Sophisticated investors possess advanced knowledge and experience in financial markets, enabling them to understand complex investment opportunities and risks. Their access to exclusive products and ability to evaluate nuanced market trends sets them apart from everyday investors. Discover how being a sophisticated investor can enhance Your financial strategy by reading the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
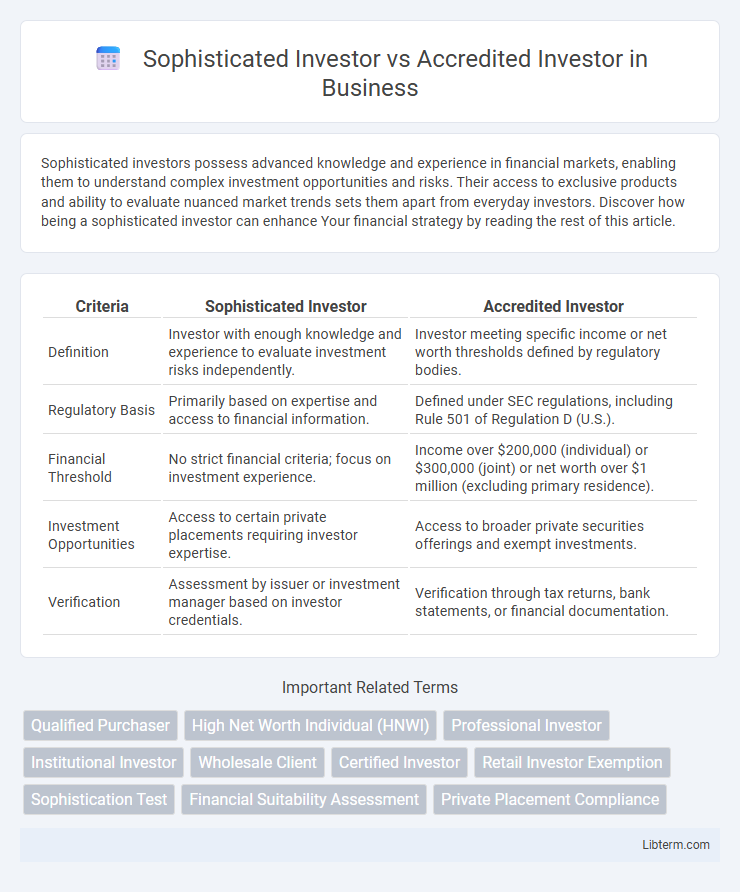
| Criteria | Sophisticated Investor | Accredited Investor |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Investor with enough knowledge and experience to evaluate investment risks independently. | Investor meeting specific income or net worth thresholds defined by regulatory bodies. |
| Regulatory Basis | Primarily based on expertise and access to financial information. | Defined under SEC regulations, including Rule 501 of Regulation D (U.S.). |
| Financial Threshold | No strict financial criteria; focus on investment experience. | Income over $200,000 (individual) or $300,000 (joint) or net worth over $1 million (excluding primary residence). |
| Investment Opportunities | Access to certain private placements requiring investor expertise. | Access to broader private securities offerings and exempt investments. |
| Verification | Assessment by issuer or investment manager based on investor credentials. | Verification through tax returns, bank statements, or financial documentation. |
Understanding Sophisticated Investors
Sophisticated investors possess extensive experience and knowledge in financial markets, enabling them to evaluate investment risks and opportunities without relying on regulatory protections. Unlike accredited investors, whose eligibility is primarily based on income or net worth thresholds, sophisticated investors are often recognized through their demonstrated expertise and professional background. This advanced understanding allows them to access private placements and complex investment instruments typically unavailable to the general public.
Defining Accredited Investors
Accredited investors are individuals or entities that meet specific financial criteria set by securities regulators, typically including a net worth exceeding $1 million (excluding primary residence) or an annual income over $200,000 for individuals ($300,000 combined for couples). This definition enables access to private investment opportunities that are not registered with financial authorities due to their higher risk. Sophisticated investors, in contrast, may not meet these financial thresholds but demonstrate sufficient knowledge and experience to evaluate investment risks independently.
Key Legal Distinctions
Sophisticated investors are individuals or entities with sufficient knowledge, experience, and financial acumen to evaluate investment risks without regulatory protections, but they do not necessarily meet specific income or net worth thresholds required for accredited investors. Accredited investors satisfy defined criteria under Regulation D of the SEC, such as having a net worth exceeding $1 million (excluding primary residence) or an annual income over $200,000 for individuals, granting them access to private securities offerings. Key legal distinctions revolve around regulatory eligibility and disclosure exemptions, where accredited investor status provides broader investment opportunities and reduced disclosure requirements compared to the more subjective assessment of sophistication.
Qualification Criteria Compared
Sophisticated investors must prove sufficient financial knowledge and investment experience, typically demonstrated through previous investment activities or professional credentials, without a strict net worth or income threshold. Accredited investors, according to the SEC, must meet specific quantitative criteria such as a net worth exceeding $1 million (excluding primary residence) or an annual income of $200,000 for individuals ($300,000 for joint filers) in the past two years. The qualification criteria for sophisticated investors emphasize expertise and decision-making capability, whereas accredited investors rely primarily on predefined financial metrics.
Investment Opportunities Available
Sophisticated investors gain access to a wider range of complex investment opportunities such as private placements, hedge funds, and venture capital funds that require deeper financial knowledge and experience, often not available to the general public. Accredited investors qualify for many of the same private investment deals but may face more regulatory restrictions compared to sophisticated investors, who demonstrate sufficient financial acumen and investment sophistication. Both categories unlock higher-yielding, less liquid investments typically excluded from retail investors, enabling portfolio diversification beyond public markets.
Risks Faced by Each Investor Type
Sophisticated investors typically possess extensive market knowledge and experience, enabling them to understand complex risks associated with alternative investments, though they may still face significant exposure to illiquid assets and market volatility. Accredited investors meet specific income or net worth thresholds, granting access to private securities but often lacking the detailed expertise to fully assess risks, increasing the potential for substantial financial loss. Both investor types confront challenges such as limited regulatory protection and high-risk investments, necessitating thorough due diligence and risk management strategies to mitigate potential damages.
Regulatory Protections and Limitations
Sophisticated investors possess sufficient knowledge and experience to evaluate investment risks but may lack the stringent financial thresholds required for accredited investor status, impacting their access to certain private securities offerings. Regulatory protections for sophisticated investors are less comprehensive compared to accredited investors, as the latter benefit from exemptions under securities laws that allow participation in high-risk, high-reward investments not registered with the SEC. Limitations for sophisticated investors include restricted investment opportunities and reduced disclosure requirements, designed to balance investor protection with market access.
Access to Private Offerings
Sophisticated investors qualify for private offerings by demonstrating sufficient knowledge and experience in financial matters, enabling access to certain private placement investments not available to the general public. Accredited investors meet stricter financial criteria defined by the SEC, such as exceeding specific income or net worth thresholds, granting them broader access to a wider range of private securities. Both designations allow participation in private markets, but accredited investors have greater eligibility, resulting in expanded opportunities for investment in venture capital, hedge funds, and private equity.
International Perspectives and Variations
Sophisticated investors are defined by their financial knowledge and experience, allowing them to assess investment risks without regulatory protection, while accredited investors meet specific income or net worth criteria set by regulatory bodies such as the SEC in the U.S. International perspectives reveal significant variations; for example, the UK's FCA classifies sophisticated investors under "high net worth" or "self-certified sophisticated" criteria, whereas Australia emphasizes both financial thresholds and investment experience under the Corporations Act. These distinctions impact cross-border investment opportunities and regulatory compliance, highlighting the importance of understanding each jurisdiction's definitions to access private capital markets effectively.
Choosing the Right Path: Which Investor Are You?
Sophisticated investors possess extensive financial knowledge and experience, enabling them to evaluate complex investment opportunities, while accredited investors meet specific income or net worth thresholds defined by regulatory bodies such as the SEC. Choosing the right path depends on assessing your financial expertise, risk tolerance, and eligibility criteria for investment opportunities that require higher accreditation levels. Understanding these distinctions ensures access to appropriate private placements, hedge funds, or venture capital deals tailored to your investor profile.
Sophisticated Investor Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com