Green bonds finance projects with positive environmental impacts, offering investors a way to support sustainability while earning returns. Conventional bonds focus primarily on financial returns without specific environmental or social objectives. Discover how choosing between green and conventional bonds can align with Your investment goals by reading the full article.
Table of Comparison
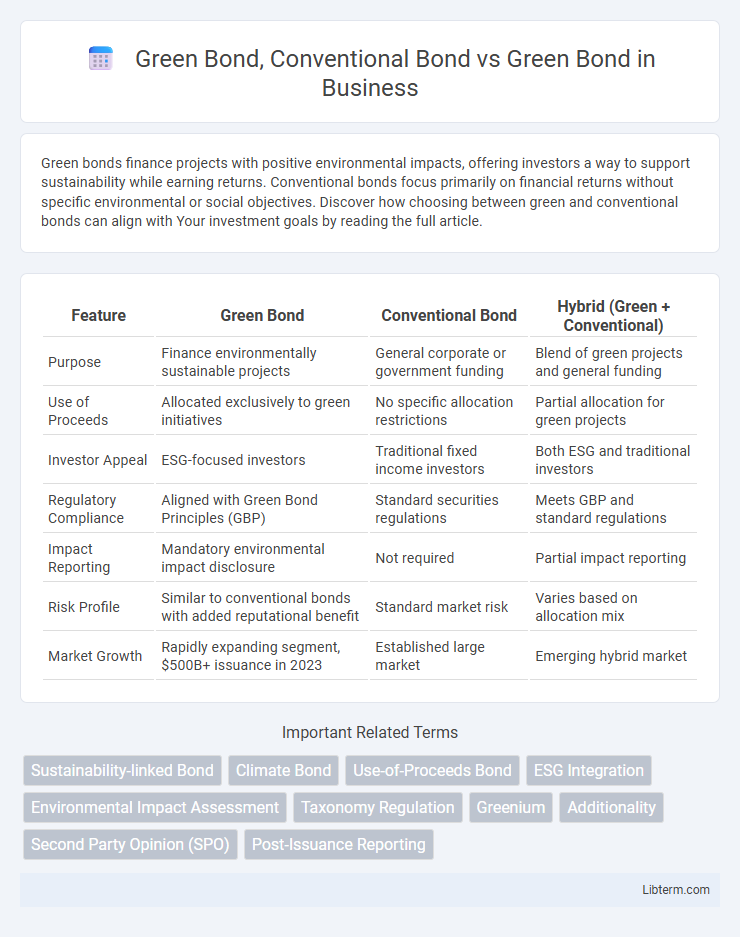
| Feature | Green Bond | Conventional Bond | Hybrid (Green + Conventional) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Finance environmentally sustainable projects | General corporate or government funding | Blend of green projects and general funding |
| Use of Proceeds | Allocated exclusively to green initiatives | No specific allocation restrictions | Partial allocation for green projects |
| Investor Appeal | ESG-focused investors | Traditional fixed income investors | Both ESG and traditional investors |
| Regulatory Compliance | Aligned with Green Bond Principles (GBP) | Standard securities regulations | Meets GBP and standard regulations |
| Impact Reporting | Mandatory environmental impact disclosure | Not required | Partial impact reporting |
| Risk Profile | Similar to conventional bonds with added reputational benefit | Standard market risk | Varies based on allocation mix |
| Market Growth | Rapidly expanding segment, $500B+ issuance in 2023 | Established large market | Emerging hybrid market |
Introduction to Green Bonds
Green bonds are debt securities issued to finance projects with positive environmental impacts, such as renewable energy, clean transportation, and sustainable water management. Unlike conventional bonds, green bonds are explicitly dedicated to funding initiatives that support climate change mitigation and environmental sustainability, making them a crucial tool for investors aiming to align portfolios with environmental, social, and governance (ESG) criteria. The green bond market has experienced rapid growth, surpassing $500 billion in annual issuance by 2023, reflecting increasing demand for sustainable investment options worldwide.
Understanding Conventional Bonds
Conventional bonds are debt instruments where investors lend money to issuers in exchange for fixed interest payments and principal repayment at maturity, primarily funding general corporate or government activities. Green bonds differ by specifically financing environmentally sustainable projects such as renewable energy, clean transportation, and conservation efforts. Understanding conventional bonds provides a foundation for recognizing how green bonds channel capital towards climate-friendly initiatives while maintaining similar financial structures and investor expectations.
Key Features of Green Bonds
Green bonds are debt instruments specifically designed to fund projects with positive environmental benefits, such as renewable energy, clean transportation, or sustainable water management. Unlike conventional bonds, green bonds include transparency in the use of proceeds, rigorous reporting standards, and third-party verification to ensure funds support environmentally friendly initiatives. Key features of green bonds include eligibility criteria for projects, impact reporting, and alignment with global frameworks like the Green Bond Principles to promote sustainable finance.
Environmental Impact of Green Bonds
Green bonds finance projects with positive environmental impacts, such as renewable energy, energy efficiency, and pollution reduction, differentiating them from conventional bonds that fund general corporate or governmental activities without specific sustainability criteria. The environmental impact of green bonds is measurable through reduced carbon emissions, enhanced resource efficiency, and support for climate resilience initiatives. Investors increasingly prioritize green bonds for their role in promoting sustainable development and meeting global environmental targets like the Paris Agreement.
Financial Mechanisms: Green vs Conventional Bonds
Green bonds are financial instruments specifically designed to fund projects with positive environmental impacts, such as renewable energy or sustainable infrastructure, offering transparency through dedicated use of proceeds and impact reporting. Conventional bonds, by contrast, raise capital for a broad range of projects without environmental stipulations, with fewer restrictions on fund allocation and less focus on sustainability outcomes. The key financial mechanism difference lies in green bonds' enhanced investor appeal through ESG (Environmental, Social, and Governance) criteria, potentially lower borrowing costs, and the ability to access specialized green finance markets.
Regulatory Frameworks for Green Bonds
Green bonds are debt instruments specifically earmarked for financing environmentally sustainable projects, differing from conventional bonds by their dedicated use of proceeds and impact reporting requirements. Regulatory frameworks for green bonds include standards such as the Green Bond Principles (GBP) and the EU Green Bond Standard, which provide transparency, disclosure, and verification guidelines to ensure the environmental credentials of funded projects. These frameworks promote market integrity and investor confidence by enforcing rigorous eligibility criteria, third-party reviews, and ongoing reporting, distinguishing green bonds from traditional debt securities.
Green Bond Market Growth and Trends
Green bonds represent a rapidly expanding segment within the fixed-income market, designed to fund environmentally sustainable projects such as renewable energy and climate resilience initiatives. Unlike conventional bonds that finance general corporate or government needs without environmental criteria, green bonds require strict compliance with use-of-proceeds frameworks and impact reporting standards. The green bond market has experienced exponential growth, reaching over $500 billion in annual issuances by 2023, driven by increasing investor demand for ESG-compliant assets and supportive regulatory frameworks worldwide.
Advantages of Green Bonds for Investors
Green bonds offer investors environmental impact transparency by financing projects with positive ecological outcomes such as renewable energy and pollution reduction. Unlike conventional bonds, green bonds attract socially responsible investors seeking alignment with sustainability goals, often providing access to new market segments and potentially lower funding costs. These bonds also contribute to portfolio diversification and risk mitigation by supporting long-term green infrastructure projects that address climate risks.
Challenges Facing Green and Conventional Bonds
Green bonds face challenges such as limited issuer diversity, lack of standardized definitions, and higher upfront costs for verification and reporting compared to conventional bonds. Conventional bonds encounter risks related to environmental regulations and shifting investor preferences toward sustainable assets, potentially leading to stranded assets and reduced demand. Both bond types must navigate evolving market expectations and regulatory frameworks, affecting liquidity and pricing efficiency.
Future Outlook: Green Bond Evolution
Green bonds are revolutionizing sustainable finance by channeling capital into environmentally-friendly projects, contrasting with conventional bonds that primarily fund general corporate or governmental activities. The future outlook for green bonds shows accelerated growth driven by rising investor demand for ESG-compliant assets and stricter global climate regulations. Expected innovations include enhanced transparency through blockchain technology and expanded frameworks for quantifying environmental impact, positioning green bonds as pivotal tools in the transition to a low-carbon economy.
Green Bond, Conventional Bond Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com