Closed sourcing restricts access to a software's source code, ensuring only authorized developers can view or modify it. This approach enhances security and control over the software's distribution, but limits flexibility for users seeking customization or collaboration. Discover how closed sourcing impacts your software choices and its role in today's digital landscape in the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
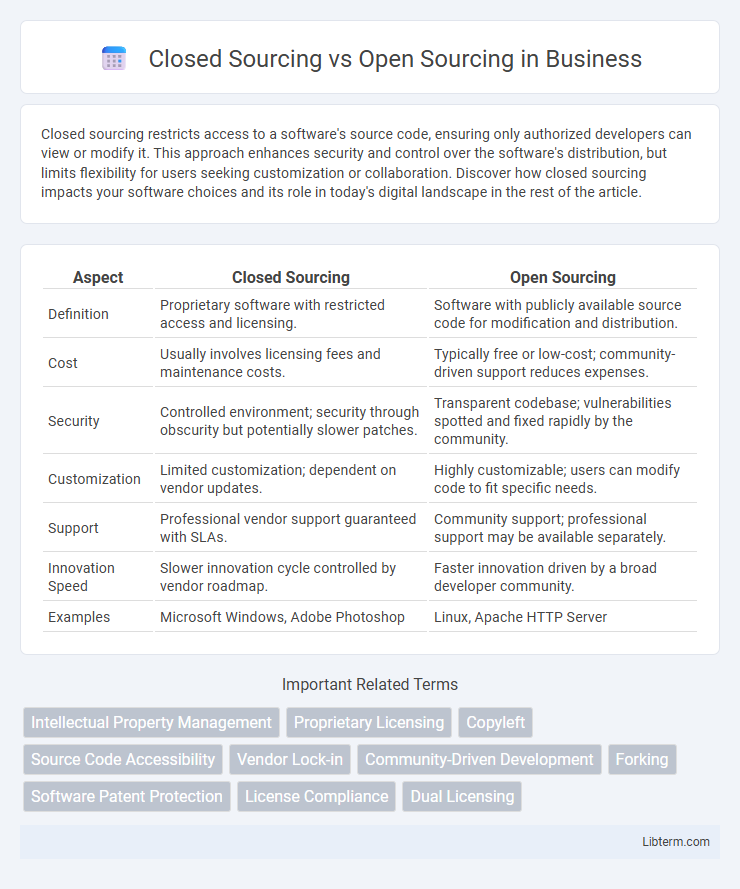
| Aspect | Closed Sourcing | Open Sourcing |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Proprietary software with restricted access and licensing. | Software with publicly available source code for modification and distribution. |
| Cost | Usually involves licensing fees and maintenance costs. | Typically free or low-cost; community-driven support reduces expenses. |
| Security | Controlled environment; security through obscurity but potentially slower patches. | Transparent codebase; vulnerabilities spotted and fixed rapidly by the community. |
| Customization | Limited customization; dependent on vendor updates. | Highly customizable; users can modify code to fit specific needs. |
| Support | Professional vendor support guaranteed with SLAs. | Community support; professional support may be available separately. |
| Innovation Speed | Slower innovation cycle controlled by vendor roadmap. | Faster innovation driven by a broad developer community. |
| Examples | Microsoft Windows, Adobe Photoshop | Linux, Apache HTTP Server |
Introduction to Open Sourcing and Closed Sourcing
Closed sourcing restricts software access, allowing only authorized users to view, modify, or distribute the code, ensuring tight control over intellectual property and often enhancing security and profitability. Open sourcing promotes transparency by making source code publicly available for use, modification, and distribution, fostering collaboration, innovation, and community-driven development. Businesses choose closed sourcing for proprietary advantage, while open sourcing encourages shared improvement and faster technology evolution.
Key Differences Between Open and Closed Source Software
Open source software provides publicly accessible source code, allowing users to modify, distribute, and customize the software freely, promoting collaboration and transparency. Closed source software restricts access to source code, maintaining proprietary control and limiting user modifications to protect intellectual property and ensure consistent performance. Key differences include licensing models, with open source using licenses like GPL or MIT, while closed source relies on proprietary licenses, impacting software security, innovation, and community involvement.
Advantages of Open Sourcing
Open sourcing offers enhanced collaboration by allowing diverse developers to contribute, accelerating innovation and improving software quality. It promotes transparency and security through public code review, reducing vulnerabilities more effectively than closed sourcing. Open source projects benefit from extensive community support, leading to faster bug fixes and continuous feature enhancements.
Benefits of Closed Sourcing
Closed sourcing offers enhanced security by restricting access to source code, reducing the risk of vulnerabilities and unauthorized modifications. It ensures consistent quality control and intellectual property protection, allowing companies to maintain a competitive advantage. Furthermore, closed source software typically provides dedicated customer support and guaranteed stability through controlled updates and testing.
Drawbacks of Open Source Projects
Open source projects often face challenges such as fragmented code quality due to varied contributor skill levels and inconsistent coding standards. Security vulnerabilities may arise from publicly accessible source code, increasing the risk of exploitation by malicious actors. Furthermore, lack of formal support and accountability can lead to slower issue resolution and maintenance difficulties.
Limitations of Closed Source Solutions
Closed source solutions restrict access to source code, limiting customization and flexibility for end users or developers. This lack of transparency can hinder security audits and slow vulnerability detection, potentially increasing risk exposure. Furthermore, reliance on proprietary vendors for updates and support can lead to higher costs and reduced innovation compared to open source alternatives.
Security Comparison: Open Source vs Closed Source
Open source software security benefits from transparency, allowing a global community to identify and fix vulnerabilities swiftly, reducing the risk of hidden backdoors. Closed source software relies on internal security measures and proprietary code, which can delay the detection of flaws and increase the risk of undisclosed vulnerabilities. Studies show that open source projects often have faster patch times and higher responsiveness to security issues compared to closed source counterparts.
Community Support and Collaboration
Closed sourcing restricts access to source code, limiting community support and collaboration to internal teams or select partners, which often slows innovation and problem-solving. Open sourcing enables a global community of developers to contribute, share knowledge, and rapidly improve software through transparent collaboration and peer review. Platforms like GitHub and GitLab foster vibrant ecosystems where diverse contributors accelerate development and enhance software security through collective scrutiny.
Licensing and Legal Considerations
Closed sourcing restricts access to source code, often protected by proprietary licenses that limit modification, redistribution, and usage rights, ensuring controlled intellectual property management. Open sourcing promotes transparency and collaboration through licenses like MIT, GPL, or Apache, which grant users varying degrees of freedom to use, modify, and distribute the software while imposing specific obligations such as attribution or copyleft. Legal considerations in closed source involve strict compliance with license agreements and potential penalties for infringement, whereas open source requires adherence to license terms to maintain software freedom and avoid legal disputes.
Choosing the Right Model for Your Project
Choosing the right model for your project depends on factors such as control, collaboration, and security needs. Closed sourcing offers proprietary control and enhanced security, suitable for projects with sensitive data or competitive advantage requirements. Open sourcing encourages community collaboration, faster innovation, and transparency, making it ideal for projects that benefit from external contributions and widespread adoption.
Closed Sourcing Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com