Subscription-based models offer consistent revenue streams by charging customers on a recurring basis for access to products or services. This approach enhances customer loyalty and allows businesses to forecast growth more accurately while providing convenience and personalized experiences to subscribers. Explore the rest of the article to discover how subscription-based strategies can transform Your business.
Table of Comparison
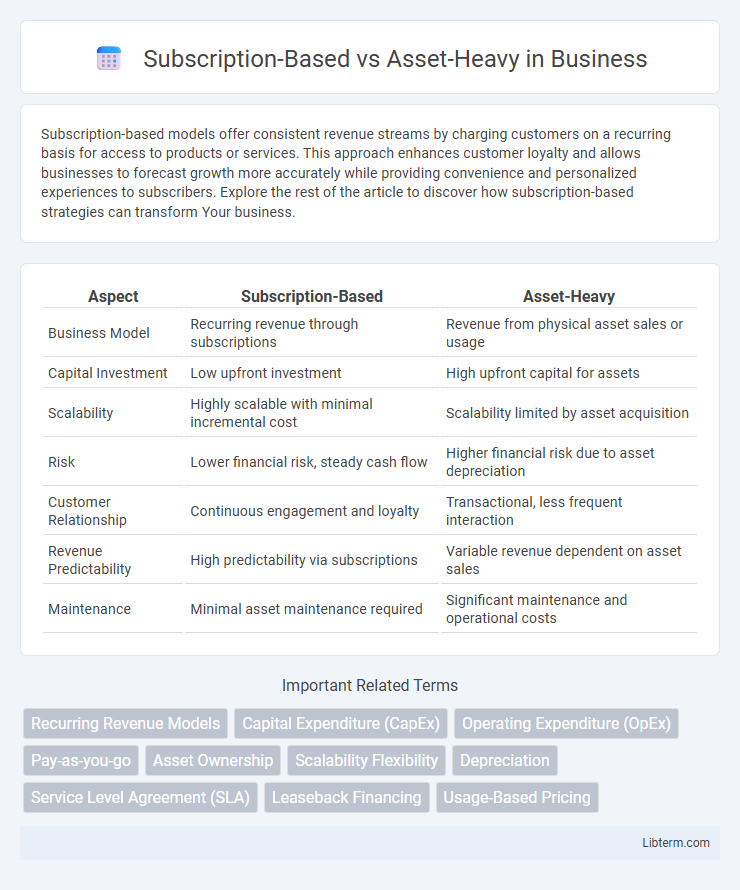
| Aspect | Subscription-Based | Asset-Heavy |
|---|---|---|
| Business Model | Recurring revenue through subscriptions | Revenue from physical asset sales or usage |
| Capital Investment | Low upfront investment | High upfront capital for assets |
| Scalability | Highly scalable with minimal incremental cost | Scalability limited by asset acquisition |
| Risk | Lower financial risk, steady cash flow | Higher financial risk due to asset depreciation |
| Customer Relationship | Continuous engagement and loyalty | Transactional, less frequent interaction |
| Revenue Predictability | High predictability via subscriptions | Variable revenue dependent on asset sales |
| Maintenance | Minimal asset maintenance required | Significant maintenance and operational costs |
Introduction to Subscription-Based and Asset-Heavy Models
Subscription-based models generate recurring revenue by offering access to services or products for a regular fee, emphasizing customer retention and predictable cash flow. Asset-heavy models rely on substantial investments in physical assets, such as manufacturing facilities or inventory, driving value through asset utilization and capital intensity. Understanding these contrasting foundations helps businesses choose strategies aligned with their operational strengths and market demands.
Key Differences Between Subscription and Asset-Heavy Approaches
Subscription-based models emphasize recurring revenue through ongoing customer access rather than ownership, promoting steady cash flow and customer retention. Asset-heavy approaches require significant upfront capital investment in physical assets, leading to higher fixed costs but potential long-term asset appreciation. The key differences lie in financial risk distribution, scalability, and operational flexibility, where subscriptions favor flexible scaling and steady income, whereas asset-heavy models depend on asset utilization and depreciation management.
Market Trends Fueling Subscription-Based Growth
Market trends driving the growth of subscription-based models include increasing consumer preference for convenience, flexibility, and personalized experiences. Digital transformation enables seamless access to services, while advancements in data analytics foster tailored offerings and customer retention. Investors favor subscription-based businesses due to their recurring revenue streams and scalability compared to asset-heavy models with substantial capital expenditures.
Advantages of Subscription-Based Business Models
Subscription-based business models offer predictable and recurring revenue streams, enhancing cash flow stability and financial forecasting. They enable companies to build long-term customer relationships through continuous engagement and personalized service, increasing customer lifetime value. Lower upfront costs and scalable infrastructure foster rapid growth and adaptability compared to asset-heavy models requiring significant capital investment and fixed assets.
Drawbacks of Subscription Services for Businesses
Subscription services can result in unpredictable revenue streams, making financial forecasting challenging for businesses reliant on recurring payments. High customer churn rates increase the cost of customer acquisition and put pressure on maintaining long-term profitability. Businesses may also face limitations in asset ownership and control, restricting flexibility in service customization and scalability.
Strengths of Asset-Heavy Business Operations
Asset-heavy business operations leverage substantial investments in physical infrastructure and equipment, leading to higher control over production quality and operational efficiency. These businesses often benefit from significant tangible assets that provide collateral for financing and create barriers to entry for competitors. The ability to scale through owned resources supports long-term stability and consistent revenue streams in capital-intensive industries.
Limitations and Risks of Asset-Heavy Models
Asset-heavy business models face significant limitations including high capital expenditure, increased fixed costs, and inflexibility in scaling operations quickly. These models carry substantial risks such as asset depreciation, market demand fluctuations impacting asset utilization, and vulnerability to technological obsolescence. Furthermore, asset-heavy companies often experience slower response times to market changes compared to subscription-based models, which can adapt with lower financial risk.
Financial Implications: Subscription vs Asset-Heavy
Subscription-based models offer predictable recurring revenue streams, improving cash flow stability and reducing upfront capital expenditures compared to asset-heavy models that require significant investment in physical assets. Asset-heavy businesses face higher depreciation costs, increased maintenance expenses, and greater risk tied to the value fluctuations of owned assets. Financial flexibility in subscription-based businesses enables faster scaling and adaptability, whereas asset-heavy models may experience slower growth due to capital-intensive requirements.
Industry Examples: Choosing the Right Model
Subscription-based models dominate companies like Netflix and Adobe, leveraging recurring revenue and digital scalability to minimize upfront costs and enhance customer engagement. Asset-heavy models are prevalent in industries such as manufacturing and airlines, where significant capital investment in physical infrastructure is essential for operational capacity and long-term value creation. Selecting the optimal business model requires analyzing industry-specific factors including capital availability, market demand, and scalability potential to align strategic objectives with operational efficiency.
Future Outlook: Evolving Business Models and Strategic Direction
Subscription-based models are projected to outpace asset-heavy approaches due to their scalability, recurring revenue streams, and alignment with customer preference for flexibility. Asset-heavy businesses face increasing pressure to integrate digital services and optimize operational efficiency to remain competitive in evolving markets. Strategic direction is shifting towards hybrid models that blend subscription flexibility with selective asset ownership to balance risk and growth potential.
Subscription-Based Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com