Net margin measures the percentage of revenue remaining after all expenses, taxes, and costs are deducted, reflecting a company's profitability. A higher net margin indicates efficient management and strong financial health, crucial for sustainable business growth. Explore the rest of the article to understand how to analyze net margin and improve your company's financial performance.
Table of Comparison
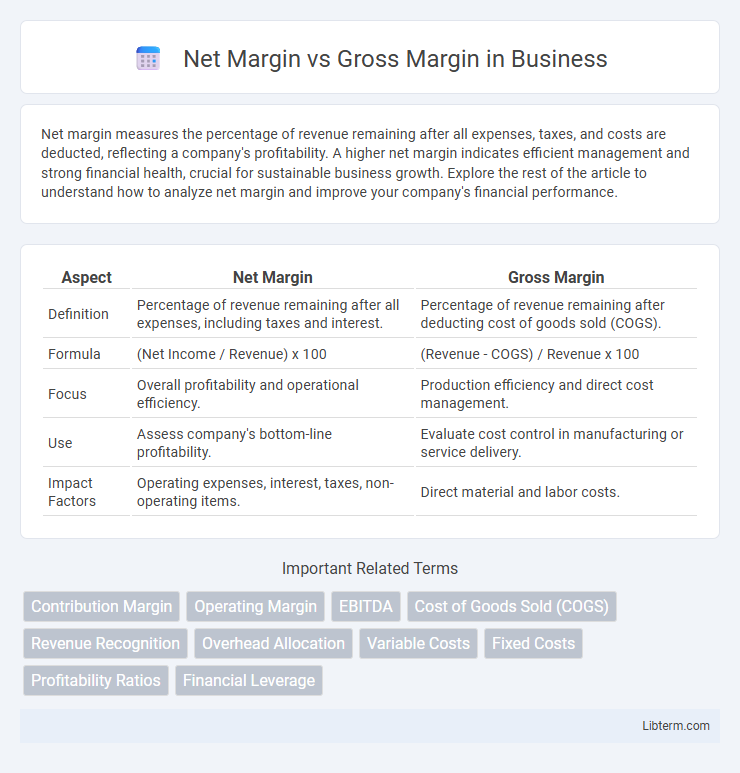
| Aspect | Net Margin | Gross Margin |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Percentage of revenue remaining after all expenses, including taxes and interest. | Percentage of revenue remaining after deducting cost of goods sold (COGS). |
| Formula | (Net Income / Revenue) x 100 | (Revenue - COGS) / Revenue x 100 |
| Focus | Overall profitability and operational efficiency. | Production efficiency and direct cost management. |
| Use | Assess company's bottom-line profitability. | Evaluate cost control in manufacturing or service delivery. |
| Impact Factors | Operating expenses, interest, taxes, non-operating items. | Direct material and labor costs. |
Understanding Net Margin and Gross Margin
Net margin represents the percentage of revenue remaining after all expenses, including operating costs, taxes, and interest, have been deducted, reflecting a company's overall profitability. Gross margin measures the percentage of revenue left after subtracting the cost of goods sold (COGS), highlighting the efficiency of production and pricing strategies. Understanding the distinction helps investors and managers assess operational efficiency versus total profitability.
Definitions: What is Gross Margin?
Gross margin represents the difference between total revenue and the cost of goods sold (COGS), expressed as a percentage of revenue. It reflects how efficiently a company produces and sells its products by showing the proportion of money left over after covering production costs. This metric is crucial for assessing core profitability before accounting for operating expenses, taxes, and interest.
Definitions: What is Net Margin?
Net margin represents the percentage of revenue remaining after all operating expenses, interest, taxes, and costs are deducted, reflecting a company's overall profitability. It is calculated by dividing net profit by total revenue and multiplying by 100 to express the result as a percentage. This metric provides a comprehensive view of how effectively a business converts sales into actual profit.
Key Differences Between Net Margin and Gross Margin
Net margin reflects a company's profitability after all expenses, including operating costs, interest, and taxes, are deducted from total revenue, whereas gross margin measures the profitability solely from core production activities by subtracting cost of goods sold (COGS) from revenue. Gross margin provides insight into production efficiency, while net margin offers a comprehensive view of overall financial health and operational efficiency. Understanding these distinctions helps in evaluating cost management and profit generation at different stages of a company's income statement.
How to Calculate Gross Margin
Gross Margin is calculated by subtracting the Cost of Goods Sold (COGS) from Total Revenue, then dividing the result by Total Revenue and multiplying by 100 to express it as a percentage. This metric reflects the efficiency of production and pricing strategies by showing the percentage of revenue that exceeds the direct costs of goods sold. Understanding Gross Margin helps businesses assess profitability before accounting for operating expenses, taxes, and interest, which are considered in Net Margin calculations.
How to Calculate Net Margin
Net margin is calculated by dividing net profit by total revenue and multiplying by 100 to express it as a percentage, reflecting the actual profitability after all expenses, taxes, and costs are deducted. Unlike gross margin, which only accounts for revenue minus the cost of goods sold (COGS), net margin provides a comprehensive view of a company's financial health by including operating expenses, interest, and tax obligations. Focusing on net margin calculation helps businesses assess their efficiency in managing overall costs relative to sales revenue.
Importance of Gross Margin in Business Analysis
Gross margin represents the percentage of revenue remaining after deducting the cost of goods sold, serving as a critical indicator of a company's production efficiency and pricing strategy. It directly impacts profitability by revealing how well a business controls its direct costs, which is essential for sustaining operations and funding growth. Understanding gross margin helps analysts identify pricing issues or cost management problems before they affect net margin and overall financial health.
Importance of Net Margin for Financial Health
Net margin measures a company's profitability after all expenses, taxes, and interest are deducted from total revenue, offering a clear indicator of financial health and operational efficiency. Unlike gross margin, which only accounts for production costs, net margin reflects overall cost management and profit generation capabilities. A higher net margin signifies stronger financial stability, enabling better reinvestment, debt reduction, and shareholder returns.
Net Margin vs Gross Margin: Real-World Examples
Net Margin and Gross Margin illustrate different profitability stages, with Gross Margin measuring revenue minus cost of goods sold, indicating production efficiency, and Net Margin reflecting overall profitability after all expenses, including taxes and interest. For example, Apple's high Gross Margin around 38% highlights efficient product manufacturing, while its Net Margin near 25% reveals strong cost management and operational efficiency beyond direct production costs. In contrast, retail companies like Walmart often show a Gross Margin around 25% but a much smaller Net Margin near 2-3%, demonstrating tight expense control challenges despite solid sales.
Which Metric Should Businesses Prioritize?
Net margin provides a comprehensive view of profitability by accounting for all expenses, including operating costs, taxes, and interest, making it essential for assessing overall business health. Gross margin focuses on core production efficiency by measuring revenue minus the cost of goods sold, useful for pricing strategy and cost control. Businesses should prioritize net margin for long-term sustainability and strategic planning, while gross margin offers valuable insights for operational efficiency and direct cost management.
Net Margin Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com