Value investing focuses on identifying undervalued stocks trading below their intrinsic worth, offering potential for significant long-term gains. This strategy relies on fundamental analysis to assess a company's financial health, competitive advantages, and market position. Explore the rest of this article to discover how you can apply value investing principles to build a robust portfolio.
Table of Comparison
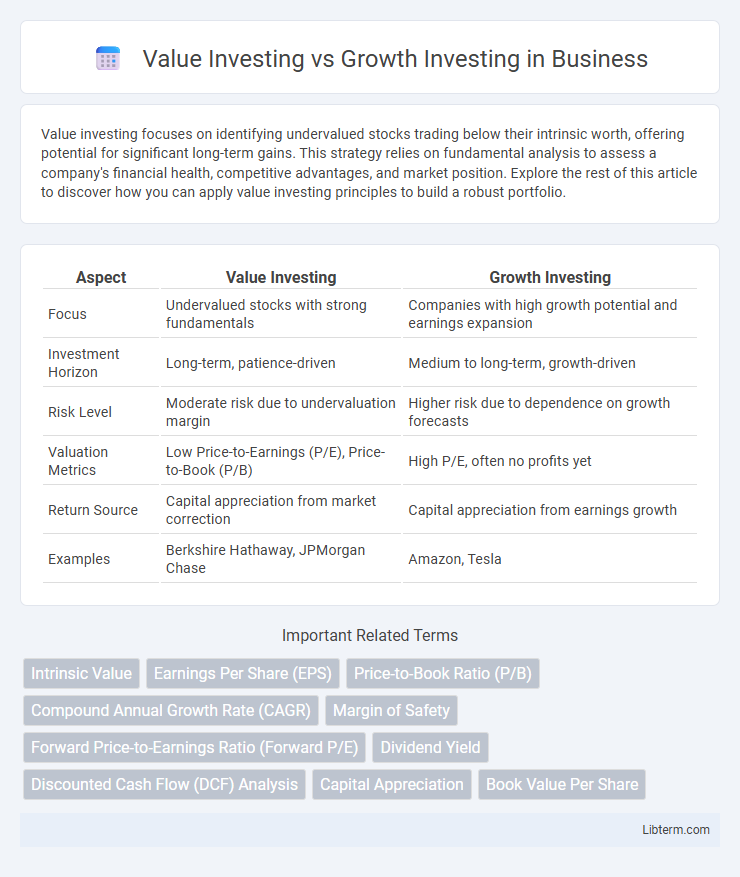
| Aspect | Value Investing | Growth Investing |
|---|---|---|
| Focus | Undervalued stocks with strong fundamentals | Companies with high growth potential and earnings expansion |
| Investment Horizon | Long-term, patience-driven | Medium to long-term, growth-driven |
| Risk Level | Moderate risk due to undervaluation margin | Higher risk due to dependence on growth forecasts |
| Valuation Metrics | Low Price-to-Earnings (P/E), Price-to-Book (P/B) | High P/E, often no profits yet |
| Return Source | Capital appreciation from market correction | Capital appreciation from earnings growth |
| Examples | Berkshire Hathaway, JPMorgan Chase | Amazon, Tesla |
Introduction to Investment Strategies
Value investing centers on identifying undervalued stocks trading below their intrinsic value, often characterized by low price-to-earnings (P/E) ratios and strong fundamentals. Growth investing targets companies with above-average earnings growth potential, emphasizing revenue expansion, market share gains, and innovation. Both strategies require thorough financial analysis, but value investing leans toward stability and dividends, while growth investing prioritizes capital appreciation.
Defining Value Investing
Value investing centers on identifying undervalued stocks trading below their intrinsic value, often measured through financial metrics like price-to-earnings (P/E) and price-to-book (P/B) ratios. This strategy emphasizes companies with strong fundamentals, stable cash flows, and solid dividend histories, aiming for long-term capital appreciation with lower risk. Investors prioritize margin of safety by purchasing shares at a discount, contrasting growth investing's focus on high revenue and earnings expansion potential.
What is Growth Investing?
Growth investing focuses on acquiring stocks of companies with above-average revenue and earnings growth potential, often in emerging industries or innovative sectors. It emphasizes capital appreciation through investing in businesses expected to expand rapidly, even if current valuations appear high compared to traditional metrics like the price-to-earnings ratio. Key growth investing targets include technology firms, healthcare innovators, and high-growth consumer companies demonstrating strong market demand and scalable business models.
Key Principles of Value Investing
Value investing centers on identifying undervalued stocks by analyzing financial statements, focusing on intrinsic value, and maintaining a margin of safety to minimize risk. Key principles include evaluating low price-to-earnings (P/E) ratios, strong dividend yields, and solid balance sheets to find bargains in the market. This approach contrasts with growth investing, which targets companies with high potential earnings growth regardless of current valuation.
Core Concepts of Growth Investing
Growth investing centers on identifying companies with strong potential for above-average revenue and earnings expansion, often in emerging industries or innovative sectors. Investors prioritize metrics like revenue growth rate, market share gains, and reinvestment strategies over immediate profitability or dividend yields. This approach typically involves higher risk and volatility but offers the possibility of substantial capital appreciation over time.
Risk and Reward: Value Versus Growth
Value investing involves targeting undervalued stocks with lower price-to-earnings ratios, offering potentially lower risk due to established fundamentals but slower capital appreciation. Growth investing focuses on companies with high earnings growth potential, often carrying higher volatility and risk in exchange for substantial long-term rewards. Balancing value and growth strategies can optimize portfolio risk-adjusted returns by leveraging stability and growth opportunities.
Historical Performance Comparison
Historical performance comparison reveals that value investing has generally outperformed growth investing during market downturns and periods of economic uncertainty, providing more stable returns through undervalued stocks with strong fundamentals. Growth investing tends to generate higher returns in bull markets by targeting companies with rapid revenue and earnings expansion, albeit with increased volatility. Long-term studies, such as those analyzing S&P 500 returns over multiple decades, indicate value strategies often yield superior risk-adjusted returns, especially when employing metrics like price-to-earnings and price-to-book ratios.
Determining Investor Suitability
Value investing suits risk-averse investors seeking steady returns through undervalued stocks with strong fundamentals and dividend potential. Growth investing appeals to investors comfortable with higher volatility, targeting companies with rapid revenue and earnings expansion for capital appreciation. Assessing individual risk tolerance, investment horizon, and financial goals is crucial in determining which strategy aligns best with an investor's profile.
Notable Investors and Case Studies
Warren Buffett exemplifies value investing with his disciplined approach of acquiring undervalued companies possessing strong fundamentals, as seen in his long-term success with Berkshire Hathaway. Conversely, growth investing is highlighted by Peter Lynch's strategy, notably his success with Fidelity Magellan Fund, which focused on companies exhibiting rapid earnings growth and innovative potential. These contrasting methodologies emphasize the importance of aligning investment strategies with individual investor goals and market conditions.
How to Choose Between Value and Growth Investing
Choosing between value and growth investing depends on your risk tolerance, investment horizon, and market conditions. Value investing targets undervalued stocks with strong fundamentals and lower risk, appealing to conservative investors seeking stability and dividends. Growth investing aims for companies with high earnings potential and rapid expansion, suitable for investors with higher risk tolerance prioritizing capital appreciation.
Value Investing Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com