Turnover reflects the total revenue generated by a business within a specific period and is a critical indicator of financial health. Understanding turnover helps you assess sales performance, market demand, and operational efficiency. Explore the rest of the article to learn how turnover impacts your business strategy and growth potential.
Table of Comparison
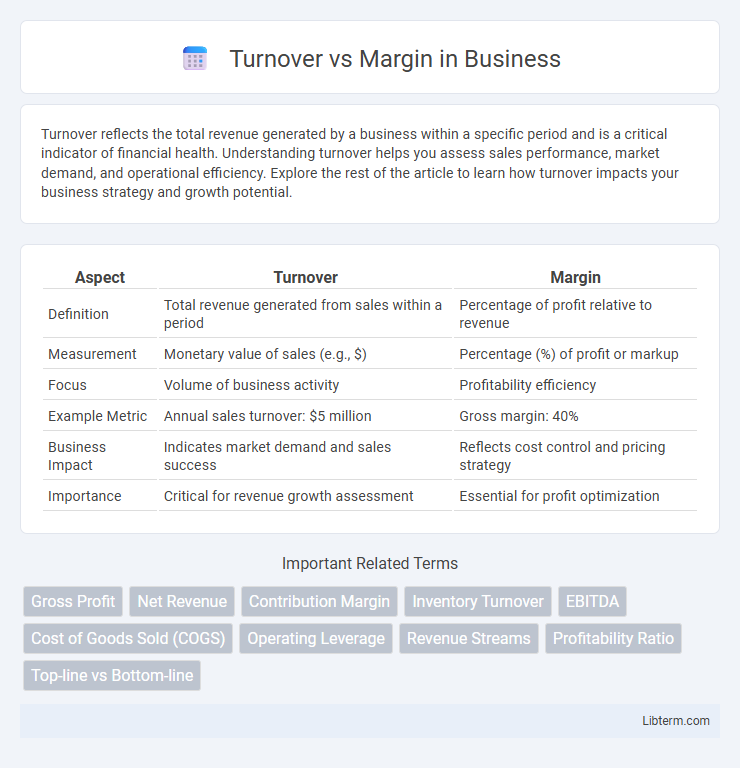
| Aspect | Turnover | Margin |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Total revenue generated from sales within a period | Percentage of profit relative to revenue |
| Measurement | Monetary value of sales (e.g., $) | Percentage (%) of profit or markup |
| Focus | Volume of business activity | Profitability efficiency |
| Example Metric | Annual sales turnover: $5 million | Gross margin: 40% |
| Business Impact | Indicates market demand and sales success | Reflects cost control and pricing strategy |
| Importance | Critical for revenue growth assessment | Essential for profit optimization |
Understanding Turnover and Margin
Turnover refers to the total sales or revenue generated by a business within a specific period, serving as a critical indicator of business activity and market demand. Margin represents the difference between the sales revenue and the cost of goods sold, often expressed as a percentage to evaluate profitability. Understanding the relationship between turnover and margin helps businesses optimize pricing strategies and control costs to maximize overall financial performance.
Key Differences Between Turnover and Margin
Turnover refers to the total revenue generated from sales within a specific period, serving as a measure of business activity volume, while margin represents the profit earned per unit of sales, expressed as a percentage of revenue. Key differences between turnover and margin lie in their financial interpretation: turnover emphasizes sales scale without accounting for costs, whereas margin focuses on profitability by subtracting expenses from revenue. Understanding the distinction is crucial for strategic decision-making, balancing volume growth against maintaining or improving profit margins.
Why Turnover Matters in Business
Turnover represents the total revenue generated by a business, directly impacting its cash flow and operational capacity. High turnover enables companies to cover fixed costs more efficiently and invest in growth opportunities, enhancing overall market competitiveness. A strong turnover foundation supports sustainable profit margins by driving volume economies and business scalability.
The Impact of Margin on Profitability
Margin significantly influences profitability by determining how much profit a company retains from its total sales revenue after covering costs. Higher margins indicate efficient cost management and the ability to generate substantial profit per unit sold, enhancing overall business sustainability. Companies with strong margins can withstand market fluctuations better and reinvest earnings to drive growth.
Calculating Turnover: Essential Metrics
Calculating turnover involves measuring total sales revenue generated within a specific period, highlighting a company's ability to convert inventory or services into revenue efficiently. Essential metrics include inventory turnover ratio, which assesses how often inventory is sold and replaced, and accounts receivable turnover, reflecting the efficiency of collecting payments from customers. Analyzing these turnover metrics provides crucial insights into operational performance and cash flow management.
How to Analyze Gross Margin and Net Margin
Gross margin analysis involves calculating the difference between revenue and cost of goods sold (COGS) divided by revenue, revealing the percentage of sales that exceeds production costs. Net margin analysis assesses overall profitability by dividing net income by total revenue, incorporating all expenses, taxes, and interest, offering insight into operational efficiency. Comparing gross and net margins helps identify cost control effectiveness and operational strengths, essential for strategic financial decision-making.
Turnover vs Margin: Which Drives Business Growth?
Turnover and margin both play critical roles in driving business growth, with turnover reflecting the total revenue generated and margin indicating profitability per unit of sales. High turnover can signal strong market demand and scale, but sustainable growth depends on maintaining healthy margins to ensure profits cover operational costs and reinvestment. Businesses that balance increasing turnover with optimizing margin tend to achieve more robust and scalable growth trajectories.
Common Mistakes When Comparing Turnover and Margin
Confusing turnover with margin often leads to misinterpretation of business performance, as turnover measures total revenue while margin reflects profitability after costs. A common mistake is assuming high turnover automatically means high profit, neglecting the impact of expenses that reduce margin. Overlooking the difference between gross margin and net margin further distorts financial analysis and decision-making effectiveness.
Strategies to Improve Both Turnover and Margin
Enhancing turnover and margin requires a dual approach focused on optimizing pricing strategies and streamlining operations to boost sales volume while controlling costs. Implementing dynamic pricing models based on market demand and customer segmentation increases revenue per unit without sacrificing turnover rate. Investing in process automation and supply chain efficiency reduces operational expenses, thereby improving margin without compromising the product turnover cycle.
Choosing the Right Focus: Turnover, Margin, or Both?
Choosing the right focus between turnover and margin depends on your business goals and industry context. High turnover emphasizes volume sales and market penetration, while strong margins prioritize profitability per unit sold, critical in industries with high fixed costs. Balancing both metrics often yields sustainable growth, as maximizing turnover without margin control can erode profits, whereas focusing solely on margin can limit scale and market share.
Turnover Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com