Equity compensation offers employees a stake in the company's success through stock options, restricted shares, or stock appreciation rights, aligning their interests with shareholders. Understanding the tax implications, vesting schedules, and potential dilution is crucial for maximizing the benefits of your equity package. Explore the rest of this article to learn how equity compensation can impact your financial future and career growth.
Table of Comparison
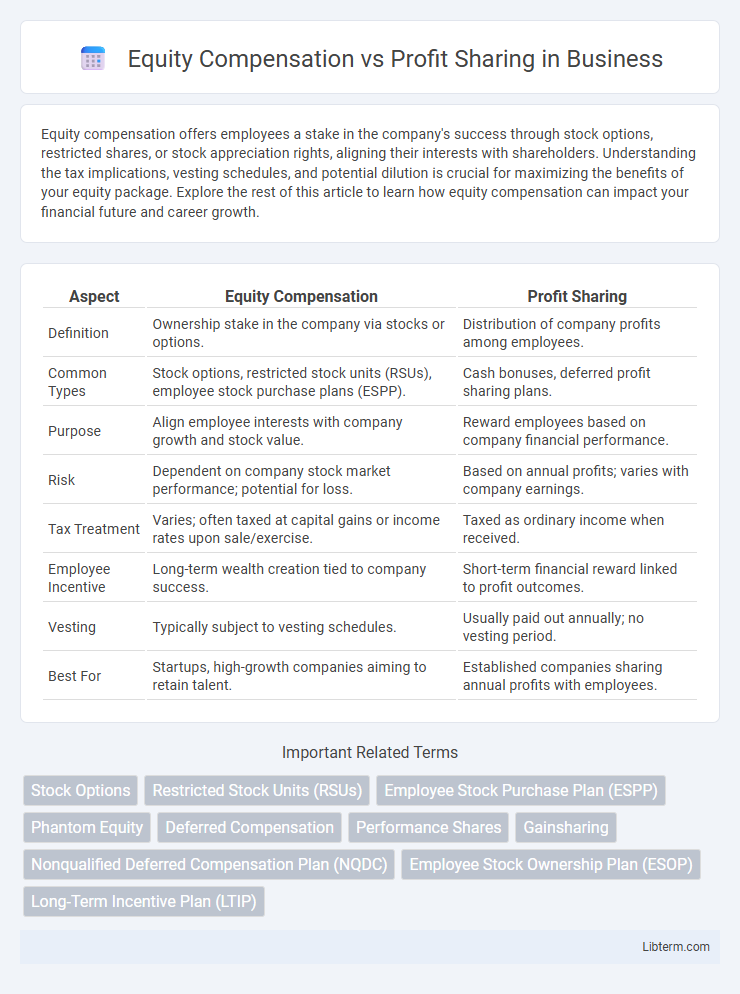
| Aspect | Equity Compensation | Profit Sharing |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Ownership stake in the company via stocks or options. | Distribution of company profits among employees. |
| Common Types | Stock options, restricted stock units (RSUs), employee stock purchase plans (ESPP). | Cash bonuses, deferred profit sharing plans. |
| Purpose | Align employee interests with company growth and stock value. | Reward employees based on company financial performance. |
| Risk | Dependent on company stock market performance; potential for loss. | Based on annual profits; varies with company earnings. |
| Tax Treatment | Varies; often taxed at capital gains or income rates upon sale/exercise. | Taxed as ordinary income when received. |
| Employee Incentive | Long-term wealth creation tied to company success. | Short-term financial reward linked to profit outcomes. |
| Vesting | Typically subject to vesting schedules. | Usually paid out annually; no vesting period. |
| Best For | Startups, high-growth companies aiming to retain talent. | Established companies sharing annual profits with employees. |
Introduction to Equity Compensation and Profit Sharing
Equity compensation grants employees ownership interest through stock options, restricted shares, or performance shares, aligning their financial incentives with company growth and long-term value creation. Profit sharing involves distributing a portion of company profits to employees, typically as cash bonuses or retirement contributions, rewarding them based on overall financial performance. Both strategies aim to enhance employee motivation and retention while driving organizational success.
Key Differences Between Equity Compensation and Profit Sharing
Equity compensation grants employees ownership stakes in the company through stock options or shares, aligning their interests with long-term company performance and stock appreciation. Profit sharing distributes a portion of the company's profits directly to employees, typically as cash bonuses, based on the company's profitability in a given period. Key differences include the form of reward (equity vs. cash), timing of benefits realization (long-term value vs. immediate payout), and risk exposure, with equity carrying market risk while profit sharing depends on current company earnings.
How Equity Compensation Works
Equity compensation grants employees ownership stakes through stock options, restricted stock units (RSUs), or employee stock purchase plans (ESPPs), aligning their interests with company growth. These equity awards typically vest over time, incentivizing long-term commitment and performance. Upon vesting, employees can sell shares or hold them, potentially benefiting from company appreciation and dividends.
Understanding Profit Sharing Plans
Profit sharing plans distribute a portion of a company's profits to employees, aligning their interests with business performance and fostering motivation without diluting ownership. These plans often provide flexible contribution structures and can be tax-advantaged, encouraging long-term employee retention. Understanding the differences in payout timing and eligibility criteria is essential for optimizing profit sharing as a strategic compensation tool.
Pros and Cons of Equity Compensation
Equity compensation offers employees ownership stakes in a company, aligning their interests with long-term corporate growth and potentially leading to substantial financial rewards if the company's stock value increases. However, its value is highly dependent on market performance and company success, introducing risk and potential dilution for employees if stock prices fall or new shares are issued. Unlike profit sharing, equity compensation may have complex tax implications and vesting schedules, which can limit immediate liquidity and create uncertainty around the actual benefit employees will receive.
Pros and Cons of Profit Sharing
Profit sharing motivates employees by directly linking rewards to company performance, fostering teamwork and productivity without diluting ownership. It can improve retention but may lead to income uncertainty for employees during downturns, reducing its appeal compared to guaranteed compensation. The variability in payouts also complicates personal financial planning and may not align employee efforts with long-term company goals.
Impact on Employee Motivation and Retention
Equity compensation grants employees ownership stakes that align their interests with company growth, significantly boosting long-term motivation and retention by fostering a sense of ownership and wealth-building potential. Profit sharing directly ties rewards to company performance, providing immediate financial incentives that enhance motivation but may be less effective in retaining talent during downturns. Combining both strategies often yields the strongest impact on employee engagement by balancing short-term rewards with long-term investment in the company's success.
Tax Implications for Employees
Equity compensation, such as stock options or restricted stock units (RSUs), often results in tax events upon vesting or exercise, triggering ordinary income tax and potentially capital gains tax upon sale. Profit sharing plans distribute a portion of company profits to employees as cash or contributions to retirement accounts, taxed as ordinary income when received or withdrawn. Understanding the timing and nature of taxable events helps employees optimize tax liabilities and maximize overall financial benefits.
Choosing the Right Plan for Your Business
Selecting the right plan between equity compensation and profit sharing depends on your business goals, growth stage, and employee motivation strategy. Equity compensation aligns employees' interests with long-term company value by offering stock options or shares, fostering ownership and retention. Profit sharing distributes a portion of company profits as cash bonuses, providing immediate financial rewards tied to business performance, ideal for enhancing short-term productivity and morale.
Conclusion: Equity Compensation vs Profit Sharing
Equity compensation offers employees ownership stakes, aligning their interests with long-term company growth and potentially higher financial rewards through stock appreciation. Profit sharing provides direct cash bonuses based on company performance, delivering immediate income incentives without diluting ownership. Choosing between equity compensation and profit sharing depends on a company's strategic goals, cash flow considerations, and the desired impact on employee motivation and retention.
Equity Compensation Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com