A credit note is a financial document issued by a seller to a buyer, confirming a reduction in the amount owed due to returned goods, pricing errors, or other adjustments. It serves as an official record for accounting purposes, ensuring transparency and accuracy in business transactions. Discover how understanding credit notes can benefit your financial management by reading the full article.
Table of Comparison
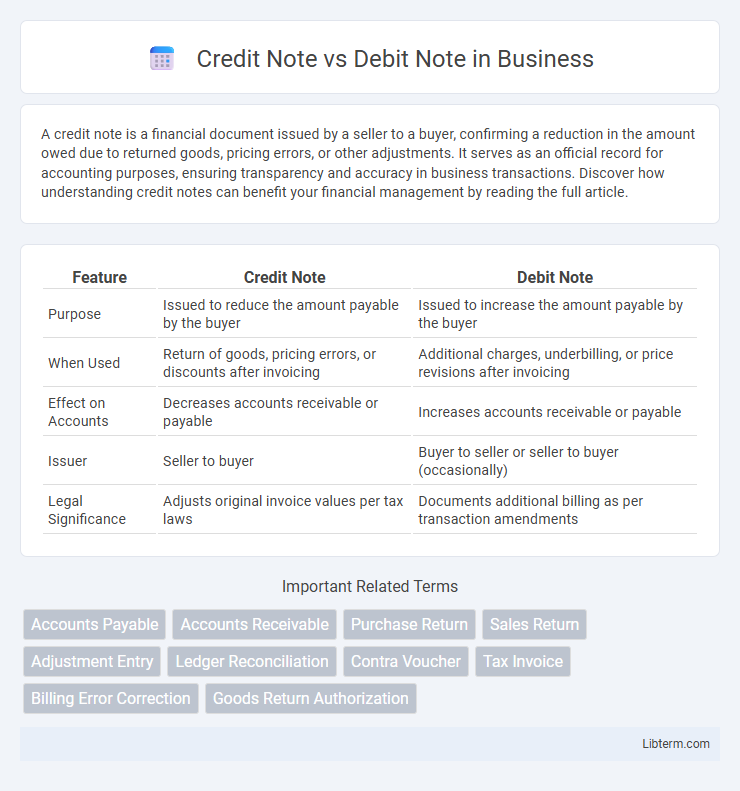
| Feature | Credit Note | Debit Note |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Issued to reduce the amount payable by the buyer | Issued to increase the amount payable by the buyer |
| When Used | Return of goods, pricing errors, or discounts after invoicing | Additional charges, underbilling, or price revisions after invoicing |
| Effect on Accounts | Decreases accounts receivable or payable | Increases accounts receivable or payable |
| Issuer | Seller to buyer | Buyer to seller or seller to buyer (occasionally) |
| Legal Significance | Adjusts original invoice values per tax laws | Documents additional billing as per transaction amendments |
Introduction to Credit Notes and Debit Notes
Credit notes are official documents issued by a seller to a buyer, indicating a reduction in the amount owed due to returns, errors, or allowances. Debit notes are sent by the buyer to the seller, requesting an increase in the invoice amount for reasons such as damaged goods or additional charges. Both credit and debit notes serve as crucial tools for adjusting financial transactions and maintaining accurate accounting records.
Definition and Purpose of Credit Notes
A credit note is a document issued by a seller to a buyer, acknowledging that a certain amount has been credited to the buyer's account due to returned goods, billing errors, or agreed discounts. Its primary purpose is to adjust the invoice amount, reflecting a reduction in the buyer's payable balance and maintaining accurate financial records. Credit notes serve as proof of transaction correction and facilitate transparent accounting between businesses.
Definition and Purpose of Debit Notes
A debit note is a formal document issued by a buyer to a seller indicating a request for a credit adjustment due to returned goods, pricing errors, or discrepancies in the invoice. It serves as a record for the increased liability or amount payable by the buyer, facilitating accurate accounting and reconciliation between parties. Debit notes help maintain transparency and control over financial transactions by clearly documenting claims for additional charges or corrections.
Key Differences Between Credit Notes and Debit Notes
Credit notes reduce the amount owed by a buyer due to returned goods or overbilling, whereas debit notes increase the amount payable for additional charges or underbilling. A credit note is issued by the seller to the buyer, while a debit note is typically raised by the buyer to request a correction in the invoice value. The primary distinction lies in their impact on accounting: credit notes decrease accounts receivable for sellers, and debit notes increase accounts payable for buyers.
Situations Requiring Credit Notes
Credit notes are issued primarily when a customer returns goods due to defects, overbilling, or canceled orders, leading to a reduction in the amount payable. They serve as official documentation to adjust the invoice value, reflecting refunds, discounts, or price corrections agreed between the seller and buyer. Situations requiring credit notes include product returns, billing errors, promotional rebates, or service cancellations that impact the original transaction amount.
Situations Requiring Debit Notes
Debit notes are issued primarily when a customer returns goods due to defects, short shipments, or overbilling errors, necessitating an adjustment in the amount owed to the supplier. They serve as formal requests for a correction in the invoice value when a buyer owes less to the seller, reflecting reductions in payable amounts for returned or faulty inventory. In accounting, debit notes help maintain accurate records by documenting reductions in purchases or receivables, ensuring proper reconciliation of financial statements between trading partners.
Legal and Accounting Implications
Credit notes legally document a reduction in the amount owed by a buyer due to returns, overcharges, or errors, directly impacting accounts receivable and revenue recognition. Debit notes serve as formal requests for additional payment, reflecting extra costs or underbillings, thus affecting accounts payable and liabilities. Accurate issuance and recording of credit and debit notes ensure compliance with tax regulations and maintain transparent financial statements.
Process of Issuing Credit and Debit Notes
The process of issuing a credit note involves the seller generating a document to reduce the amount previously invoiced, typically due to returned goods, pricing errors, or allowances. In contrast, a debit note is issued by the buyer or seller to request additional payment or correct under-billed amounts, highlighting discrepancies in the original invoice. Both documents require clear referencing of the original invoice number, detailed descriptions, and approval from authorized personnel to ensure accurate financial records and compliance with accounting standards.
Common Mistakes and How to Avoid Them
Confusing credit notes with debit notes often leads to incorrect accounting entries, impacting financial statements and tax reporting accuracy. A common mistake is issuing a credit note instead of a debit note when increasing a customer's payable balance, which reverses intended transactions. To avoid errors, ensure thorough staff training on distinguishing the purpose: credit notes reduce amounts owed by customers, while debit notes increase receivables or record additional charges.
Best Practices for Managing Credit and Debit Notes
Best practices for managing credit and debit notes include maintaining accurate records and promptly issuing documents to ensure proper financial reconciliation and compliance with accounting standards. Implementing automated invoicing systems helps track and validate credit and debit notes, reducing errors and improving audit trails. Clear communication with customers and suppliers about the reasons for credit or debit adjustments fosters transparency and minimizes disputes.
Credit Note Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com