Vertical integration enhances operational efficiency by controlling multiple stages of the supply chain, reducing costs, and improving product quality. It allows businesses to respond swiftly to market changes and gain a competitive advantage through better coordination and resource management. Explore the rest of this article to understand how vertical integration can transform your company's growth and profitability.
Table of Comparison
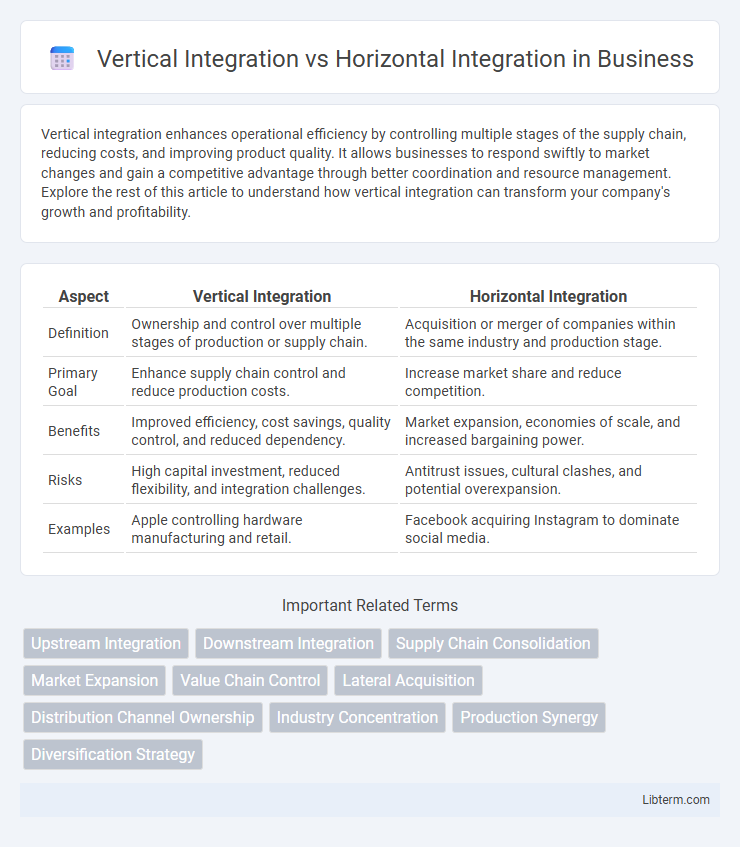
| Aspect | Vertical Integration | Horizontal Integration |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Ownership and control over multiple stages of production or supply chain. | Acquisition or merger of companies within the same industry and production stage. |
| Primary Goal | Enhance supply chain control and reduce production costs. | Increase market share and reduce competition. |
| Benefits | Improved efficiency, cost savings, quality control, and reduced dependency. | Market expansion, economies of scale, and increased bargaining power. |
| Risks | High capital investment, reduced flexibility, and integration challenges. | Antitrust issues, cultural clashes, and potential overexpansion. |
| Examples | Apple controlling hardware manufacturing and retail. | Facebook acquiring Instagram to dominate social media. |
Introduction to Business Integration Strategies
Vertical integration involves a company expanding its operations by acquiring or merging with entities along its supply chain, enhancing control over production and distribution processes. Horizontal integration occurs when a business merges with or acquires competitors within the same industry to increase market share and reduce competition. Understanding these integration strategies is crucial for optimizing business growth, operational efficiency, and competitive advantage.
Defining Vertical Integration
Vertical integration refers to a business strategy where a company expands its operations into different stages of production within the same industry, controlling supply chains from raw materials to distribution. This approach enhances operational efficiency, reduces costs, and improves supply chain coordination by owning multiple layers of the production process. Companies practicing vertical integration can better control quality, delivery timing, and market access compared to those relying on external suppliers or distributors.
Understanding Horizontal Integration
Horizontal integration involves a company expanding its operations by acquiring or merging with competitors in the same industry to increase market share, reduce competition, and achieve economies of scale. This growth strategy enhances product diversity and market reach while potentially driving down costs through consolidated resources. Understanding horizontal integration reveals its role in creating larger corporate entities that dominate specific sectors and influence market dynamics.
Key Differences Between Vertical and Horizontal Integration
Vertical integration involves a company expanding its operations into different stages of production or distribution within the same industry, enhancing control over the supply chain and reducing costs. Horizontal integration occurs when a company acquires or merges with competitors operating at the same stage, increasing market share and reducing competition. Key differences include the scope of control, with vertical integration focusing on different levels of the supply chain, while horizontal integration targets growth within the same market level.
Advantages of Vertical Integration
Vertical integration enhances supply chain control, reducing costs by minimizing intermediaries and improving efficiency. It increases product quality consistency through direct oversight of production and distribution processes. Firms gain competitive advantages by securing critical resources and enabling faster response to market changes.
Benefits of Horizontal Integration
Horizontal integration enhances market share by consolidating competitors within the same industry, enabling economies of scale and increased operational efficiency. It fosters product diversification and broadens customer base access, supporting revenue growth and competitive advantage. This strategy also facilitates resource sharing and reduces costs through streamlined processes and improved bargaining power with suppliers.
Challenges and Risks of Vertical Integration
Vertical integration faces challenges such as high capital investment and complexity in managing diverse operations across the supply chain, which can lead to inefficiencies. Risks include reduced flexibility to adapt to market changes and potential antitrust issues due to increased market power. Companies must also navigate coordination difficulties between different stages of production, impacting overall performance and profitability.
Potential Drawbacks of Horizontal Integration
Horizontal integration can lead to significant drawbacks such as reduced competition, which often triggers antitrust scrutiny from regulatory authorities like the Federal Trade Commission. This consolidation may cause market monopolization, limiting consumer choices and potentially leading to higher prices. Furthermore, managing a larger, more diverse company can increase operational complexities and integration challenges, impacting overall efficiency.
Real-World Examples of Integration Strategies
Tesla exemplifies vertical integration by controlling its supply chain, manufacturing batteries, and operating charging networks, enhancing efficiency and reducing dependency on suppliers. Facebook's acquisition of Instagram and WhatsApp represents horizontal integration, expanding its social media market share and consolidating user data across platforms. Amazon combines both strategies, integrating vertically through fulfillment centers and horizontally by acquiring Whole Foods, boosting both product control and market reach.
Choosing the Right Integration Approach for Your Business
Choosing the right integration approach depends on your business goals and market conditions. Vertical integration enhances control over the supply chain and can reduce costs by consolidating production stages, ideal for businesses seeking efficiency and quality management. Horizontal integration focuses on expanding market share and reducing competition through acquiring or merging with competitors, suitable for companies aiming to increase scale and broaden customer base.
Vertical Integration Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com