Horizontal integration consolidates companies operating within the same industry to increase market share, reduce competition, and achieve economies of scale. This strategy enables businesses to enhance their product offerings, expand geographic reach, and improve operational efficiency. Discover how horizontal integration can transform Your business by exploring the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
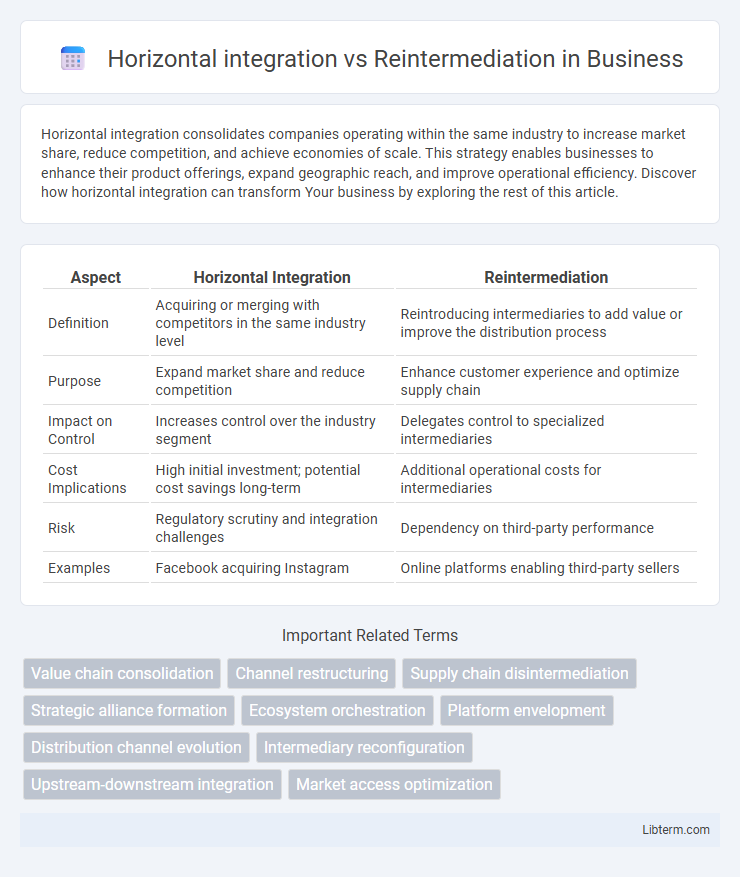
| Aspect | Horizontal Integration | Reintermediation |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Acquiring or merging with competitors in the same industry level | Reintroducing intermediaries to add value or improve the distribution process |
| Purpose | Expand market share and reduce competition | Enhance customer experience and optimize supply chain |
| Impact on Control | Increases control over the industry segment | Delegates control to specialized intermediaries |
| Cost Implications | High initial investment; potential cost savings long-term | Additional operational costs for intermediaries |
| Risk | Regulatory scrutiny and integration challenges | Dependency on third-party performance |
| Examples | Facebook acquiring Instagram | Online platforms enabling third-party sellers |
Understanding Horizontal Integration: Definition and Purpose
Horizontal integration involves a company acquiring or merging with competitors at the same stage of production to increase market share, reduce competition, and achieve economies of scale. Its primary purpose is to consolidate resources, streamline operations, and enhance product offerings within the same industry. This strategy contrasts with reintermediation, which involves introducing new intermediaries to improve supply chain efficiency or customer experience.
What is Reintermediation? An Overview
Reintermediation refers to the process of reintroducing intermediaries into a supply chain or market where they were previously eliminated by direct interactions, such as online platforms reconnecting customers with service providers. It contrasts with horizontal integration, which involves a company acquiring or merging with competitors at the same industry level to expand market share. Reintermediation enhances efficiency by adding value through specialized intermediaries that facilitate transactions, improve customer service, or provide essential market functions.
Key Differences Between Horizontal Integration and Reintermediation
Horizontal integration involves a company expanding its operations by acquiring or merging with competitors at the same stage of the supply chain, enhancing market share and reducing competition. Reintermediation refers to the process of reintroducing intermediaries into the supply chain, often driven by digital platforms to add value through services like aggregation, personalization, or customer support. The key difference lies in horizontal integration's focus on consolidation within the same industry level, while reintermediation emphasizes creating or reestablishing intermediary roles to improve market efficiency and customer experience.
Strategic Advantages of Horizontal Integration
Horizontal integration enables companies to expand market share and reduce competition by acquiring or merging with competitors in the same industry. This strategy allows businesses to achieve economies of scale, lower production costs, and increase bargaining power with suppliers and distributors. By consolidating resources and capabilities, firms can enhance innovation, broaden product offerings, and strengthen brand presence in targeted markets.
Benefits and Risks of Reintermediation
Reintermediation introduces new intermediaries to streamline transactions, enhance customer service, and provide specialized expertise, leading to improved market efficiency and increased consumer trust. However, risks include higher operational costs, potential complexity in supply chains, and reduced direct control over customer relationships. Horizontal integration, by contrast, consolidates firms at the same supply chain level to achieve economies of scale and market dominance but may lack the adaptability and customer-focused benefits gained through reintermediation.
Market Dynamics Influencing Both Strategies
Market dynamics such as technological advancements, shifting consumer preferences, and evolving competitive landscapes drive both horizontal integration and reintermediation strategies. Horizontal integration leverages economies of scale and market power by acquiring or merging with competitors, while reintermediation responds to changes in distribution channels by introducing new intermediaries to enhance efficiency and customer reach. Both strategies are influenced by digital transformation and regulatory environments shaping industry consolidation and value chain restructuring.
Case Studies: Horizontal Integration Success Stories
Horizontal integration strategies have been successfully demonstrated in case studies like Disney's acquisition of Pixar, which strengthened its market position in the animation industry by combining creative talents and distribution networks. Facebook's acquisition of Instagram exemplifies horizontal integration by expanding its social media dominance through eliminating competition and diversifying user engagement. These success stories highlight how companies leverage market consolidation to increase economies of scale, reduce competition, and enhance product or service offerings effectively.
Reintermediation in the Digital Age: Trends and Examples
Reintermediation in the digital age refers to the reintroduction of intermediaries between producers and consumers, often through new digital platforms that add value by enhancing personalization, trust, and transaction efficiency. Trends include the rise of fintech companies acting as financial intermediaries, online marketplaces aggregating diverse sellers, and subscription services curating content or products, which optimize customer experience and data-driven marketing. Examples such as Amazon's marketplace, digital travel agencies like Expedia, and payment processors like PayPal illustrate how reintermediation reshapes traditional supply chains by leveraging technology to facilitate complex interactions and improve service delivery.
Choosing the Right Strategy: Factors to Consider
Choosing the right strategy between horizontal integration and reintermediation depends on market dynamics, competitive landscape, and company capabilities. Horizontal integration leverages economies of scale and market share expansion by acquiring or merging with competitors in the same industry. Reintermediation introduces new intermediaries or platforms to improve customer experience and operational efficiency, especially in digital markets where direct-to-consumer models are evolving.
Future Outlook: Evolving Business Models and Industry Impact
Horizontal integration drives industry consolidation by enabling companies to acquire competitors, expanding market share and enhancing economies of scale, which shapes competitive dynamics across sectors. Reintermediation introduces new intermediaries leveraging digital platforms, transforming traditional supply chains and fostering innovative business models that cater to evolving consumer demands. Future business landscapes will increasingly blend these approaches, as firms balance consolidation with technological adaptation to optimize value delivery and sustain growth in disrupted markets.
Horizontal integration Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com