An ecosystem is a complex network of living organisms interacting with their physical environment to sustain life. It encompasses diverse species, natural resources, and processes that maintain ecological balance and support biodiversity. Explore the rest of the article to understand how ecosystems function and why they are vital to Your planet's health.
Table of Comparison
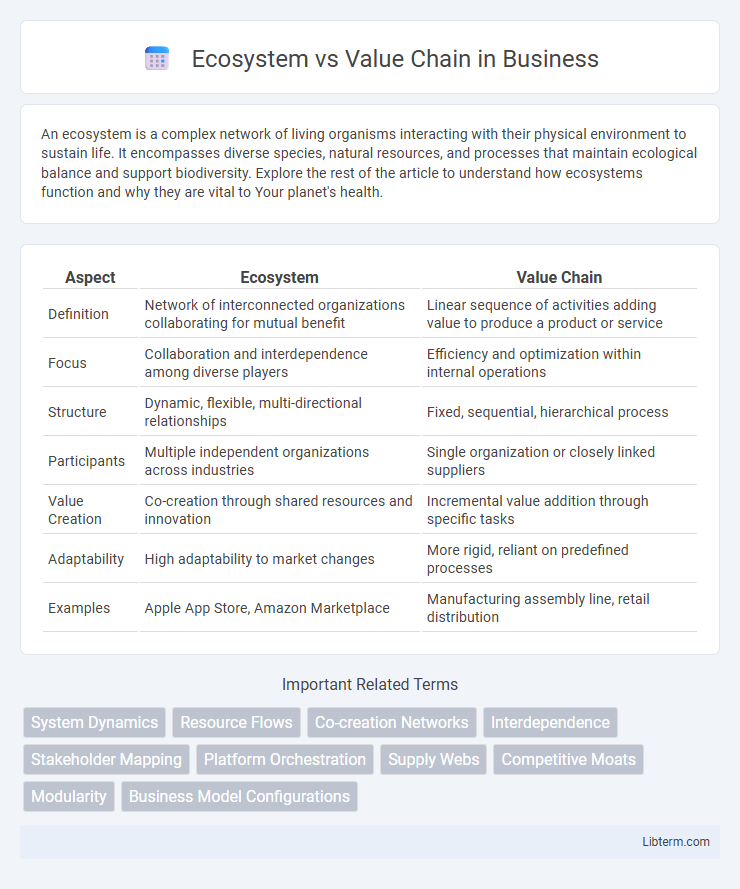
| Aspect | Ecosystem | Value Chain |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Network of interconnected organizations collaborating for mutual benefit | Linear sequence of activities adding value to produce a product or service |
| Focus | Collaboration and interdependence among diverse players | Efficiency and optimization within internal operations |
| Structure | Dynamic, flexible, multi-directional relationships | Fixed, sequential, hierarchical process |
| Participants | Multiple independent organizations across industries | Single organization or closely linked suppliers |
| Value Creation | Co-creation through shared resources and innovation | Incremental value addition through specific tasks |
| Adaptability | High adaptability to market changes | More rigid, reliant on predefined processes |
| Examples | Apple App Store, Amazon Marketplace | Manufacturing assembly line, retail distribution |
Understanding Ecosystems and Value Chains
Ecosystems represent interconnected networks of organizations, technologies, and processes that collaboratively create value through mutual dependencies, while value chains depict linear sequences of activities transforming inputs into finished products or services. Understanding ecosystems involves analyzing dynamic relationships and co-creation among participants that drive innovation and competitive advantage, whereas value chains emphasize efficiency and optimization of discrete operational steps. Both frameworks are essential for strategic decision-making, with ecosystems fostering adaptability and resilience, and value chains enhancing process control and cost management.
Key Definitions: Ecosystem vs Value Chain
An ecosystem is a dynamic network of interconnected organizations, technologies, and stakeholders collaborating to create value through shared resources and innovation. A value chain refers to a linear sequence of activities within a single organization or industry that transforms raw materials into finished products and delivers them to customers. Ecosystems emphasize interdependence and co-creation across multiple entities, while value chains focus on efficiency and optimization within a structured process.
Core Components of Ecosystems
Core components of ecosystems include interconnected networks of organizations, resources, and stakeholders collaborating to create shared value and drive innovation. Unlike linear value chains, ecosystems emphasize dynamic interactions, co-creation, and adaptability across diverse participants such as suppliers, customers, partners, and regulators. Digital platforms, data exchange, and enabling technologies often form the structural backbone facilitating these multi-directional relationships and collective efficiency.
Essential Elements of a Value Chain
A value chain comprises essential elements such as inbound logistics, operations, outbound logistics, marketing and sales, and service, all aimed at creating value and competitive advantage. Each stage integrates resources, processes, and activities to optimize efficiency and deliver products or services to end customers. In contrast, an ecosystem extends beyond the linear flow of the value chain by encompassing a network of interconnected organizations collaborating and co-evolving in a shared market environment.
Differences Between Ecosystem and Value Chain
Ecosystems involve multiple interconnected organizations co-creating value through collaboration and shared resources, while value chains represent a linear sequence of activities transforming inputs into outputs within a single company or a tightly controlled group. Ecosystems emphasize network effects, adaptability, and innovation across diverse participants, contrasting with value chains that focus on efficiency, cost reduction, and optimization of each step within a defined process. The ecosystem model supports dynamic interactions and value exchange beyond traditional supplier-buyer relationships, whereas value chains maintain a hierarchical structure with clear, sequential responsibilities.
Advantages of Business Ecosystems
Business ecosystems foster collaboration among diverse stakeholders, enabling innovation through shared resources and complementary capabilities. These interconnected networks enhance adaptability and resilience by leveraging collective strengths, driving sustainable growth beyond traditional linear value chains. Ecosystems also open new market opportunities by integrating various industries and technologies, creating comprehensive solutions that meet evolving customer needs.
Value Chain Benefits and Optimization
Value chains streamline business processes by breaking down production into sequential activities that add measurable value, enhancing efficiency and cost management. Optimizing value chains involves aligning suppliers, operations, and distribution channels to reduce waste, improve quality, and accelerate time-to-market. This structured approach drives competitive advantage through improved resource allocation, scalability, and customer satisfaction.
When to Use an Ecosystem Model
Use an ecosystem model when businesses require dynamic collaboration across multiple industries to co-create value and innovate beyond traditional boundaries. This approach suits complex environments where interdependent participants provide complementary products or services, enhancing customer experience and market reach. Ecosystem models excel in rapidly evolving markets driven by technology and shifting consumer demands, fostering adaptability and resilience.
When a Value Chain Approach is More Effective
A value chain approach is more effective when a business needs to optimize internal processes and enhance operational efficiency by focusing on linear activities from raw materials to final delivery. This approach excels in industries with clear, sequential stages like manufacturing, where cost control and process improvement directly impact competitiveness. Emphasizing value chain analysis enables companies to identify bottlenecks, reduce waste, and increase profitability by managing each step within their own control.
Future Trends: Ecosystems and Value Chains in Business
Future trends in business emphasize the integration of digital ecosystems and value chains to enhance agility, innovation, and customer-centricity. Ecosystems leverage interconnected networks of partners, technologies, and platforms to create collaborative value, while value chains focus on optimizing internal processes and sequential activities for efficiency. The convergence of these models enables companies to harness real-time data, foster co-creation, and respond rapidly to market changes, driving sustainable competitive advantage.
Ecosystem Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com