Insourcing enhances operational control by utilizing internal resources to manage tasks traditionally outsourced, leading to improved quality and faster decision-making. It reduces dependency on external vendors and aligns processes closely with your company's core objectives. Explore the article to understand how insourcing can transform your business efficiency and cost management.
Table of Comparison
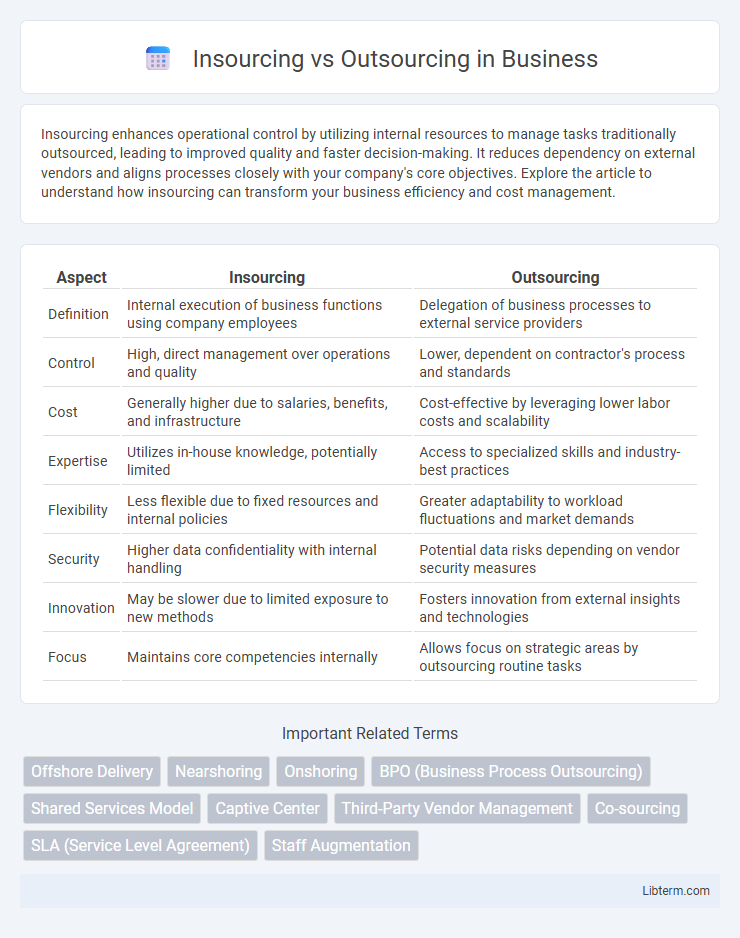
| Aspect | Insourcing | Outsourcing |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Internal execution of business functions using company employees | Delegation of business processes to external service providers |
| Control | High, direct management over operations and quality | Lower, dependent on contractor's process and standards |
| Cost | Generally higher due to salaries, benefits, and infrastructure | Cost-effective by leveraging lower labor costs and scalability |
| Expertise | Utilizes in-house knowledge, potentially limited | Access to specialized skills and industry-best practices |
| Flexibility | Less flexible due to fixed resources and internal policies | Greater adaptability to workload fluctuations and market demands |
| Security | Higher data confidentiality with internal handling | Potential data risks depending on vendor security measures |
| Innovation | May be slower due to limited exposure to new methods | Fosters innovation from external insights and technologies |
| Focus | Maintains core competencies internally | Allows focus on strategic areas by outsourcing routine tasks |
Introduction to Insourcing and Outsourcing
Insourcing involves assigning tasks or projects to internal teams within an organization, leveraging in-house expertise and resources to maintain control and ensure quality. Outsourcing entails contracting external vendors or service providers to perform specific functions, aiming to reduce costs and access specialized skills. Both strategies impact operational efficiency, cost management, and scalability based on a company's strategic goals and resource availability.
Key Definitions: Insourcing vs Outsourcing
Insourcing involves utilizing internal resources and employees to perform business functions, enhancing control and aligning closely with company culture. Outsourcing delegates specific tasks or services to external vendors, often to reduce costs and access specialized expertise. The decision between insourcing and outsourcing depends on factors such as cost efficiency, quality control, and strategic priorities.
Advantages of Insourcing
Insourcing enhances control over processes, ensuring higher quality and faster adjustments to project requirements due to direct oversight and communication within the company. It promotes deeper institutional knowledge and skill development among employees, leading to long-term innovation and competitive advantage. Cost efficiency is achieved by reducing dependency on external vendors, minimizing risks linked to confidentiality and compliance.
Advantages of Outsourcing
Outsourcing offers cost savings by leveraging lower labor and operational expenses in specialized external providers. It enhances focus on core business activities by delegating non-core functions to experts, improving efficiency and innovation. Access to advanced technology and skilled talent through outsourcing accelerates project timelines and drives competitive advantage.
Challenges of Insourcing
Insourcing presents challenges such as higher operational costs due to the need for specialized in-house expertise and infrastructure investment, which can strain company resources. Managing internal teams requires continuous training and development to keep pace with technological advancements, leading to potential productivity bottlenecks. Additionally, maintaining scalability and flexibility in rapidly changing markets can be difficult without the diverse capabilities and economies of scale provided by outsourcing partners.
Challenges of Outsourcing
Outsourcing challenges include communication barriers, loss of control over processes, and quality inconsistency. Time zone differences and cultural gaps often hinder collaboration and affect project timelines. Dependency on external vendors increases security risks and can lead to hidden costs.
Cost Comparison: Insourcing vs Outsourcing
Insourcing often incurs higher fixed costs due to salaries, training, and infrastructure investments, whereas outsourcing can reduce upfront expenses by leveraging external vendors' scalable resources. Outsourcing typically offers variable cost advantages, allowing companies to pay only for services used, which can lead to significant savings in labor and operational costs. However, insourcing provides greater control over quality and processes, potentially minimizing expenses related to rework and vendor management.
Impact on Business Flexibility and Scalability
Insourcing enhances business flexibility by allowing direct control over processes and quicker adaptation to changing market demands, while outsourcing offers scalability through access to external resources and expertise without the need for significant internal investment. Outsourcing enables rapid scaling of operations during peak periods, minimizing fixed costs, whereas insourcing requires more substantial infrastructure adjustments to accommodate growth. Balancing insourcing and outsourcing strategies can optimize both flexibility and scalability, aligning resource management with long-term business goals.
Choosing the Right Strategy for Your Business
Selecting between insourcing and outsourcing depends on factors such as cost efficiency, control over processes, and the complexity of tasks. Insourcing allows for better quality control and alignment with company culture, ideal for core competencies, while outsourcing can reduce operational costs and provide access to specialized expertise. Evaluating business goals, resource availability, and long-term scalability is essential to determine the optimal strategy for sustainable growth and competitive advantage.
Future Trends in Insourcing and Outsourcing
Emerging future trends in insourcing emphasize increased reliance on advanced automation, artificial intelligence, and skilled in-house talent to enhance innovation and operational control. Outsourcing is evolving with a growing focus on strategic partnerships, cloud-based services, and specialized providers enabling cost efficiency and scalability. Both models are integrating hybrid approaches, leveraging digital transformation and data analytics to optimize performance and competitiveness in dynamic markets.
Insourcing Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com