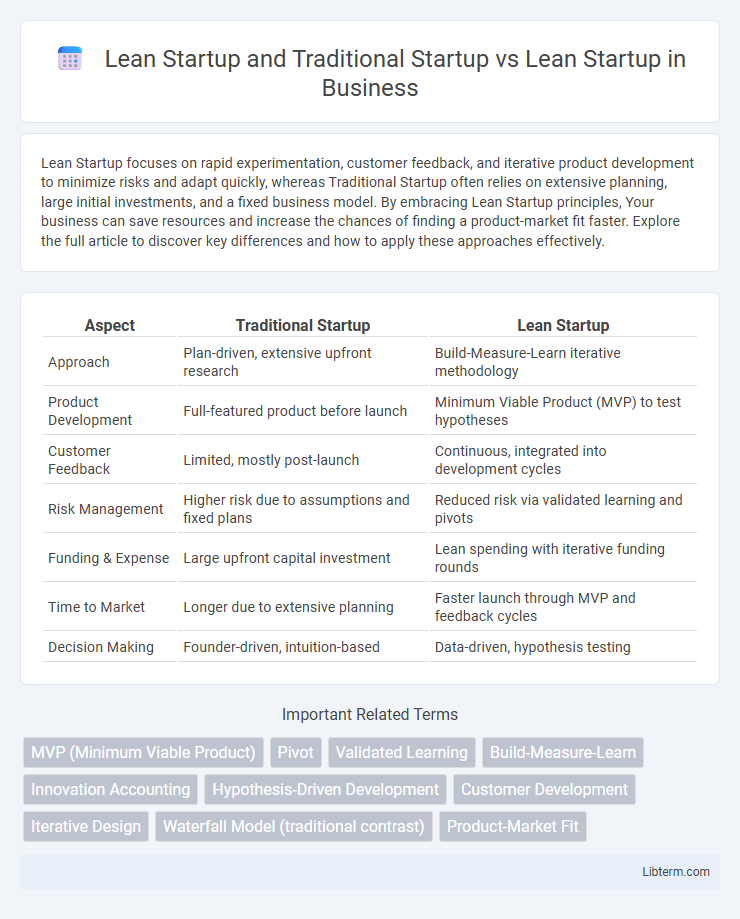
| Aspect | Traditional Startup | Lean Startup |
|---|---|---|
| Approach | Plan-driven, extensive upfront research | Build-Measure-Learn iterative methodology |
| Product Development | Full-featured product before launch | Minimum Viable Product (MVP) to test hypotheses |
| Customer Feedback | Limited, mostly post-launch | Continuous, integrated into development cycles |
| Risk Management | Higher risk due to assumptions and fixed plans | Reduced risk via validated learning and pivots |
| Funding & Expense | Large upfront capital investment | Lean spending with iterative funding rounds |
| Time to Market | Longer due to extensive planning | Faster launch through MVP and feedback cycles |
| Decision Making | Founder-driven, intuition-based | Data-driven, hypothesis testing |
Understanding Lean Startup: Core Principles
Lean Startup emphasizes rapid experimentation, validated learning, and iterative product development to efficiently meet customer needs and reduce market risks. Core principles include building minimum viable products (MVPs), measuring real user feedback, and pivoting based on data-driven insights. In contrast to traditional startups, which often rely on extensive upfront planning, Lean Startup fosters agility and continuous adaptation to maximize resource efficiency and accelerate time to market.
Defining Traditional Startup Methodologies
Traditional startup methodologies emphasize extensive upfront planning, relying on detailed business plans, market research, and long development cycles before product launch. This approach often involves significant capital investment and fixed strategies that may limit flexibility when responding to market feedback. In contrast, Lean Startup prioritizes iterative development, customer feedback, and minimal viable products (MVPs) to reduce risk and adapt quickly to changing market demands.
Key Differences: Lean Startup vs. Traditional Startup
Lean Startup emphasizes iterative product development and validated learning through customer feedback, reducing waste and accelerating market fit. Traditional Startup often relies on extensive planning and upfront funding, with fixed business models that may delay adaptation to real customer needs. Key differences include Lean Startup's focus on experimentation and pivoting versus the Traditional Startup's structured approach and risk tolerance.
The MVP (Minimum Viable Product) Approach
The Lean Startup methodology centers on the MVP (Minimum Viable Product) approach, emphasizing rapid development and early customer feedback to iterate and improve a product efficiently. Traditional startups often invest significant resources in fully developed products before market validation, increasing the risk of misalignment with customer needs. The MVP strategy reduces time to market and resource expenditure by launching simplified versions, enabling data-driven decisions and pivoting based on validated learning.
Customer Feedback Loops in Lean Startup
Lean Startup emphasizes continuous customer feedback loops to rapidly iterate and refine products based on real user needs, drastically reducing market risks compared to Traditional Startups. Unlike Traditional Startups, which often rely on extensive upfront planning and assumptions, Lean Startup integrates validated learning through build-measure-learn cycles to adapt business models dynamically. This customer-centric approach accelerates product-market fit and optimizes resource allocation by prioritizing direct consumer insights over speculative development.
Risk Management: Lean vs. Traditional Startups
Lean startups mitigate risk through iterative testing, customer feedback, and validated learning, allowing rapid adaptation to market needs and minimizing resource waste. Traditional startups often follow a linear plan with significant upfront investment, increasing the risk of product-market misalignment and financial loss. By embracing experimentation and pivoting quickly, lean startups reduce uncertainty and enhance long-term viability compared to traditional models.
Speed to Market: Accelerating Innovation
Lean Startup methodology emphasizes rapid iteration and validated learning, enabling quicker product launches compared to Traditional Startup approaches, which often follow lengthy planning and development cycles. Speed to market is accelerated through continuous testing, customer feedback integration, and minimal viable product (MVP) strategies inherent to Lean Startup practices. This agility fosters faster innovation, reduces time wasted on unproven concepts, and increases the likelihood of market success.
Resource Allocation and Cost Efficiency
Lean Startup methodology emphasizes iterative development and validated learning, allowing startups to allocate resources more efficiently by focusing on customer feedback and minimizing wasted efforts. Traditional startups often invest heavily in extensive planning and upfront development, leading to higher initial costs and potential resource misallocation. Lean Startup's approach reduces expenses through rapid prototyping and pivoting, enhancing cost efficiency and better adapting to market demands.
Pivoting Strategies in Startup Growth
Lean Startup emphasizes rapid product iteration and validated learning through customer feedback, enabling entrepreneurs to pivot quickly based on real market data. In contrast, Traditional Startup methods often follow a fixed business plan with limited flexibility, making pivots more challenging and riskier. Effective pivoting strategies in Lean Startup drive sustainable growth by reducing waste, optimizing product-market fit, and adapting to evolving customer needs efficiently.
Choosing the Right Startup Method for Your Business
Choosing the right startup method hinges on your business goals, market uncertainty, and resource availability. Lean Startup emphasizes validated learning through rapid experimentation and customer feedback, reducing risks and optimizing product-market fit. Traditional Startup methods rely on extensive upfront planning and significant capital investment, making them suitable for ventures with clearer market demands and established business models.
Lean Startup and Traditional Startup Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com