Preferred stock offers investors fixed dividends and priority over common stockholders in asset liquidation, providing a balance between equity and debt features. It is particularly appealing for those seeking steady income without the voting rights typical of common shares. Discover how preferred stock can enhance Your investment portfolio by exploring the detailed advantages and considerations in the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
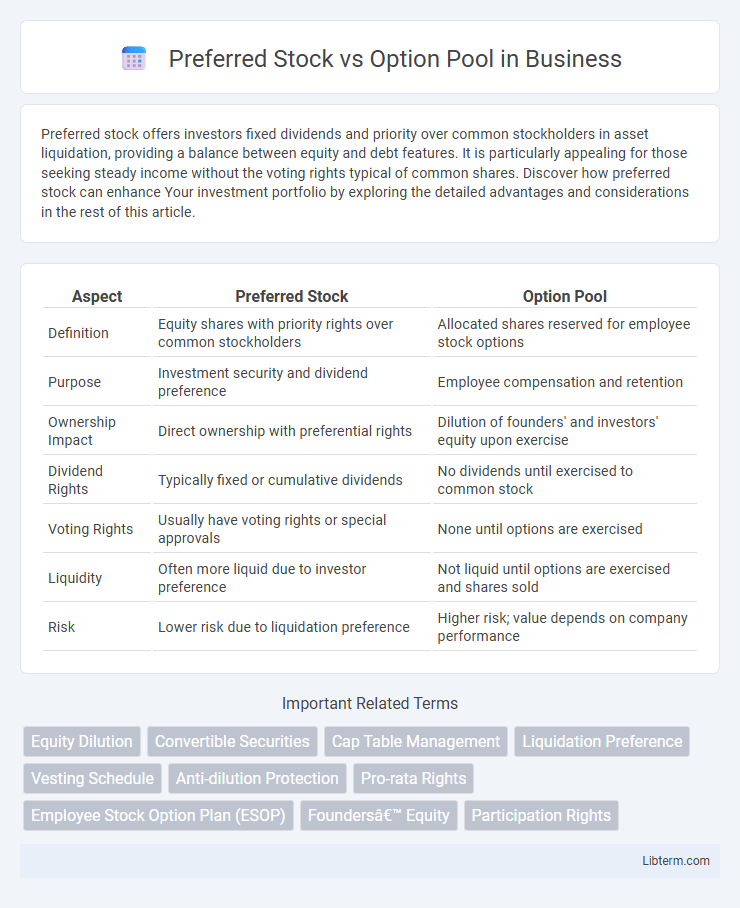
| Aspect | Preferred Stock | Option Pool |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Equity shares with priority rights over common stockholders | Allocated shares reserved for employee stock options |
| Purpose | Investment security and dividend preference | Employee compensation and retention |
| Ownership Impact | Direct ownership with preferential rights | Dilution of founders' and investors' equity upon exercise |
| Dividend Rights | Typically fixed or cumulative dividends | No dividends until exercised to common stock |
| Voting Rights | Usually have voting rights or special approvals | None until options are exercised |
| Liquidity | Often more liquid due to investor preference | Not liquid until options are exercised and shares sold |
| Risk | Lower risk due to liquidation preference | Higher risk; value depends on company performance |
Understanding Preferred Stock
Preferred stock represents equity ownership with priority over common stockholders in dividend payments and asset liquidation, often including voting rights and anti-dilution protections. It is commonly issued to investors in funding rounds, providing security and potential preference during exit events. Understanding preferred stock is crucial for founders and investors to balance control, risk, and financial returns within a startup's capital structure.
What Is an Option Pool?
An option pool is a reserved percentage of a company's shares set aside for future issuance to employees, advisors, and consultants as equity compensation, typically ranging from 10% to 20% of the total shares. Unlike preferred stock, which represents ownership with specific rights and preferences, option pools are intended to incentivize and retain talent by granting stock options that vest over time. Establishing an option pool impacts the company's equity structure and dilution, requiring careful consideration during fundraising and valuation.
Key Differences Between Preferred Stock and Option Pool
Preferred stock represents equity ownership with priority on dividends and assets in liquidation, offering investors fixed dividends and voting rights, whereas an option pool consists of shares reserved to incentivize employees through stock options. Preferred stockholders have immediate ownership stakes and financial benefits, while option pools grant potential future equity contingent on employee vesting. The key difference lies in immediate equity rights of preferred stock versus contingent ownership rights embedded in the option pool for talent retention.
Purpose and Role in Startup Financing
Preferred stock provides investors with equity ownership, priority in dividends, and liquidation preferences, securing their investment in startup financing. An option pool is created to attract and retain key employees by granting stock options, aligning their incentives with the company's growth without immediate equity dilution. Both instruments play crucial roles in balancing investor protection and employee motivation during fundraising rounds.
Impact on Company Ownership Structure
Preferred stock grants investors specific rights, including dividends and liquidation preferences, which can dilute common shareholders and impact voting control within the company. Option pools reserved for employee stock options dilute ownership by increasing the total number of shares outstanding, directly affecting founders' and early investors' equity percentages. The careful management of both preferred stock issuance and the size of the option pool is critical to maintaining a balanced ownership structure while incentivizing stakeholders.
Dilution Effects for Founders and Investors
Preferred stock issuance dilutes founders' ownership by decreasing their equity percentage but often comes with liquidation preferences that protect investors' returns, balancing risk and reward. Option pools dilute both founders and investors by reserving shares for future employees, impacting overall equity distribution but incentivizing growth and company value. Founders face more immediate dilution from option pools, while investors primarily experience dilution from preferred stock issuance, influencing control and exit outcomes.
Rights and Privileges: Preferred Stock vs Option Pool
Preferred stock grants shareholders specific rights and privileges such as dividend preferences, liquidation priorities, and voting power, providing enhanced control and financial benefits compared to common equity. The option pool consists of stock options allocated to employees, offering future equity ownership contingent on vesting schedules, but typically lacks voting rights and immediate financial entitlements. These distinctions highlight preferred stock as an investment tool for securing prioritized returns and governance influence, whereas the option pool serves as a motivational instrument aimed at aligning employee incentives with company performance.
Negotiation Strategies for Each Instrument
Negotiating preferred stock requires emphasizing valuation, liquidation preferences, and anti-dilution provisions to protect investor interests while maintaining founder control. For option pools, negotiation centers on pool size, vesting schedules, and refresh grants to balance employee incentives and shareholder dilution. Both instruments demand clear alignment of rights and expectations to ensure sustainable capitalization and growth potential.
Implications for Employee Compensation
Preferred stock offers employees potential equity with dividend rights and liquidation preferences, which can enhance long-term retention and align interests with shareholders. Option pools provide employees with stock options granting the right to purchase common stock at a predetermined price, incentivizing performance through potential appreciation. The choice impacts dilution, tax treatment, and employee motivation, making it critical for startups to balance immediate compensation costs with future equity incentives.
Best Practices for Balancing Preferred Stock and Option Pools
Balancing preferred stock and option pools requires allocating sufficient equity to attract talent while preserving investor value, typically reserving 10-20% for the option pool. Founders and investors should negotiate option pool sizes pre-financing to minimize dilution impact on preferred shareholders. Implementing a clear vesting schedule and regularly reviewing option pool adequacy ensures alignment between company growth and employee incentives.
Preferred Stock Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com