Specialization enhances efficiency and expertise by allowing individuals or organizations to focus on a specific area, leading to improved skills and higher quality outcomes. It fosters innovation and competitive advantage by deepening knowledge and mastering particular processes or subjects. Explore the rest of the article to discover how specialization can elevate your performance and drive success.
Table of Comparison
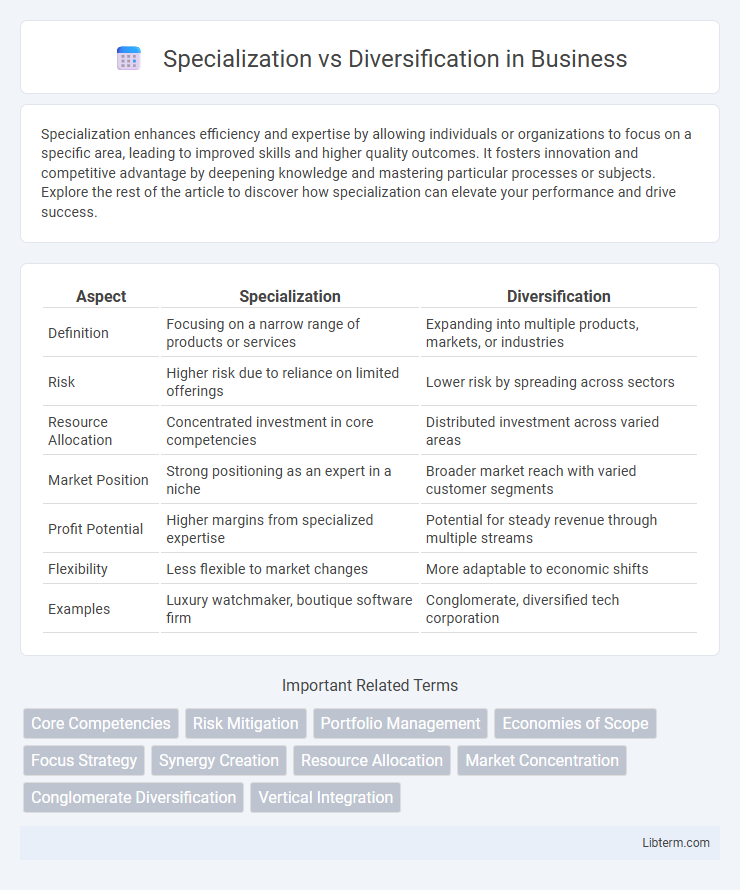
| Aspect | Specialization | Diversification |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Focusing on a narrow range of products or services | Expanding into multiple products, markets, or industries |
| Risk | Higher risk due to reliance on limited offerings | Lower risk by spreading across sectors |
| Resource Allocation | Concentrated investment in core competencies | Distributed investment across varied areas |
| Market Position | Strong positioning as an expert in a niche | Broader market reach with varied customer segments |
| Profit Potential | Higher margins from specialized expertise | Potential for steady revenue through multiple streams |
| Flexibility | Less flexible to market changes | More adaptable to economic shifts |
| Examples | Luxury watchmaker, boutique software firm | Conglomerate, diversified tech corporation |
Understanding Specialization and Diversification
Specialization emphasizes focusing resources and efforts on a narrow range of skills or products to enhance efficiency, expertise, and competitive advantage. Diversification involves expanding into different markets or product lines to spread risk and increase growth opportunities. Understanding these strategies helps businesses balance depth of expertise with market breadth to optimize profitability and resilience.
Key Differences Between Specialization and Diversification
Specialization involves focusing resources and expertise on a narrow field to achieve high efficiency and deep knowledge, often leading to competitive advantages within a specific market. Diversification spreads investments or business activities across multiple sectors or products to reduce risk and capitalize on various growth opportunities. Key differences include risk exposure, resource allocation, and strategic focus, where specialization leans toward depth and efficiency, while diversification emphasizes breadth and risk mitigation.
Advantages of Specialization
Specialization enhances productivity by allowing individuals or businesses to focus on a specific skill or product, leading to higher efficiency and expertise. It promotes innovation and quality improvements as concentrated efforts foster deep knowledge and mastery. Specialization also reduces costs through economies of scale and streamlines workflows, resulting in competitive advantages in the marketplace.
Benefits of Diversification
Diversification enhances risk management by spreading investments across various asset classes and industries, reducing exposure to any single market downturn. It enables access to multiple growth opportunities, increasing the potential for steady returns regardless of sector performance fluctuations. A diversified portfolio also improves financial stability and long-term resilience against economic volatility.
Risks and Limitations of Specialization
Specialization concentrates resources and expertise in a narrow field, increasing vulnerability to market shifts, technological changes, and demand fluctuations that can render the specialized skills or products obsolete. The reliance on a limited range of activities or products heightens exposure to industry-specific risks, reducing adaptability and resilience. Firms and individuals face potential stagnation and loss of competitive advantage if diversification strategies are not considered to mitigate these inherent limitations.
Challenges Associated with Diversification
Diversification presents challenges such as increased complexity in management, higher operational costs, and potential dilution of core competencies. Companies may struggle with maintaining consistent quality and brand identity across diverse product lines or markets. Market unfamiliarity and resource allocation difficulties further complicate successful diversification strategies.
Factors Influencing the Choice Between Specialization and Diversification
Market demand and industry characteristics play a crucial role in determining whether a business should pursue specialization or diversification, with niche markets favoring specialization for expertise development. Resource availability, including financial capital, human skills, and technological capabilities, influences the feasibility of diversification strategies to spread risk and capture new opportunities. Competitive pressure and organizational goals also guide this choice, as firms seek to either dominate a specific segment or expand their portfolio to enhance resilience and growth potential.
Real-World Examples: Specialization vs Diversification
Specialization in businesses like Apple, which focuses on premium consumer electronics, drives innovation and brand loyalty through concentrated expertise. Diversification exemplified by conglomerates such as Amazon, expanding from e-commerce to cloud computing and entertainment, mitigates risk by spreading investments across various industries. Real-world outcomes show specialization yields deep competitive advantages in niche markets, while diversification enhances resilience against market volatility.
Industry-Specific Considerations
Industry-specific considerations for specialization versus diversification hinge on market volatility, competitive intensity, and resource availability. Industries with rapid technological advances, such as biotechnology or information technology, often benefit from specialization to build deep expertise and maintain a competitive edge. Conversely, sectors like consumer goods or conglomerates may leverage diversification to spread risk and capitalize on multiple market opportunities.
Choosing the Right Strategy for Sustainable Growth
Specialization enhances expertise and operational efficiency by concentrating resources on a specific niche, driving competitive advantage and higher profit margins. Diversification spreads risk across multiple markets or products, fostering resilience against market fluctuations and opening new revenue streams. Selecting the right strategy for sustainable growth depends on market conditions, company capabilities, and long-term goals to balance focus with adaptability.
Specialization Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com