Layering is a versatile styling technique that involves wearing multiple clothing pieces to create depth, texture, and visual interest in an outfit. This approach not only enhances your aesthetic appeal but also provides practical benefits like adapting to changing weather throughout the day. Explore the rest of this article to master layering strategies that elevate your wardrobe.
Table of Comparison
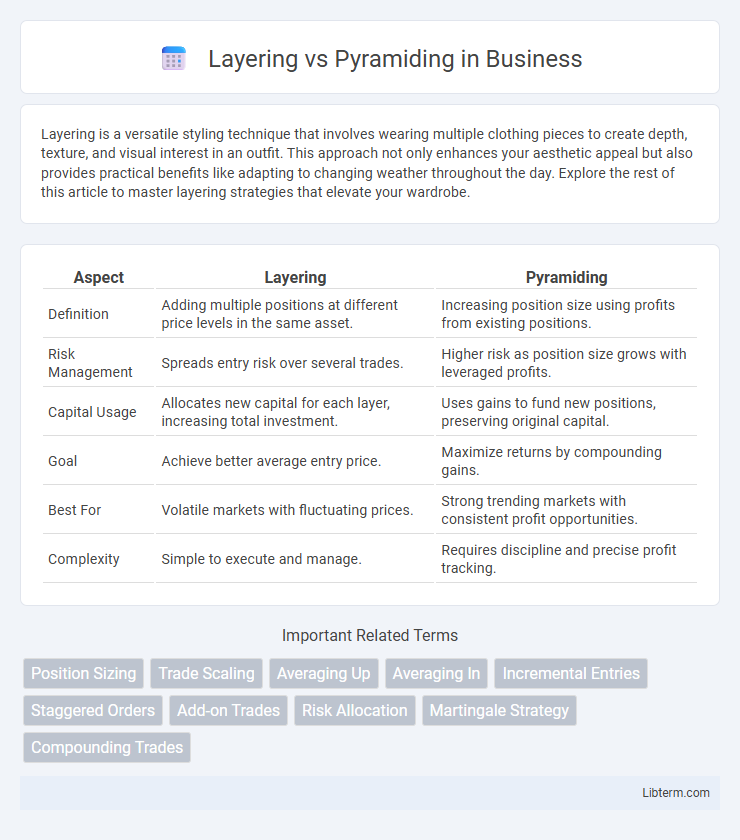
| Aspect | Layering | Pyramiding |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Adding multiple positions at different price levels in the same asset. | Increasing position size using profits from existing positions. |
| Risk Management | Spreads entry risk over several trades. | Higher risk as position size grows with leveraged profits. |
| Capital Usage | Allocates new capital for each layer, increasing total investment. | Uses gains to fund new positions, preserving original capital. |
| Goal | Achieve better average entry price. | Maximize returns by compounding gains. |
| Best For | Volatile markets with fluctuating prices. | Strong trending markets with consistent profit opportunities. |
| Complexity | Simple to execute and manage. | Requires discipline and precise profit tracking. |
Introduction to Layering and Pyramiding
Layering involves entering multiple smaller positions incrementally to manage risk and average entry price, ideal for volatile markets or uncertain trends. Pyramiding entails adding to a winning position by increasing exposure as the trade moves favorably, maximizing profit potential during strong trends. Both techniques require disciplined risk management and strategic timing to optimize returns while controlling exposure.
Defining Layering in Investment Strategies
Layering in investment strategies involves placing multiple buy or sell orders at different price levels to influence market perception and create artificial liquidity. This technique aims to manipulate order books by balancing genuine and deceptive orders, thereby impacting price movements. Understanding layering is essential for recognizing market manipulation tactics and enforcing regulatory compliance in trading environments.
Understanding Pyramiding: A Brief Overview
Pyramiding is a trading strategy that involves increasing the size of a position incrementally as the asset's price moves favorably, aiming to maximize profits while managing risk. Traders add to winning positions using profits from previous trades, which helps to leverage gains without significantly increasing initial exposure. This method contrasts with layering, which places multiple orders at different price levels to influence market perception or gauge demand.
Key Differences Between Layering and Pyramiding
Layering involves entering multiple positions at different price levels to average out the entry price, while pyramiding focuses on adding to winning positions to maximize profits as the trend continues. Layering is typically used to manage risk by spreading entry points, whereas pyramiding aims to capitalize on momentum by scaling into a successful trade. The key difference lies in layering's emphasis on price averaging versus pyramiding's emphasis on increasing exposure in a trending market.
Pros and Cons of Layering
Layering in trading allows for multiple entry points, reducing the risk of entering a position at an unfavorable price and providing flexibility in managing trades. However, it can increase transaction costs due to multiple orders and may complicate position management, potentially leading to overexposure. Traders must balance the benefits of diversified entry with the challenge of timing and complexity associated with layering strategies.
Advantages and Risks of Pyramiding
Pyramiding offers the advantage of maximizing potential profits by adding to winning positions using accumulated unrealized gains, leveraging the momentum of a successful trade. This strategy increases exposure and can significantly amplify returns when markets trend strongly in favor. However, pyramiding carries heightened risk as it involves increasing investment in a single asset, potentially resulting in substantial losses if the market reverses unexpectedly or volatility spikes, which requires strict risk management and disciplined stop-loss orders.
Practical Examples: Layering vs Pyramiding in Action
Layering involves entering multiple smaller positions at different price levels to manage risk, such as buying 100 shares of a stock at $50, then another 100 at $48 as it dips. Pyramiding, on the other hand, consists of adding to a winning position by using profits from earlier trades, for example, buying 100 shares at $50, then adding 50 shares at $55 as the stock rises. Practical use of layering suits volatile markets to average entry price, while pyramiding leverages upward momentum to maximize gains on trending assets.
Choosing the Right Approach for Your Portfolio
Choosing between layering and pyramiding depends on your risk tolerance and investment goals. Layering involves building positions gradually at different price levels to manage risk and capture value, while pyramiding focuses on adding to winning positions to maximize gains during upward trends. Evaluate your portfolio's volatility and market conditions to select the strategy that aligns with your objectives and capital deployment preferences.
Common Mistakes to Avoid With Each Strategy
Common mistakes in layering include adding too many simultaneous trades, which increases risk exposure and dilutes potential profits. In pyramiding, traders often over-leverage by adding positions too aggressively, leading to significant losses when the trend reverses. Both strategies require disciplined position sizing and strict adherence to predefined entry and exit points to avoid these pitfalls.
Conclusion: Which Is Better For You?
Choosing between layering and pyramiding depends on your trading goals, risk tolerance, and experience level. Layering offers more flexibility with smaller incremental trades, reducing risk exposure, while pyramiding aims to maximize profits by adding to winning positions but increases potential losses. Traders seeking steady growth with controlled risk may prefer layering, whereas those confident in strong trends might opt for pyramiding to capitalize on momentum.
Layering Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com