Convertible bonds offer investors the unique advantage of fixed-income returns with the potential to convert into equity shares, blending the benefits of bonds and stocks. These financial instruments can enhance portfolio diversification while providing downside protection through the bond's principal repayment feature. Explore the rest of the article to understand how convertible bonds can fit into your investment strategy.
Table of Comparison
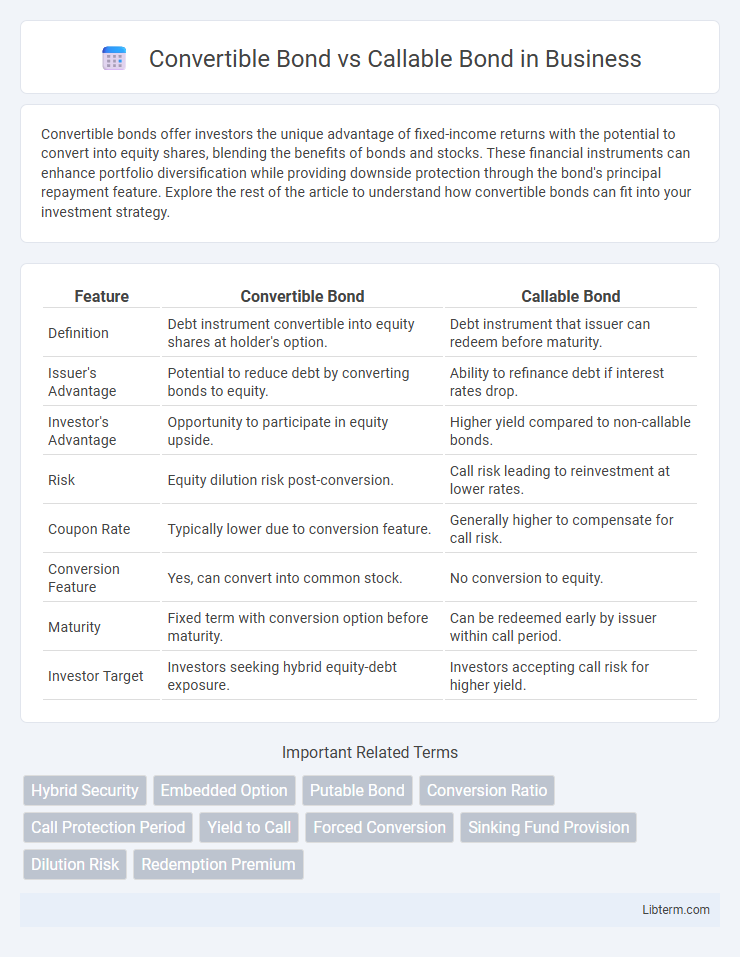
| Feature | Convertible Bond | Callable Bond |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Debt instrument convertible into equity shares at holder's option. | Debt instrument that issuer can redeem before maturity. |
| Issuer's Advantage | Potential to reduce debt by converting bonds to equity. | Ability to refinance debt if interest rates drop. |
| Investor's Advantage | Opportunity to participate in equity upside. | Higher yield compared to non-callable bonds. |
| Risk | Equity dilution risk post-conversion. | Call risk leading to reinvestment at lower rates. |
| Coupon Rate | Typically lower due to conversion feature. | Generally higher to compensate for call risk. |
| Conversion Feature | Yes, can convert into common stock. | No conversion to equity. |
| Maturity | Fixed term with conversion option before maturity. | Can be redeemed early by issuer within call period. |
| Investor Target | Investors seeking hybrid equity-debt exposure. | Investors accepting call risk for higher yield. |
Introduction to Convertible Bonds and Callable Bonds
Convertible bonds offer investors the option to convert debt into a predetermined number of shares, combining fixed income with potential equity upside. Callable bonds grant issuers the right to redeem the bond before maturity at a specified call price, providing flexibility to refinance debt if interest rates decline. Understanding these features helps investors evaluate risk, return, and strategic implications in fixed-income portfolios.
Key Features of Convertible Bonds
Convertible bonds offer investors the unique advantage of converting their bonds into a predetermined number of common shares, enabling participation in potential equity upside while receiving fixed interest payments. These bonds typically have a lower coupon rate compared to callable bonds due to the added conversion option, and they provide downside protection by ensuring bondholder repayment if conversion is not exercised. The convertible feature adds flexibility, allowing issuers to raise capital at a lower cost while giving investors equity exposure without immediate dilution.
Essential Characteristics of Callable Bonds
Callable bonds grant issuers the right to redeem the bond before maturity, typically at a premium, providing flexibility to refinance debt if interest rates decline. These bonds often feature higher coupon rates to compensate investors for the call risk, which limits potential price appreciation compared to non-callable bonds. The essential characteristic of callable bonds is the embedded call option, which exposes investors to reinvestment risk and influences the bond's yield and market value.
How Convertible Bonds Work
Convertible bonds allow investors to convert their bonds into a predetermined number of shares of the issuing company's stock, providing potential equity upside while receiving fixed interest payments. These bonds typically feature a conversion ratio and conversion price, which determine how many shares the bondholder can obtain upon conversion. The conversion option adds value by offering downside protection through bond interest and upside potential through stock appreciation, differentiating them from callable bonds that primarily give issuers the right to redeem the bonds before maturity.
How Callable Bonds Function
Callable bonds grant the issuer the right to redeem the bond before its maturity date, typically at a predefined call price, allowing them to refinance debt when interest rates decline. This feature protects issuers against falling rates by limiting interest payments but introduces reinvestment risk for investors. Investors often demand higher yields on callable bonds to compensate for the uncertainty of early redemption and potential loss of future interest income.
Major Differences Between Convertible and Callable Bonds
Convertible bonds allow investors to convert their bonds into a predetermined number of the issuing company's shares, offering potential equity upside, while callable bonds enable the issuer to redeem the bonds before maturity, typically to refinance at lower interest rates. Convertible bonds generally feature lower interest rates due to their embedded conversion option, whereas callable bonds often offer higher yields as compensation for call risk. The key distinction lies in investor benefits: convertibles offer participation in equity gains, whereas callable bonds expose investors to reinvestment risk due to early redemption.
Advantages of Investing in Convertible Bonds
Convertible bonds offer investors the advantage of potential equity upside by allowing conversion into a predetermined number of shares, providing capital appreciation alongside fixed income. They typically exhibit lower risk compared to stocks due to their bond-like characteristics, including regular interest payments and principal repayment at maturity. This hybrid nature also provides some downside protection during market volatility, making convertible bonds an attractive option for risk-conscious investors seeking both income and growth.
Pros and Cons of Callable Bonds
Callable bonds offer issuers flexibility to redeem debt before maturity, often benefiting from declining interest rates by refinancing at lower costs. Investors face reinvestment risk and potential loss of higher income if bonds are called early, typically receiving a premium that may not fully compensate for lost future yields. Despite offering higher initial yields to attract investors, callable bonds are less attractive for those seeking stable, long-term income due to uncertainty and price compression.
Risk Factors: Convertible vs Callable Bonds
Convertible bonds carry risk related to the issuer's equity performance, as their value fluctuates with the underlying stock price, exposing investors to market volatility and potential dilution. Callable bonds present reinvestment risk, since the issuer can redeem the bond before maturity, often when interest rates decline, forcing investors to reinvest at lower yields. Both instruments involve credit risk tied to the issuer's financial stability, but convertible bonds add equity market risk while callable bonds emphasize interest rate and call risk.
Choosing Between Convertible and Callable Bonds
Choosing between convertible and callable bonds depends on the investor's risk tolerance and investment goals. Convertible bonds offer the potential for equity upside by allowing conversion into stock, which is attractive in a bullish market, while callable bonds provide higher yields but carry the risk of early redemption by the issuer, limiting long-term returns. Investors seeking growth through equity participation may prefer convertible bonds, whereas those prioritizing income with some downside protection might opt for callable bonds.
Convertible Bond Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com