Profit represents the financial gain achieved when revenue exceeds expenses within a business operation. Maximizing profit involves strategic management of costs, pricing, and sales performance while adapting to market changes. Discover effective methods to boost Your profit and enhance overall business success in the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
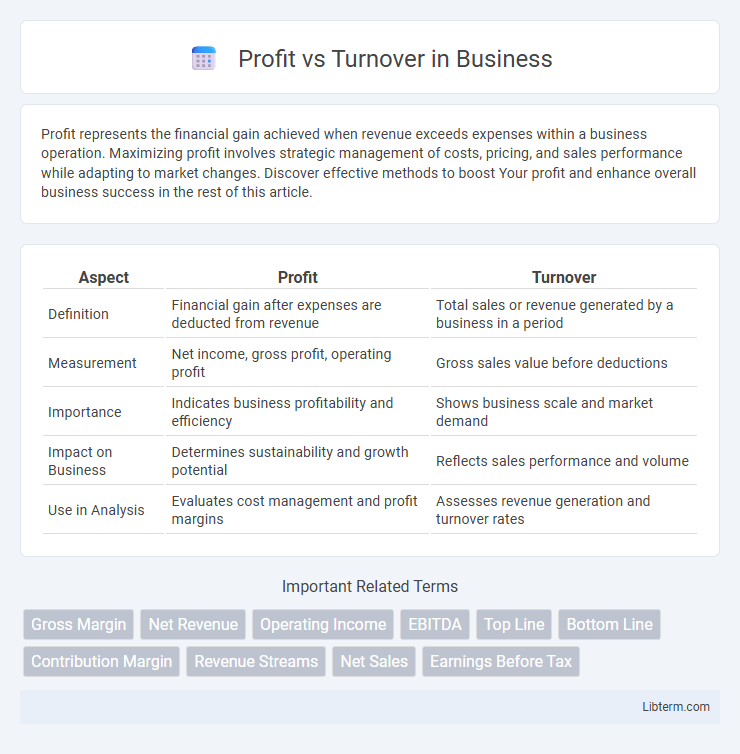
| Aspect | Profit | Turnover |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Financial gain after expenses are deducted from revenue | Total sales or revenue generated by a business in a period |
| Measurement | Net income, gross profit, operating profit | Gross sales value before deductions |
| Importance | Indicates business profitability and efficiency | Shows business scale and market demand |
| Impact on Business | Determines sustainability and growth potential | Reflects sales performance and volume |
| Use in Analysis | Evaluates cost management and profit margins | Assesses revenue generation and turnover rates |
Understanding Profit and Turnover: Key Definitions
Profit represents the financial gain after deducting all expenses from total revenue, indicating the company's actual earnings. Turnover refers to the total sales or revenue generated by a business within a specific period, reflecting the volume of business operations. Understanding the distinction between profit and turnover is crucial for assessing a company's financial health and operational efficiency.
The Fundamental Differences Between Profit and Turnover
Profit represents the financial gain remaining after all expenses, taxes, and costs are deducted from total revenue, serving as a key indicator of business success and sustainability. Turnover, or total revenue, reflects the total value of sales generated by a company within a given period, highlighting market demand and operational scale. Understanding the fundamental difference between profit and turnover is essential for accurate financial analysis, as high turnover does not necessarily equate to high profit due to varying expense structures.
Why Turnover Doesn’t Equal Profit
Turnover represents the total revenue generated from sales before deducting any expenses, while profit reflects the actual financial gain after all costs, such as production, salaries, and taxes, have been subtracted. High turnover can be misleading if profit margins are thin or expenses are high, meaning a company can have substantial sales but still operate at a loss. Understanding the distinction between turnover and profit is crucial for evaluating a company's financial health and sustainability.
The Role of Revenue in Business Growth
Revenue serves as the foundational metric indicating the total income generated from sales, directly influencing a company's ability to invest in growth initiatives. While turnover reflects the scale of business operations, profit reveals the efficiency and sustainability of those activities. Maximizing revenue enables businesses to fund innovation, expand market reach, and enhance competitive advantage, driving long-term growth.
How to Calculate Profit vs Turnover
Profit is calculated by subtracting total expenses from total revenue, while turnover refers to the total sales generated within a specific period. To calculate profit, use the formula: Profit = Total Revenue - Total Expenses, and for turnover, sum all sales invoices or receipts during the chosen timeframe. Comparing profit to turnover involves dividing profit by turnover to assess profitability margin, expressed as Profit Margin = (Profit / Turnover) x 100%.
Importance of Profit Margins for Sustainable Success
Profit margins are crucial indicators of a company's financial health, reflecting the percentage of revenue that translates into actual profit after expenses. High profit margins enable businesses to reinvest in growth, withstand market fluctuations, and achieve long-term sustainability. Unlike turnover, which measures total sales revenue without accounting for costs, profit margins provide a clearer picture of operational efficiency and true profitability.
Common Misconceptions about Profit and Turnover
Many confuse turnover with profit, mistakenly assuming high turnover means high profit, but turnover refers to total sales revenue while profit accounts for all expenses deducted from revenue. Businesses with large turnover can still incur losses if costs exceed sales income, highlighting the need to analyze net profit margins rather than revenue alone. Understanding the distinction between gross profit, net profit, and turnover is essential for accurate financial assessments and decision-making.
Impact of Expenses on Profitability
Profit represents the financial gain after deducting all expenses from turnover, which is the total revenue generated from sales. High expenses, including operational costs, salaries, and overheads, significantly reduce profit margins despite strong turnover figures. Effective expense management directly enhances profitability by maximizing the difference between turnover and costs.
Profit vs Turnover: Which Should You Focus On?
Profit and turnover are key financial metrics, but focusing on profit provides a clearer indication of a business's financial health since profit reflects actual earnings after expenses. Turnover, or revenue, shows the total sales volume but does not account for costs, making it less effective for measuring true business success. Prioritizing profit helps optimize operational efficiency and sustainable growth, ensuring long-term viability beyond just increasing sales figures.
Maximizing Profit Without Compromising Turnover
Maximizing profit without compromising turnover requires strategic pricing, cost control, and efficient sales processes to maintain a healthy cash flow while increasing net margins. Leveraging data analytics to identify high-margin products and customer segments enables targeted marketing and optimized resource allocation. Streamlining operations and reducing variable costs support sustaining turnover levels while improving overall profitability.
Profit Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com