Understanding cost price is crucial for managing your business profitability, as it represents the total expense incurred to produce or purchase a product. Accurately calculating cost price helps in setting appropriate selling prices and maximizing revenue. Explore the rest of the article to learn effective strategies for determining and optimizing your cost price.
Table of Comparison
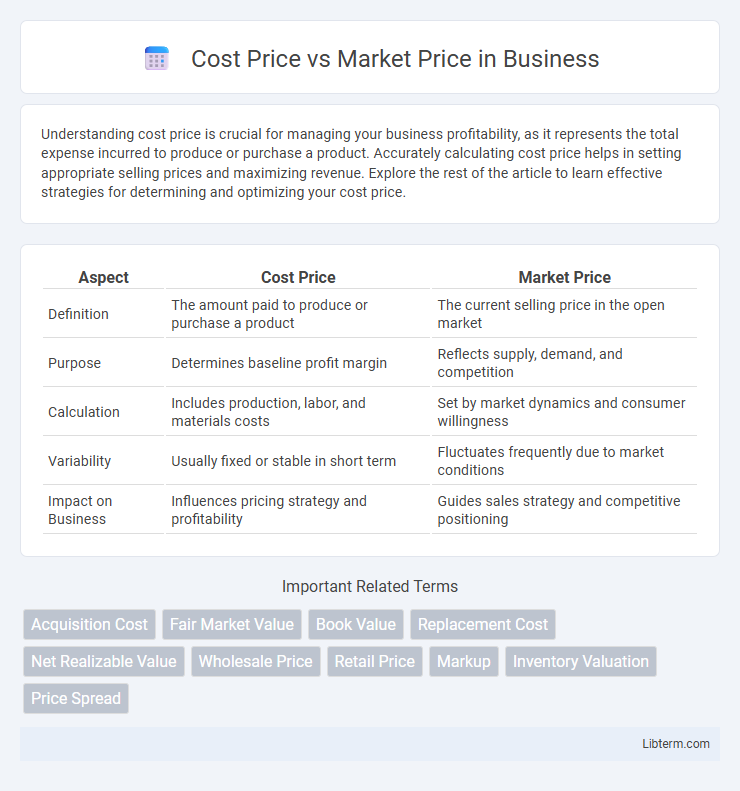
| Aspect | Cost Price | Market Price |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | The amount paid to produce or purchase a product | The current selling price in the open market |
| Purpose | Determines baseline profit margin | Reflects supply, demand, and competition |
| Calculation | Includes production, labor, and materials costs | Set by market dynamics and consumer willingness |
| Variability | Usually fixed or stable in short term | Fluctuates frequently due to market conditions |
| Impact on Business | Influences pricing strategy and profitability | Guides sales strategy and competitive positioning |
Understanding Cost Price: Definition and Importance
Cost price refers to the total expenditure incurred by a business to produce or purchase a product, encompassing raw materials, labor, and overhead costs. Understanding cost price is crucial for setting competitive selling prices, ensuring profitability, and managing financial performance effectively. Accurate cost price calculation enables businesses to avoid losses and make informed decisions on pricing strategies and inventory management.
What is Market Price? Key Features Explained
Market price represents the current value at which an asset or commodity can be bought or sold in a competitive marketplace, reflecting real-time supply and demand dynamics. Key features include its variability due to market forces, transparency influenced by buyer and seller interactions, and its role as a benchmark for trading decisions. Unlike cost price, which is the expense incurred to produce or acquire a product, market price is externally determined and fluctuates continuously.
Core Differences Between Cost Price and Market Price
Cost price represents the actual expense incurred to produce or purchase a product, including materials, labor, and overhead costs. Market price is the amount at which the product is sold to consumers, influenced by factors such as demand, competition, and perceived value. The core difference lies in cost price reflecting production expenditure, while market price reflects the selling value determined by market dynamics.
Factors Influencing Cost Price Calculation
Cost price calculation is influenced by raw materials, labor costs, manufacturing overhead, and transportation expenses, which together determine the total expenditure to produce a product. Market demand, competition, and supplier pricing also affect the cost price by causing fluctuations in input costs. Accurate cost price assessment is essential for setting competitive market prices and maintaining profitability.
Market Forces Impacting Market Price
Market price fluctuates primarily due to supply and demand dynamics, where increased demand or reduced supply drives prices upward, while surplus supply or decreased demand lowers them. External factors such as consumer preferences, seasonal trends, economic conditions, and competitor actions also significantly influence market price variations. Understanding these market forces is crucial for businesses to strategically set prices that maximize profitability while remaining competitive.
How to Determine Cost Price Accurately
Determining cost price accurately involves calculating all expenses incurred in producing or purchasing a product, including raw materials, labor, overhead, and shipping costs. Utilizing detailed accounting records and inventory management systems enhances precision by capturing variable and fixed costs comprehensively. Consistent cost price evaluation ensures better pricing strategies and profitability analysis in comparison to fluctuating market price trends.
Methods for Setting Market Price
Methods for setting market price include cost-plus pricing, where a fixed percentage markup is added to the cost price to ensure profit; competitive pricing, which involves setting prices based on competitors' pricing strategies to maintain market position; and value-based pricing, focusing on the perceived value to customers rather than just the cost incurred. Penetration pricing is used to quickly gain market share by setting a lower price initially, while skimming pricing targets early adopters at a high price before lowering it over time. Each method aligns with specific business goals, market conditions, and consumer behavior to effectively balance profitability and competitiveness.
Cost Price vs Market Price: Real-world Examples
Cost Price vs Market Price highlights how businesses adjust pricing strategies based on production costs versus current market demand and competition, affecting profitability. For example, in the automotive industry, manufacturers set the cost price by summing raw materials, labor, and overhead, while the market price fluctuates due to factors like consumer trends and competitor pricing. In real estate, cost price represents construction and acquisition expenses, whereas market price varies by location, economic conditions, and buyer interest, demonstrating dynamic pricing in practice.
The Role of Cost and Market Price in Profit Margins
Cost price represents the total expenditure incurred to produce or purchase a product, serving as the foundational benchmark for setting sales prices. Market price reflects the current price at which goods are bought and sold, influenced by supply, demand, and competitive dynamics in the marketplace. The difference between market price and cost price determines profit margins, directly impacting a business's profitability and pricing strategies.
Strategies to Align Cost Price with Market Price
Aligning cost price with market price involves strategic pricing analysis and cost control measures. Businesses use techniques such as value engineering, competitive benchmarking, and supply chain optimization to reduce production costs while maintaining product quality. Adjusting pricing strategies based on market demand, competitor pricing, and customer perceived value ensures the cost price stays viable within the targeted market price range.
Cost Price Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com