Acquisition involves obtaining assets, companies, or rights to expand business capabilities and market reach. Mastering acquisition strategies can significantly enhance your competitive advantage and drive growth. Explore the rest of the article to understand key acquisition methods and best practices.
Table of Comparison
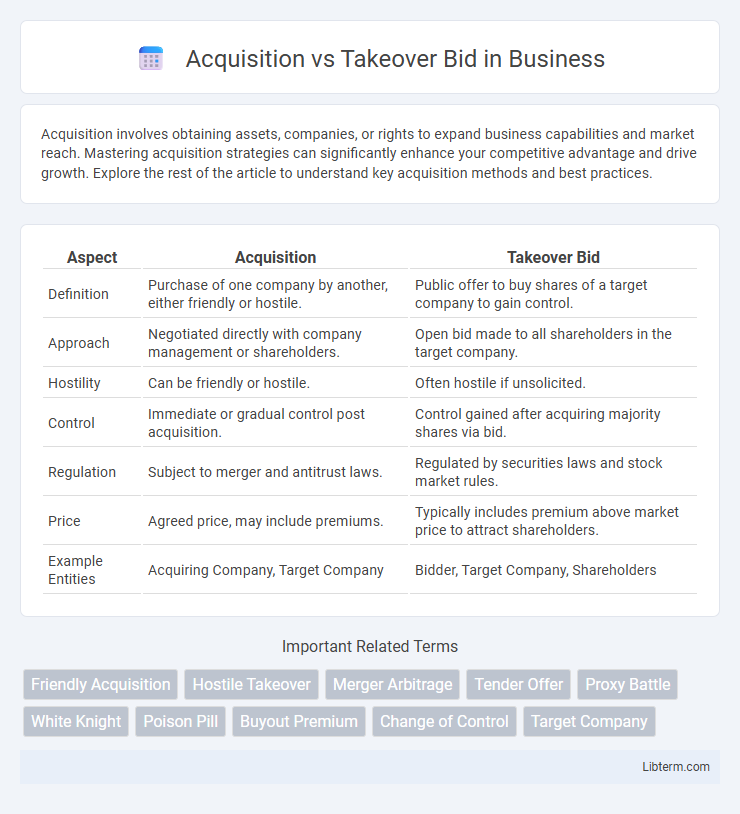
| Aspect | Acquisition | Takeover Bid |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Purchase of one company by another, either friendly or hostile. | Public offer to buy shares of a target company to gain control. |
| Approach | Negotiated directly with company management or shareholders. | Open bid made to all shareholders in the target company. |
| Hostility | Can be friendly or hostile. | Often hostile if unsolicited. |
| Control | Immediate or gradual control post acquisition. | Control gained after acquiring majority shares via bid. |
| Regulation | Subject to merger and antitrust laws. | Regulated by securities laws and stock market rules. |
| Price | Agreed price, may include premiums. | Typically includes premium above market price to attract shareholders. |
| Example Entities | Acquiring Company, Target Company | Bidder, Target Company, Shareholders |
Introduction to Acquisition and Takeover Bid
Acquisition and takeover bid are strategic methods for a company to gain control over another business. An acquisition involves purchasing a significant portion or all of the target company's assets or shares, often negotiated privately, while a takeover bid is a public offer to shareholders, typically targeting a controlling stake in the company. Both approaches aim to expand market presence, achieve synergies, and enhance competitive advantage in the industry.
Defining Acquisition and Takeover Bid
An acquisition involves one company purchasing a controlling interest or all shares of another company to gain control, often through negotiated agreements. A takeover bid is a public offer made by an acquiring company directly to shareholders to buy their shares at a specified price, typically aiming for a controlling stake. The key difference lies in acquisition being broader, encompassing various methods of gaining control, while a takeover bid specifically refers to a formal, often hostile or friendly, public offer to shareholders.
Key Differences Between Acquisition and Takeover Bid
Acquisition involves a company purchasing a controlling stake in another business, often through negotiation and agreement with the target's management, whereas a takeover bid is typically an offer made directly to shareholders, sometimes hostile, to gain control without management consent. Acquisitions tend to be strategic and collaborative, focusing on long-term integration, while takeover bids can be aggressive and opportunistic, aiming for quick control. Legal regulations and shareholder rights also differ, as takeover bids require compliance with strict disclosure and tender offer rules to protect minority investors.
Types of Acquisitions and Takeover Bids
Types of acquisitions include friendly acquisitions, where both companies agree on terms, and hostile acquisitions, initiated without the target company's consent. Takeover bids are typically classified as voluntary takeover bids, where the acquirer offers to purchase shares at a premium, or compulsory takeover bids, triggered by reaching a certain ownership threshold. Strategic, financial, and management buyouts represent specific acquisition types, while tender offers and proxy contests are common approaches in takeover bids.
Legal Aspects and Regulatory Framework
Acquisitions and takeover bids are governed by distinct legal frameworks designed to protect shareholders and ensure market transparency. Acquisition transactions often require compliance with corporate laws, securities regulations, and antitrust rules specific to jurisdictions like the U.S. Securities Exchange Act and the European Union's Takeover Directive. Takeover bids involve stringent disclosure obligations, mandatory bid thresholds, and regulatory approvals to prevent coercive practices and promote fair treatment of minority shareholders.
Strategic Objectives Behind Acquisitions and Takeovers
Strategic objectives behind acquisitions typically involve expanding market share, acquiring new technologies, or entering new geographic markets to enhance long-term competitive advantage. Takeover bids often aim to gain control of a target company to restructure its operations, achieve cost synergies, or unlock shareholder value through management changes. Both approaches seek to optimize resource allocation and drive growth, but acquisitions are usually more collaborative, whereas takeovers may be hostile and focus on rapid control transfer.
Benefits and Risks of Each Approach
Acquisition offers benefits such as streamlined control, potential cost synergies, and long-term strategic alignment, but it carries risks like integration challenges and cultural clashes. Takeover bids provide an opportunity for rapid expansion and market share acquisition but pose risks including hostile resistance, regulatory hurdles, and premium pricing. Evaluating financial impact, shareholder response, and legal frameworks is essential for choosing the optimal approach.
Famous Examples: Acquisition vs Takeover Bid
The acquisition of LinkedIn by Microsoft in 2016 for $26.2 billion exemplifies a strategic acquisition aimed at expanding market reach and integrating services seamlessly. In contrast, the hostile takeover bid by Kraft Heinz for Unilever in 2017, valued at $143 billion, highlighted aggressive tactics to gain control despite management resistance. These examples illustrate the distinct approaches and outcomes between cooperative acquisitions and contentious takeover bids.
Impact on Stakeholders and Market Value
Acquisitions often lead to collaborative integration, benefiting stakeholders through sustained employment and enhanced operational synergies that can increase market value. Takeover bids, frequently hostile, may create uncertainty for employees and customers, potentially causing stock price volatility and short-term market value fluctuations. The strategic approach of acquisitions tends to foster long-term shareholder value, whereas takeover bids can trigger rapid shifts in ownership, influencing market perceptions and stakeholder confidence.
Choosing the Right Strategy: Acquisition or Takeover Bid?
Choosing between an acquisition and a takeover bid depends on the company's strategic goals, financial capacity, and desired level of control. Acquisitions often allow for a more collaborative approach, enabling negotiated terms and smoother integration, while takeover bids are typically aggressive, aiming for rapid control through share purchases, sometimes without the target's consent. Evaluating the target company's market position, shareholder structure, and regulatory environment is crucial to determine the most effective strategy for maximizing value and minimizing risks.
Acquisition Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com