A lender provides financial resources to individuals or businesses in exchange for repayment with interest over a specified period. Understanding different types of lenders, such as banks, credit unions, and private lenders, can help you choose the best option for your financial needs. Explore the rest of the article to learn how to identify the right lender for your situation and secure favorable loan terms.
Table of Comparison
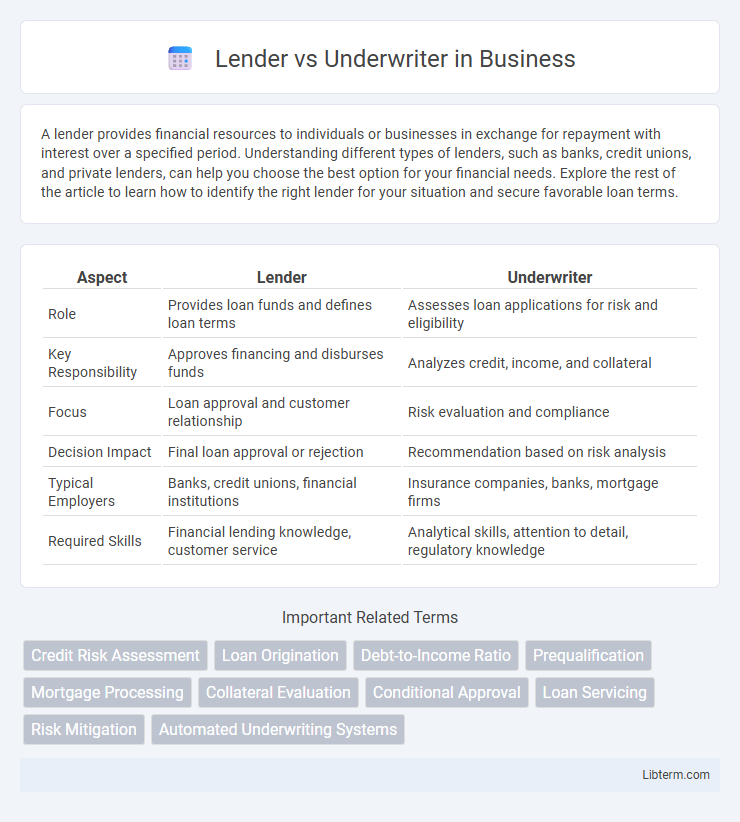
| Aspect | Lender | Underwriter |
|---|---|---|
| Role | Provides loan funds and defines loan terms | Assesses loan applications for risk and eligibility |
| Key Responsibility | Approves financing and disburses funds | Analyzes credit, income, and collateral |
| Focus | Loan approval and customer relationship | Risk evaluation and compliance |
| Decision Impact | Final loan approval or rejection | Recommendation based on risk analysis |
| Typical Employers | Banks, credit unions, financial institutions | Insurance companies, banks, mortgage firms |
| Required Skills | Financial lending knowledge, customer service | Analytical skills, attention to detail, regulatory knowledge |
Introduction to Lenders and Underwriters
Lenders are financial institutions or individuals who provide funds to borrowers with the expectation of repayment, often including interest, serving as the primary source of capital in lending transactions. Underwriters assess the risk of lending by evaluating borrowers' creditworthiness, financial history, and loan applications to determine approval eligibility and terms. The collaboration between lenders and underwriters ensures informed decision-making in the loan approval process, balancing risk management and funding allocation.
Defining the Role of a Lender
A lender is a financial institution or individual that provides funds to borrowers with the expectation of repayment, typically with interest. They assess creditworthiness, set loan terms, and disburse funds to facilitate purchases such as homes, vehicles, or business investments. Unlike underwriters who evaluate the risk and validity of loan applications, lenders make the final decision to approve and fund the loan.
Understanding the Underwriter’s Responsibilities
The underwriter evaluates loan applications by assessing the borrower's creditworthiness, verifying financial documents, and determining risk factors to ensure compliance with lending guidelines. This role involves analyzing income, employment history, and debt-to-income ratios to make informed approval decisions. Understanding the underwriter's responsibilities is crucial for lenders to mitigate default risks and maintain portfolio quality.
Key Differences Between Lenders and Underwriters
Lenders primarily provide the funds for loans and decide on loan approval based on creditworthiness, income, and repayment ability, while underwriters assess the risk of issuing the loan by verifying documentation and evaluating financial information. Underwriters apply strict guidelines to ensure compliance with lending standards and reduce default risk, often acting as a gatekeeper before loan disbursement. The key difference lies in lenders making the final loan decision and funding, whereas underwriters perform detailed risk analysis and approval validation.
The Lending Process: Where Each Fits In
The lending process involves both lenders and underwriters, with lenders initiating the loan application and determining borrower eligibility based on creditworthiness and financial background. Underwriters perform a detailed risk assessment by analyzing credit reports, employment verification, and property appraisal to validate the applicant's ability to repay the loan. This sequential collaboration ensures accurate loan approval, balancing lender risk management with regulatory compliance.
How Lenders Assess Loan Applications
Lenders assess loan applications by analyzing the borrower's credit history, income stability, debt-to-income ratio, and collateral value to determine repayment ability. They evaluate risk factors using credit scores, employment verification, and financial statements to ensure compliance with lending criteria. This thorough assessment helps lenders make informed approval decisions while minimizing default risks.
The Underwriting Process Explained
The underwriting process involves a thorough evaluation of a borrower's financial background, credit history, and ability to repay a loan, ensuring that risks are minimized for the lender. Underwriters analyze documentation such as income statements, credit reports, and debt-to-income ratios to determine loan eligibility and terms. This process is critical in approving or denying loans, differentiating underwriters' responsibilities from lenders who fund the loans.
Impact on Borrowers: Lender vs Underwriter Decisions
Lender decisions directly affect borrowers by determining loan approval, terms, and interest rates based on creditworthiness and financial capacity, impacting overall loan accessibility and cost. Underwriters evaluate risk by verifying borrower information and assessing eligibility, influencing whether a loan application passes regulatory and risk standards. The combined actions of lenders and underwriters shape the borrower's ability to secure financing and the quality of the loan offered.
Common Misconceptions about Lenders and Underwriters
Lenders and underwriters serve distinct roles in the loan approval process, yet many mistakenly believe they perform the same functions, causing confusion about their responsibilities. Lenders primarily evaluate a borrower's overall creditworthiness and decide whether to offer a loan, whereas underwriters assess the risk and verify the accuracy of the application, credit reports, and supporting documentation. Misunderstanding these roles can lead to unrealistic borrower expectations regarding timelines and decision-making authority during mortgage approvals.
Choosing the Right Partner: Insights for Borrowers
Borrowers benefit from understanding that lenders provide the funds and set loan terms, while underwriters assess risk and approve loan applications, ensuring borrower eligibility. Choosing the right partner involves evaluating the lender's loan products, interest rates, and customer service alongside the underwriter's reputation for thorough and fair risk assessment. Effective collaboration between lenders and underwriters can streamline approvals, making it crucial for borrowers to select entities aligned with their financial goals and credit profiles.
Lender Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com