Open Innovation transforms traditional research by encouraging companies to leverage external ideas and technologies alongside internal resources. It accelerates product development, reduces costs, and fosters collaboration across industries and disciplines. Explore the rest of the article to discover how you can implement open innovation strategies in your organization.
Table of Comparison
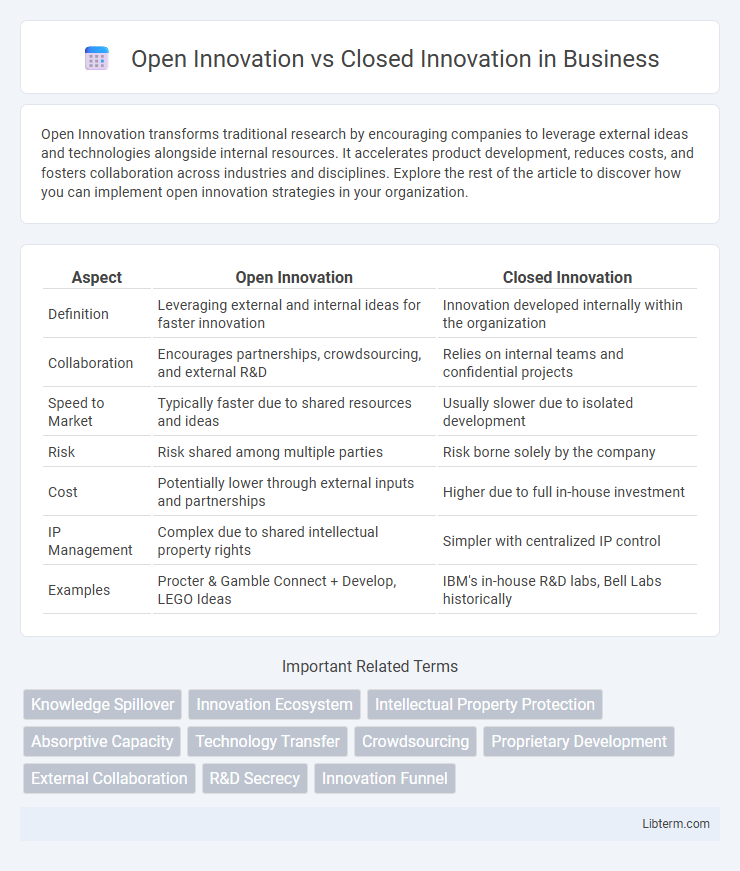
| Aspect | Open Innovation | Closed Innovation |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Leveraging external and internal ideas for faster innovation | Innovation developed internally within the organization |
| Collaboration | Encourages partnerships, crowdsourcing, and external R&D | Relies on internal teams and confidential projects |
| Speed to Market | Typically faster due to shared resources and ideas | Usually slower due to isolated development |
| Risk | Risk shared among multiple parties | Risk borne solely by the company |
| Cost | Potentially lower through external inputs and partnerships | Higher due to full in-house investment |
| IP Management | Complex due to shared intellectual property rights | Simpler with centralized IP control |
| Examples | Procter & Gamble Connect + Develop, LEGO Ideas | IBM's in-house R&D labs, Bell Labs historically |
Introduction to Open Innovation vs Closed Innovation
Open Innovation leverages external ideas, collaborations, and pathways to market, enabling companies to accelerate innovation and reduce risks by integrating diverse knowledge sources. Closed Innovation relies on internal resources, proprietary research, and confidential development processes, maintaining full control over intellectual property and innovation outcomes. Understanding the distinction between Open Innovation and Closed Innovation is crucial for organizations seeking to optimize their innovation strategies in a competitive landscape.
Defining Open Innovation
Open innovation refers to the strategic approach where companies leverage external ideas, technologies, and pathways alongside internal resources to accelerate innovation and reduce costs. This model contrasts with closed innovation, which relies solely on internal R&D and proprietary knowledge to develop new products or services. By embracing open innovation, organizations gain access to a broader pool of expertise, partnerships, and market insights, fostering faster adaptation and competitive advantage.
Defining Closed Innovation
Closed innovation is a traditional research and development model where companies rely exclusively on internal resources, expertise, and intellectual property to create new products and technologies. This approach emphasizes confidentiality and tight control over innovation processes to maintain competitive advantage. By limiting external collaboration, closed innovation aims to protect proprietary knowledge and prevent information leakage.
Key Differences Between Open and Closed Innovation
Open Innovation leverages external ideas and collaborations to accelerate research and development, whereas Closed Innovation relies solely on internal resources and proprietary knowledge. The key differences include the flow of information--open innovation encourages knowledge sharing across organizational boundaries, while closed innovation restricts access to internal teams. Open innovation aims to enhance agility and diversify problem-solving sources, unlike closed innovation which prioritizes control and confidentiality.
Advantages of Open Innovation
Open Innovation accelerates product development by leveraging external expertise and resources, reducing internal R&D costs and risks. It enhances creativity and problem-solving through diverse collaborations across industries and academia, leading to breakthrough innovations. Companies adopting Open Innovation benefit from faster market entry and expanded innovation ecosystems, increasing competitive advantage.
Limitations of Open Innovation
Open Innovation faces limitations such as increased risks to intellectual property security, potential loss of competitive advantage, and challenges in managing external partnerships effectively. The dependency on external knowledge sources can lead to reduced control over the innovation process, complicating coordination and integration. Furthermore, differences in organizational cultures and objectives may hinder seamless collaboration and slow down the development timeline.
Benefits of Closed Innovation
Closed Innovation enables companies to maintain full control over intellectual property, reducing risks related to knowledge leaks and competitive exposure. This approach fosters intense internal focus, allowing organizations to streamline processes and ensure consistency in product development and quality. By leveraging exclusive expertise and resources, firms can build strong proprietary advantages and reinforce market positioning.
Drawbacks of Closed Innovation
Closed Innovation limits access to external ideas and technologies, restricting a company's innovation potential and slowing product development cycles. This inward-focused approach often results in higher research and development costs due to redundancy and missed opportunities for collaboration. Companies practicing Closed Innovation risk falling behind competitors who leverage open innovation ecosystems to accelerate growth and diversify their innovation sources.
When to Choose Open or Closed Innovation
Open innovation is ideal when companies seek diverse external ideas, faster problem-solving, and access to broader technology pools, especially in rapidly evolving industries. Closed innovation suits businesses aiming for full control over intellectual property, maintaining strict confidentiality, and when internal R&D capabilities are strong and well-resourced. Firms should evaluate factors like risk tolerance, collaboration readiness, and strategic goals to determine whether open or closed innovation aligns best with their innovation objectives.
Future Trends in Innovation Strategies
Future trends in innovation strategies emphasize the growing adoption of open innovation models, leveraging external collaborations, crowdsourcing, and co-creation to accelerate product development and market entry. Closed innovation remains relevant for protecting proprietary technologies and maintaining competitive advantages in highly regulated industries, but integration with open innovation platforms enhances adaptability and resource utilization. The convergence of digital transformation, data sharing, and artificial intelligence drives hybrid approaches that optimize both internal R&D and external knowledge networks for sustainable innovation ecosystems.
Open Innovation Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com