A Service Level Agreement (SLA) defines the expected performance and quality metrics between a service provider and the customer, ensuring clear accountability and mutual understanding. It outlines specific responsibilities, response times, and remedies if service commitments are not met, helping to safeguard Your business operations. Discover how a well-crafted SLA can enhance your service reliability and customer satisfaction by reading the full article.
Table of Comparison
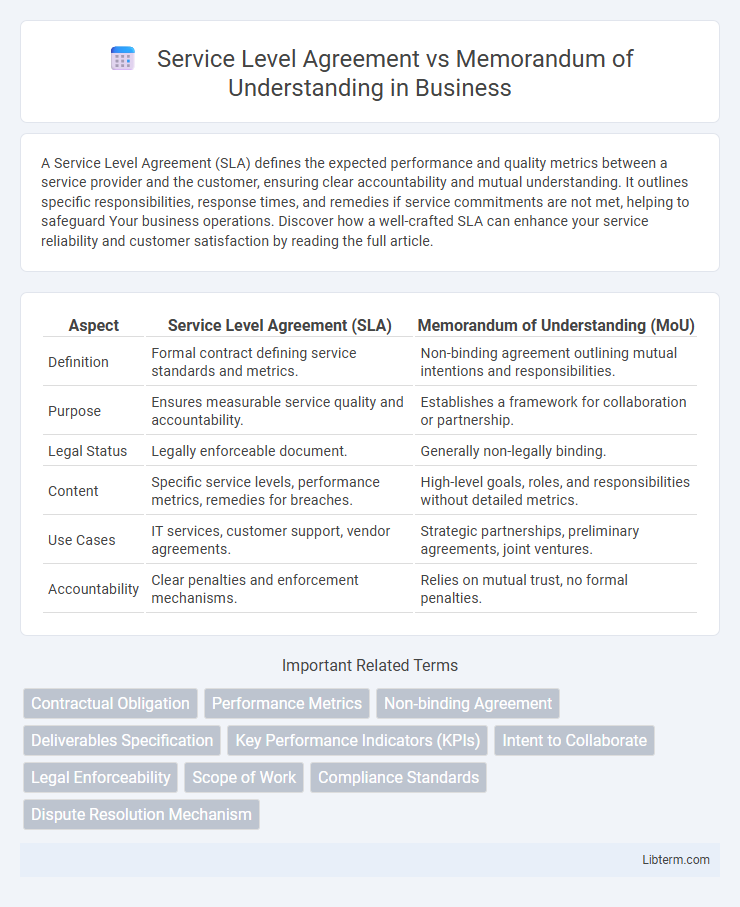
| Aspect | Service Level Agreement (SLA) | Memorandum of Understanding (MoU) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Formal contract defining service standards and metrics. | Non-binding agreement outlining mutual intentions and responsibilities. |
| Purpose | Ensures measurable service quality and accountability. | Establishes a framework for collaboration or partnership. |
| Legal Status | Legally enforceable document. | Generally non-legally binding. |
| Content | Specific service levels, performance metrics, remedies for breaches. | High-level goals, roles, and responsibilities without detailed metrics. |
| Use Cases | IT services, customer support, vendor agreements. | Strategic partnerships, preliminary agreements, joint ventures. |
| Accountability | Clear penalties and enforcement mechanisms. | Relies on mutual trust, no formal penalties. |
Introduction to Service Level Agreements and Memoranda of Understanding
Service Level Agreements (SLAs) define specific performance metrics and responsibilities between service providers and clients, ensuring measurable standards for service quality and delivery. Memoranda of Understanding (MOUs) outline the terms of cooperation and intentions between parties without legally binding obligations. Both SLAs and MOUs establish foundational agreements, with SLAs focusing on operational performance and MOUs emphasizing collaboration frameworks.
Defining Service Level Agreements (SLAs)
Service Level Agreements (SLAs) establish specific, measurable criteria for the performance and quality of services between providers and clients, focusing on key metrics such as uptime, response time, and resolution deadlines. Unlike Memoranda of Understanding (MOUs), which outline general intentions without binding obligations, SLAs create legally enforceable commitments to achieve agreed service standards. Clear SLA definitions enhance accountability and ensure both parties have a mutual understanding of service expectations and consequences for non-compliance.
Understanding Memoranda of Understanding (MOUs)
Memoranda of Understanding (MOUs) establish a clear framework outlining the mutual intentions and responsibilities between parties without creating legally binding obligations, serving as a foundation for future agreements. MOUs typically define the scope, objectives, and roles to facilitate collaboration and ensure aligned expectations prior to formal contract development. Unlike Service Level Agreements (SLAs), MOUs emphasize partnership and strategic intent rather than specific performance metrics or penalties.
Key Differences Between SLA and MOU
Service Level Agreements (SLAs) define specific performance metrics, responsibilities, and penalties for service delivery, ensuring accountability and measurable outcomes between parties. Memorandums of Understanding (MOUs) outline general terms of cooperation and shared intentions without binding obligations or detailed performance criteria. SLAs are legally binding contracts emphasizing enforceability and service standards, while MOUs serve as formal but non-binding agreements focused on mutual understanding and collaboration.
When to Use an SLA vs. an MOU
A Service Level Agreement (SLA) is best used when defining specific performance metrics, responsibilities, and service expectations between service providers and clients, ensuring measurable accountability. A Memorandum of Understanding (MOU) is appropriate for establishing a formal, but non-binding, agreement outlining general terms and shared intentions between parties in collaborative or preliminary partnerships. Choose an SLA for operational clarity and enforceability, while selecting an MOU for early-stage agreements or when legal obligations are not yet required.
Essential Components of an SLA
Essential components of a Service Level Agreement (SLA) include clearly defined service scope, performance metrics, and responsibilities of each party to ensure accountability. SLAs specify measurable targets such as uptime guarantees, response times, and resolution deadlines to maintain service quality. Unlike a Memorandum of Understanding (MOU), which outlines general intentions, an SLA provides detailed, enforceable provisions for service delivery and penalties for non-compliance.
Core Elements of an MOU
A Memorandum of Understanding (MOU) outlines the shared goals, responsibilities, and expectations between parties without legally binding obligations, focusing on mutual intent and cooperation. Core elements of an MOU include the purpose of the agreement, roles and responsibilities of each party, terms of collaboration, duration, and provisions for monitoring progress and resolving disputes. Unlike a Service Level Agreement (SLA), which defines specific performance metrics and penalties, an MOU emphasizes consensus and foundational understanding between organizations.
Legal Implications: SLA vs MOU
Service Level Agreements (SLAs) are legally binding contracts that define specific performance metrics, obligations, and penalties enforceable by law, ensuring accountability between parties. Memorandums of Understanding (MOUs) usually serve as non-binding agreements that outline mutual intentions and general terms without legal enforceability. The legal implications of SLAs involve clear remedies for breaches, whereas MOUs focus on collaboration and intent with limited legal consequences.
Benefits and Limitations of Each Agreement
A Service Level Agreement (SLA) clearly defines measurable performance standards and responsibilities, ensuring accountability and consistent service delivery but may lack flexibility in dynamic business environments. A Memorandum of Understanding (MOU) outlines general terms and mutual intentions, fostering collaboration and understanding without legally binding obligations, which can limit enforceability and clarity. SLAs benefit organizations needing strict compliance and performance metrics, while MOUs suit partnerships requiring flexibility and informal agreements.
Choosing the Right Agreement for Your Business Needs
Service Level Agreements (SLAs) define specific performance metrics and responsibilities between service providers and clients to ensure measurable service quality, while Memorandums of Understanding (MOUs) establish general terms of cooperation without legally binding obligations. Choosing the right agreement depends on the criticality of service delivery, desired accountability, and the level of formality required for business relationships. SLA suits businesses needing clear, enforceable service standards, whereas MOU is ideal for outlining collaborative intentions or preliminary partnerships.
Service Level Agreement Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com