Commodities such as oil, gold, and agricultural products play a crucial role in global markets by influencing prices and economic stability. Understanding how supply and demand impact commodity prices can help you make informed investment decisions and manage risk effectively. Explore the rest of the article to discover key strategies and trends shaping the commodities market.
Table of Comparison
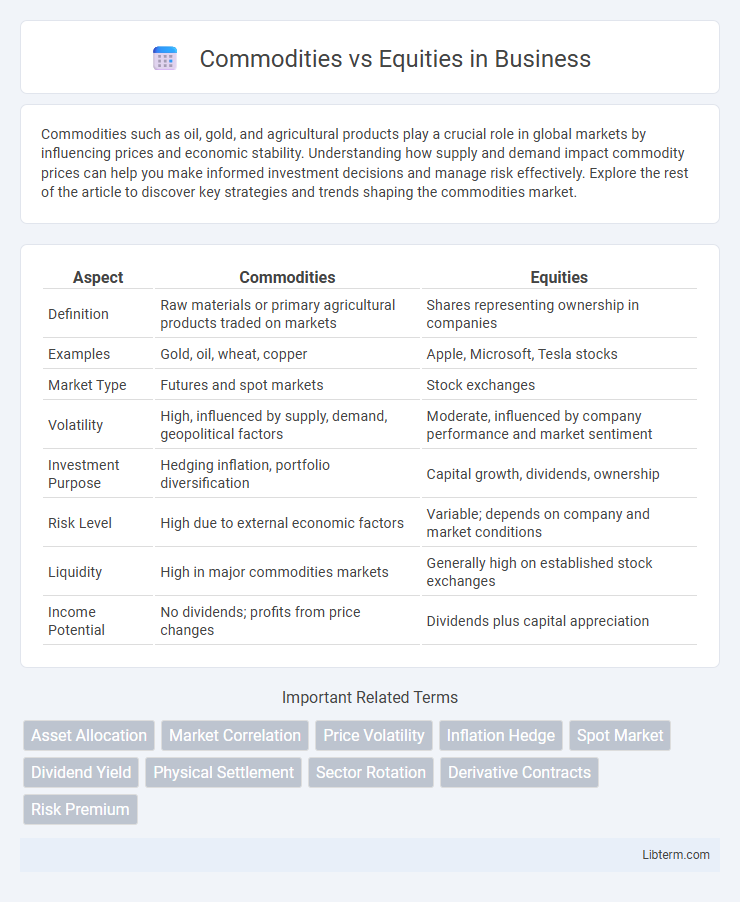
| Aspect | Commodities | Equities |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Raw materials or primary agricultural products traded on markets | Shares representing ownership in companies |
| Examples | Gold, oil, wheat, copper | Apple, Microsoft, Tesla stocks |
| Market Type | Futures and spot markets | Stock exchanges |
| Volatility | High, influenced by supply, demand, geopolitical factors | Moderate, influenced by company performance and market sentiment |
| Investment Purpose | Hedging inflation, portfolio diversification | Capital growth, dividends, ownership |
| Risk Level | High due to external economic factors | Variable; depends on company and market conditions |
| Liquidity | High in major commodities markets | Generally high on established stock exchanges |
| Income Potential | No dividends; profits from price changes | Dividends plus capital appreciation |
Overview of Commodities and Equities
Commodities are physical goods such as metals, energy resources, and agricultural products traded on specialized markets, serving as essential inputs for industries and consumption. Equities represent ownership shares in companies, providing investors with potential dividends and capital appreciation through stock exchanges. Both asset classes offer diversification but differ in risk profiles, market behavior, and sensitivity to economic factors like inflation and corporate earnings.
Key Differences Between Commodities and Equities
Commodities represent physical goods such as gold, oil, and agricultural products, while equities are ownership shares in publicly traded companies. Commodities trading is influenced primarily by supply and demand factors, weather conditions, and geopolitical events, whereas equities are driven by company performance, earnings reports, and broader market sentiment. Investors often use commodities for diversification and hedging against inflation, whereas equities are favored for growth potential and dividend income.
Market Structure and Accessibility
Commodities markets operate through exchanges like the Chicago Mercantile Exchange (CME) and are influenced by supply-demand dynamics, geopolitical events, and seasonality, offering futures and options contracts with standardized terms. Equities markets involve shares of publicly traded companies listed on stock exchanges such as NYSE or NASDAQ, featuring high liquidity, diverse sectors, and regulatory oversight by entities like the SEC. Accessibility to commodities often requires understanding futures margins and contract specifications, while equities trading is more straightforward via brokerage accounts with lower entry barriers and real-time market data.
Factors Influencing Commodities Prices
Commodities prices are primarily influenced by supply and demand dynamics, weather conditions, geopolitical tensions, and currency fluctuations, which can cause significant volatility in markets like oil, gold, and agricultural products. In contrast to equities, commodities lack earnings reports and dividends, making their valuations more sensitive to physical market factors and global economic events. Inventory levels, production costs, and government policies, such as tariffs and subsidies, further impact commodity prices by altering availability and cost structures.
Drivers of Equities Performance
Equities performance is primarily driven by company earnings growth, macroeconomic factors such as GDP expansion, and investor sentiment influenced by interest rates and monetary policy. Corporate profitability and revenue projections directly impact stock valuations, while economic indicators like inflation and unemployment rates affect market confidence. Market liquidity and geopolitical events also play significant roles in shaping equity price movements.
Risk and Volatility Comparison
Commodities often experience higher volatility and risk due to factors like geopolitical events, weather conditions, and supply-demand imbalances impacting prices rapidly. Equities typically exhibit lower volatility, influenced mainly by company performance, economic indicators, and market sentiment, providing relatively more predictable returns. Risk management strategies are essential for both asset classes, but commodities require closer monitoring of external variables that can cause sudden price swings.
Portfolio Diversification Benefits
Commodities and equities offer distinct portfolio diversification benefits by reducing overall risk through varying correlation patterns, as commodities often exhibit low or negative correlation with stocks. Incorporating commodities such as gold, oil, or agricultural products can enhance portfolio stability during market volatility and inflationary periods where equities might underperform. This strategic allocation improves risk-adjusted returns by balancing growth potential from equities with the inflation hedge and safe-haven qualities of commodities.
Liquidity and Trading Hours
Commodities markets generally offer extended trading hours, often operating nearly 24 hours on electronic platforms, enhancing liquidity and allowing for greater flexibility in adjusting positions. Equities trading is mostly confined to regular exchange hours, such as the NYSE and NASDAQ operating from 9:30 AM to 4:00 PM EST, which can result in lower liquidity outside these windows. Commodity futures experience high liquidity during peak market hours, driven by global demand factors, while equities liquidity is heavily influenced by market opening and closing periods.
Historical Performance Analysis
Historical performance analysis reveals that equities have generally provided higher long-term returns compared to commodities, driven by corporate earnings growth and economic expansion. Commodities display greater volatility and are influenced heavily by supply-demand imbalances, geopolitical events, and inflationary pressures, often serving as a hedge against inflation. Over extended periods, equities outperform commodities in total return, but commodities offer diversification benefits during periods of economic uncertainty and inflation spikes.
Choosing Between Commodities and Equities for Investment
Choosing between commodities and equities hinges on investment goals, risk tolerance, and market conditions. Commodities offer diversification and hedge against inflation through physical assets like gold and oil, while equities provide ownership in companies with potential for dividends and capital appreciation. Evaluating volatility, liquidity, and time horizon helps investors align their portfolios with desired financial outcomes.
Commodities Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com