Performance audit evaluates the efficiency, effectiveness, and economy of an organization's operations to ensure optimal use of resources. This type of audit identifies areas for improvement and helps enhance overall organizational performance. Discover how a performance audit can benefit your organization by reading the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
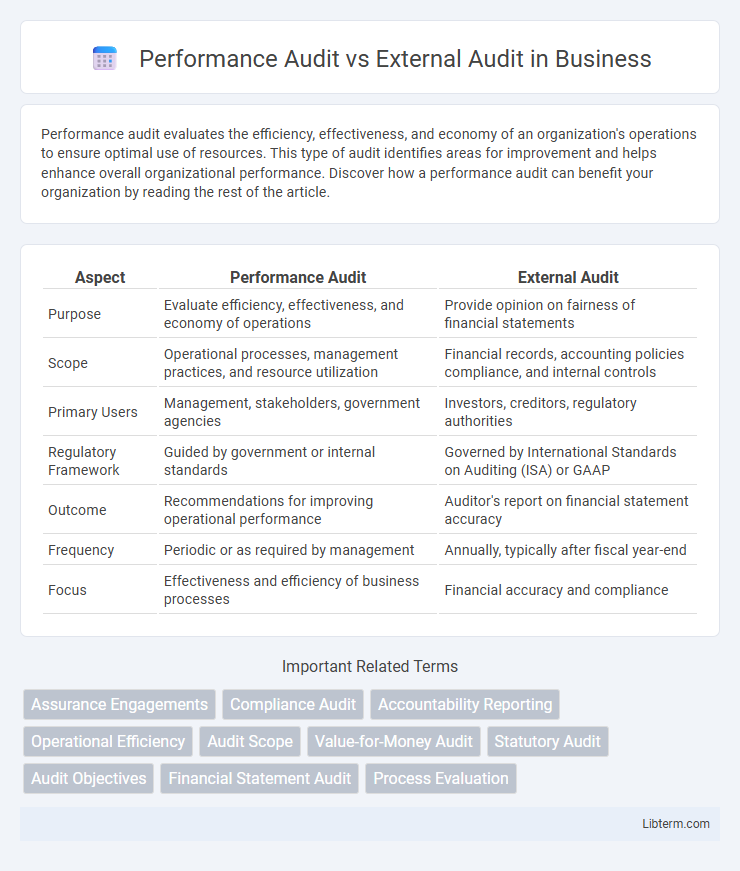
| Aspect | Performance Audit | External Audit |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Evaluate efficiency, effectiveness, and economy of operations | Provide opinion on fairness of financial statements |
| Scope | Operational processes, management practices, and resource utilization | Financial records, accounting policies compliance, and internal controls |
| Primary Users | Management, stakeholders, government agencies | Investors, creditors, regulatory authorities |
| Regulatory Framework | Guided by government or internal standards | Governed by International Standards on Auditing (ISA) or GAAP |
| Outcome | Recommendations for improving operational performance | Auditor's report on financial statement accuracy |
| Frequency | Periodic or as required by management | Annually, typically after fiscal year-end |
| Focus | Effectiveness and efficiency of business processes | Financial accuracy and compliance |
Introduction to Performance Audit and External Audit
Performance audit evaluates an organization's efficiency, effectiveness, and economy in using resources to achieve objectives, providing insights beyond financial accuracy. External audit primarily focuses on verifying the fairness and accuracy of financial statements, conducted by independent auditors to ensure compliance with accounting standards. Both audits contribute to organizational accountability but serve distinct purposes in assessing operations and financial integrity.
Definition and Scope of Performance Audit
Performance audit evaluates the efficiency, effectiveness, and economy of government programs and operations by assessing whether resources are used optimally to achieve objectives. It focuses on value for money, operational processes, and compliance with policies beyond financial statements. Unlike external audit, which primarily assesses the accuracy of financial records and compliance with accounting standards, performance audit covers broader organizational performance issues and program outcomes.
Definition and Scope of External Audit
External audit is an independent examination of financial statements conducted by certified auditors to ensure accuracy and compliance with accounting standards and legal requirements. Its scope primarily covers verification of financial records, assessment of internal controls related to financial reporting, and providing an opinion on the fairness of financial statements. Performance audit, by contrast, evaluates the efficiency, effectiveness, and economy of organizational operations beyond just financial data, focusing on how well resources are utilized to achieve objectives.
Key Objectives: Performance vs. External Audit
Performance audits primarily focus on evaluating the efficiency, effectiveness, and economy of an organization's operations to ensure optimal resource utilization and achievement of objectives. External audits concentrate on providing an independent opinion on the accuracy and fairness of financial statements in accordance with accounting standards and regulatory requirements. While performance audits assess operational performance and compliance, external audits emphasize financial integrity and stakeholder assurance.
Methodologies Used in Both Audits
Performance audits utilize risk assessment, process evaluation, and benchmarking methodologies to measure efficiency, effectiveness, and economy in organizational operations. External audits primarily employ substantive testing, analytical procedures, and compliance verification to provide an independent opinion on financial statement accuracy. Both audits rely on sampling techniques, evidence collection, and standards such as the International Standards for the Professional Practice of Internal Auditing (IPPF) or Generally Accepted Auditing Standards (GAAS) to ensure thoroughness and reliability.
Key Differences Between Performance and External Audits
Performance audits evaluate the efficiency, effectiveness, and economy of government programs or projects, focusing on achieving intended outcomes and improving public accountability. External audits primarily assess an organization's financial statements for accuracy and compliance with accounting standards, providing assurance to stakeholders. Key differences include the scope--performance audits analyze operational aspects, whereas external audits concentrate on financial records--and the objectives, with performance audits aiming to enhance program performance and external audits verifying financial integrity.
Advantages of Performance Audit
Performance audits provide a comprehensive evaluation of program effectiveness and efficiency, identifying areas for cost savings and improved resource allocation. Unlike external audits that primarily focus on financial accuracy and compliance, performance audits assess operational outcomes and recommend actionable improvements. This enables organizations to enhance overall performance and achieve strategic goals more effectively.
Advantages of External Audit
External audit provides an independent and objective evaluation of financial statements, enhancing credibility for stakeholders such as investors and regulators. It ensures compliance with relevant accounting standards and legal requirements, reducing the risk of fraud and financial misstatements. The external audit's systematic approach and expert insight facilitate improved financial transparency and trust in an organization's reporting.
When to Choose Performance Audit or External Audit
Choose a performance audit when the objective is to assess the efficiency, effectiveness, and economy of government programs or organizational processes, focusing on value for money and program outcomes. Opt for an external audit when the primary need is to verify the accuracy and fairness of financial statements, ensuring compliance with accounting standards and identifying any material misstatements. Organizations facing regulatory requirements or seeking assurance on financial reporting integrity should prioritize external audits, while those aiming to improve operational performance and accountability benefit more from performance audits.
Conclusion: Which Audit Is Right for Your Organization?
Performance audits evaluate an organization's efficiency, effectiveness, and economy in resource use, providing insights for operational improvements. External audits focus on verifying financial statements' accuracy and compliance with accounting standards, ensuring stakeholder confidence. Choosing the right audit depends on whether your organization needs in-depth operational analysis or assurance of financial integrity.
Performance Audit Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com