Virtual environments transform how you interact with digital content by creating immersive, computer-generated spaces that simulate real or imagined worlds. These technologies enhance experiences in gaming, education, training, and remote collaboration, offering dynamic opportunities to engage beyond physical limitations. Explore the article to discover how virtual solutions can elevate your digital interactions and unlock new possibilities.
Table of Comparison
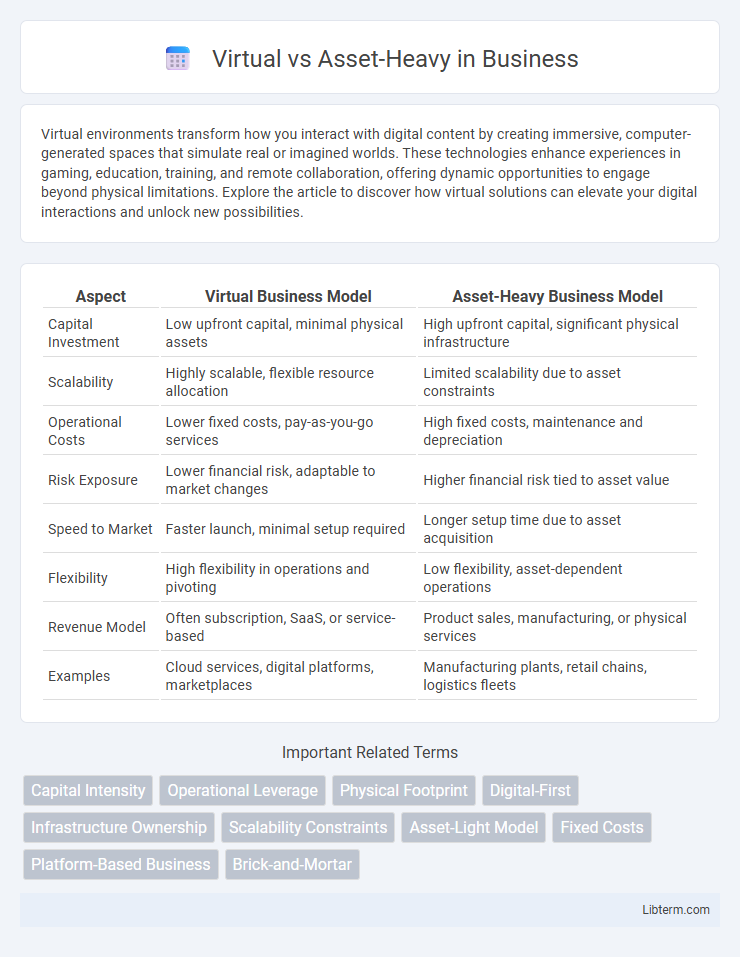
| Aspect | Virtual Business Model | Asset-Heavy Business Model |
|---|---|---|
| Capital Investment | Low upfront capital, minimal physical assets | High upfront capital, significant physical infrastructure |
| Scalability | Highly scalable, flexible resource allocation | Limited scalability due to asset constraints |
| Operational Costs | Lower fixed costs, pay-as-you-go services | High fixed costs, maintenance and depreciation |
| Risk Exposure | Lower financial risk, adaptable to market changes | Higher financial risk tied to asset value |
| Speed to Market | Faster launch, minimal setup required | Longer setup time due to asset acquisition |
| Flexibility | High flexibility in operations and pivoting | Low flexibility, asset-dependent operations |
| Revenue Model | Often subscription, SaaS, or service-based | Product sales, manufacturing, or physical services |
| Examples | Cloud services, digital platforms, marketplaces | Manufacturing plants, retail chains, logistics fleets |
Introduction to Virtual vs Asset-Heavy Business Models
Virtual business models prioritize digital infrastructure and intangible assets, leveraging technology to deliver services with minimal physical resources. Asset-heavy models rely on substantial investments in physical assets like manufacturing plants, machinery, or real estate to generate revenue. The distinction influences capital expenditure, operational flexibility, and scalability, shaping strategic priorities and competitive advantages in various industries.
Key Characteristics of Virtual Businesses
Virtual businesses operate primarily through digital platforms, minimizing physical assets and real estate investments to reduce overhead costs and increase scalability. They leverage cloud computing, remote workforces, and digital marketing strategies to swiftly adapt to market changes and expand globally. Key characteristics include low capital expenditure, high flexibility, and a focus on intangible assets such as intellectual property and data-driven customer insights.
Defining Asset-Heavy Organizations
Asset-heavy organizations maintain large physical infrastructures, such as manufacturing plants, warehouses, and distribution centers, requiring significant capital investment and operational costs. These companies leverage tangible assets to control production, ensure quality, and manage supply chains directly, often resulting in higher fixed costs but greater control over operations. In contrast, virtual organizations minimize physical assets by outsourcing key functions, emphasizing flexibility and reduced capital expenditure.
Advantages of Virtual Operations
Virtual operations reduce capital expenditures by minimizing the need for physical assets, enabling businesses to allocate resources more efficiently. They provide greater flexibility and scalability, allowing rapid adjustments to market demands without the constraints of heavy infrastructure. Enhanced agility in virtual models fosters innovation and quicker deployment of services, driving competitive advantage.
Challenges Faced by Asset-Heavy Companies
Asset-heavy companies encounter significant challenges including high capital expenditures for maintaining and upgrading physical infrastructure, which limit operational flexibility and increase financial risk. They often struggle with slower response times to market changes due to fixed assets and extensive regulatory compliance requirements tied to tangible property. Furthermore, asset-heavy firms face difficulties in scalability and technological adaptation compared to virtual counterparts, impacting competitive agility in rapidly evolving industries.
Cost Efficiency: Virtual vs Asset-Heavy
Virtual business models typically achieve higher cost efficiency by minimizing capital expenditure on physical assets, reducing maintenance and operational costs. Asset-heavy models require significant upfront investment and ongoing costs related to property, equipment, and infrastructure, which can limit flexibility and scalability. Leveraging digital platforms, virtual firms reduce overhead and can rapidly adapt to market changes, enhancing overall cost efficiency compared to asset-heavy counterparts.
Scalability and Flexibility Comparison
Virtual business models excel in scalability by leveraging digital infrastructure, enabling rapid expansion without significant capital investment, unlike asset-heavy models that face physical constraints and higher fixed costs. Asset-heavy businesses offer limited flexibility due to dependencies on tangible resources and slower adaptation to market changes, whereas virtual models can quickly pivot operations and scale services globally. The lean structure of virtual enterprises supports dynamic growth and responsiveness, essential for rapidly evolving markets and customer demands.
Risk Management in Both Models
Virtual business models leverage digital tools to minimize physical asset exposure, reducing capital-intensive risks and enabling agile responses to market fluctuations. Asset-heavy models face greater operational risks tied to maintenance, depreciation, and asset obsolescence, requiring robust risk mitigation strategies and compliance monitoring. Effective risk management in both frameworks involves continuous assessment of financial, operational, and market risks to ensure resilience and sustainable growth.
Industry Examples: Virtual and Asset-Heavy Leaders
Virtual companies like Uber and Airbnb leverage digital platforms to connect users without owning physical assets, enabling rapid scalability and lower operational costs. In contrast, asset-heavy industry leaders such as Boeing and General Motors maintain substantial physical infrastructure, including manufacturing plants and inventory, to ensure control over product quality and supply chain reliability. This distinction highlights how virtual firms capitalize on technology-driven efficiency whereas asset-heavy companies emphasize tangible resources for competitive advantage.
Choosing the Right Model for Your Business
Choosing the right business model between virtual and asset-heavy approaches depends on factors like capital investment, scalability, and operational control. Virtual business models minimize upfront costs by leveraging digital platforms and outsourced services, ideal for startups seeking rapid growth and flexibility. Asset-heavy models demand significant investment in physical resources, offering greater control and potential long-term stability for established companies with predictable market demand.
Virtual Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com