A Non-Disclosure Agreement (NDA) is a legal contract that safeguards confidential information shared between parties, ensuring it remains private and protected from unauthorized disclosure. NDAs are crucial in business transactions, collaborations, or employment to maintain trust and secure sensitive data. Explore the full article to understand how an NDA can protect your interests and when to implement one.
Table of Comparison
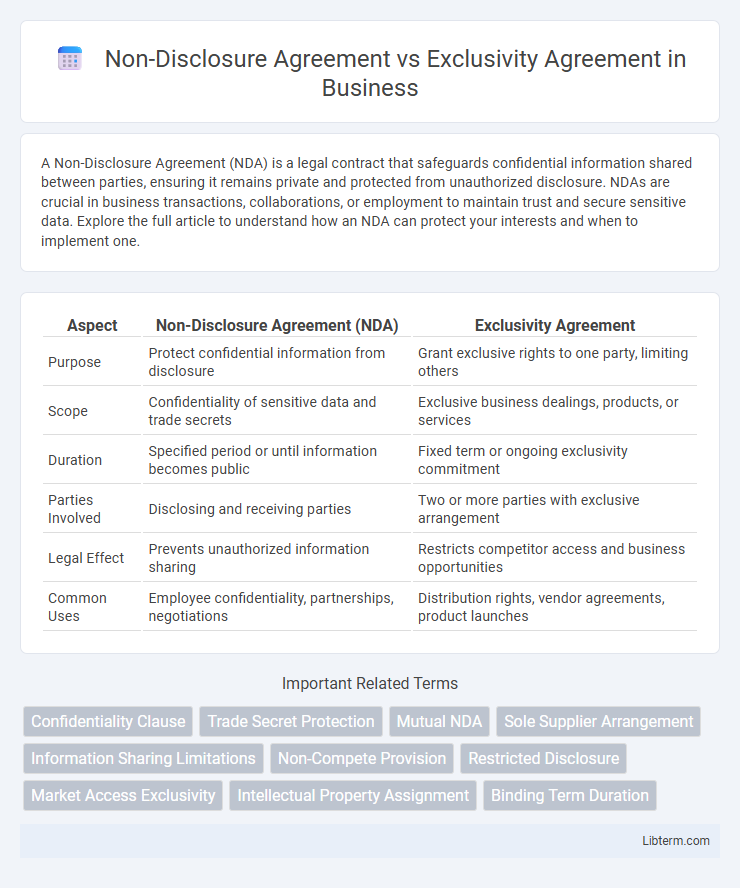
| Aspect | Non-Disclosure Agreement (NDA) | Exclusivity Agreement |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Protect confidential information from disclosure | Grant exclusive rights to one party, limiting others |
| Scope | Confidentiality of sensitive data and trade secrets | Exclusive business dealings, products, or services |
| Duration | Specified period or until information becomes public | Fixed term or ongoing exclusivity commitment |
| Parties Involved | Disclosing and receiving parties | Two or more parties with exclusive arrangement |
| Legal Effect | Prevents unauthorized information sharing | Restricts competitor access and business opportunities |
| Common Uses | Employee confidentiality, partnerships, negotiations | Distribution rights, vendor agreements, product launches |
Understanding Non-Disclosure Agreements (NDAs)
Non-Disclosure Agreements (NDAs) are legal contracts designed to protect confidential information shared between parties during business dealings or collaborations. NDAs restrict recipients from disclosing or using proprietary data, trade secrets, or sensitive material without authorization. These agreements enhance trust and safeguard intellectual property, ensuring that private information remains secure throughout negotiations or partnerships.
What is an Exclusivity Agreement?
An Exclusivity Agreement is a legally binding contract where one party agrees to purchase exclusively from another or to sell exclusively to them, ensuring that no competitive transactions occur during the agreement period. This type of agreement protects business relationships by preventing partners from engaging with competitors, thereby securing market share or supply chain stability. Unlike a Non-Disclosure Agreement (NDA), which primarily safeguards confidential information, an Exclusivity Agreement establishes a commitment to restrict business dealings within an agreed scope.
Key Differences Between NDAs and Exclusivity Agreements
Non-Disclosure Agreements (NDAs) primarily protect confidential information shared between parties by legally preventing unauthorized disclosure, while Exclusivity Agreements restrict parties from engaging with competitors or other entities during a specified period. NDAs focus on safeguarding sensitive data, trade secrets, or proprietary knowledge, whereas Exclusivity Agreements emphasize restricting business relationships to maintain competitive advantage. The enforceability of NDAs centers on information confidentiality, whereas Exclusivity Agreements hinge on limiting market competition and exclusive dealings.
Core Purposes: Protecting Information vs Limiting Partnerships
A Non-Disclosure Agreement (NDA) primarily safeguards confidential information by legally preventing parties from sharing sensitive data outside the agreed terms. In contrast, an Exclusivity Agreement restricts business partnerships or dealings by ensuring one party receives exclusive rights to collaborate or sell within a defined scope or market. While NDAs focus on information protection, Exclusivity Agreements emphasize limiting competitors and controlling partnership opportunities.
Typical Clauses Found in NDAs
Non-Disclosure Agreements (NDAs) typically include clauses covering the definition of confidential information, obligations of the receiving party, duration of confidentiality, and exceptions to disclosure. These agreements often specify the permitted use of confidential information and remedies for breach, such as injunctive relief or damages. In contrast, Exclusivity Agreements focus more on restrictions related to business relationships or sales territories rather than information confidentiality.
Common Provisions in Exclusivity Agreements
Exclusivity agreements commonly include provisions such as the duration of exclusivity, specifying the time period during which the parties agree to limit or fully restrict transactions with others, and territorial scope, defining the geographic boundaries of the exclusivity. They often outline the scope of exclusivity to clarify the specific products, services, or business activities covered by the agreement, and include remedies or penalties for breach of exclusivity to incentivize compliance. Confidentiality clauses may also be present, overlapping with non-disclosure agreements by protecting sensitive information shared during the exclusive arrangement.
When to Use an NDA vs an Exclusivity Agreement
Use a Non-Disclosure Agreement (NDA) when protecting confidential information during initial business discussions, ensuring that sensitive data such as trade secrets and proprietary details remain private. An Exclusivity Agreement is appropriate when one party requires exclusive rights to negotiate or enter into a partnership, preventing the other party from engaging with competitors for a specified period. NDAs mainly safeguard information confidentiality, while Exclusivity Agreements secure a commitment to limit negotiations or sales to a single party.
Legal Implications of Breaching NDAs and Exclusivity Agreements
Breaching a Non-Disclosure Agreement (NDA) typically results in legal consequences such as injunctions to prevent further disclosure, monetary damages for losses incurred, and potential punitive damages in cases of willful misconduct. Violating an Exclusivity Agreement can lead to breach of contract claims, including compensatory damages for lost profits and specific performance orders to enforce exclusivity terms. Courts assess the scope, duration, and legitimate business interests protected by these agreements when determining remedies and enforcing legal obligations.
Combining NDAs and Exclusivity Agreements in Business Deals
Combining Non-Disclosure Agreements (NDAs) and Exclusivity Agreements in business deals enhances protection by safeguarding confidential information while restricting parties from engaging with competitors or third parties. This strategic combination ensures proprietary data remains confidential and business relationships maintain competitive advantage during negotiations. Effective integration of these agreements requires clear definitions of scope, duration, and obligations to minimize risks and foster trust between involved parties.
Choosing the Right Agreement for Your Business Needs
Choosing the right agreement for your business needs involves understanding the core purpose of a Non-Disclosure Agreement (NDA) versus an Exclusivity Agreement. An NDA is essential for protecting sensitive information and trade secrets during collaborations, while an Exclusivity Agreement restricts parties from engaging with competitors or offering similar services, thereby securing market advantages. Evaluate your business priorities, such as confidentiality versus competitive control, to select the agreement that aligns with your strategic goals and risk management.
Non-Disclosure Agreement Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com