Stock options provide a powerful way for employees to participate in a company's growth by granting the right to purchase shares at a predetermined price, aligning personal success with corporate performance. Understanding how stock options work, including vesting periods and tax implications, is crucial for maximizing their financial benefits. Explore the full article to discover how stock options can enhance your investment strategy and future wealth.
Table of Comparison
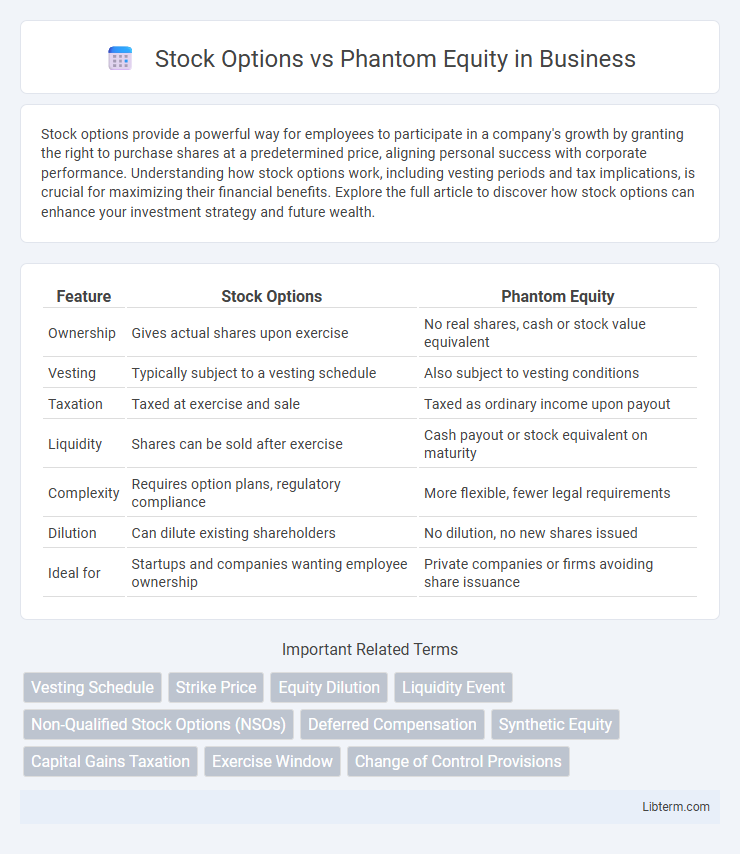
| Feature | Stock Options | Phantom Equity |
|---|---|---|
| Ownership | Gives actual shares upon exercise | No real shares, cash or stock value equivalent |
| Vesting | Typically subject to a vesting schedule | Also subject to vesting conditions |
| Taxation | Taxed at exercise and sale | Taxed as ordinary income upon payout |
| Liquidity | Shares can be sold after exercise | Cash payout or stock equivalent on maturity |
| Complexity | Requires option plans, regulatory compliance | More flexible, fewer legal requirements |
| Dilution | Can dilute existing shareholders | No dilution, no new shares issued |
| Ideal for | Startups and companies wanting employee ownership | Private companies or firms avoiding share issuance |
Introduction to Stock Options and Phantom Equity
Stock options grant employees the right to purchase company shares at a predetermined price, incentivizing ownership and aligning interests with company growth. Phantom equity provides employees with cash bonuses tied to the value of company shares without transferring actual stock ownership. Both serve as effective equity compensation tools, with stock options offering potential capital gains and phantom equity delivering value linked to share appreciation without equity dilution.
Key Differences Between Stock Options and Phantom Equity
Stock options grant employees the right to purchase company shares at a set price, creating potential equity ownership and alignment with shareholder interests. Phantom equity provides cash bonuses tied to the company's stock value without actual share issuance, thus avoiding dilution of ownership. Unlike stock options, phantom equity does not confer voting rights or dividends, focusing solely on financial rewards linked to company performance.
How Stock Options Work
Stock options grant employees the right to purchase company shares at a predetermined price, known as the exercise or strike price, after a vesting period. When the stock price exceeds the exercise price, employees can buy shares at the lower price and potentially sell at a profit, realizing financial gain. This incentive aligns employee interests with company performance but requires stock price appreciation to be valuable.
Understanding Phantom Equity Plans
Phantom equity plans provide employees with benefits similar to stock options without granting actual shares, offering value tied to company performance or stock price appreciation. These plans create synthetic equity stakes that pay out cash or equivalent benefits based on the company's valuation at a liquidity event, such as a sale or IPO. Understanding phantom equity involves recognizing its role in aligning employee incentives with company growth while avoiding dilution of ownership and complexities of share issuance.
Tax Implications for Employees
Stock options often trigger taxable events when exercised, with employees taxed on the difference between the exercise price and the fair market value as ordinary income, followed by capital gains tax on any subsequent sale. Phantom equity typically results in ordinary income tax at payout, as employees receive cash or shares equivalent to the company's value increase without actual stock ownership or exercise requirements. Understanding the timing and type of taxation is crucial for employees to optimize after-tax compensation when choosing between stock options and phantom equity plans.
Employer Considerations: Pros and Cons
Stock options offer employers the advantage of aligning employee incentives with company stock performance, motivating long-term value creation, but they may dilute equity and involve complex regulatory compliance. Phantom equity provides a flexible, non-dilutive alternative that mimics stock ownership benefits without transferring actual shares, reducing administrative burden and preserving shareholder control. However, phantom equity can create future cash flow obligations and may lack the same motivational impact as genuine stock options for employees.
Vesting Schedules and Liquidity Events
Vesting schedules for stock options typically require employees to earn their shares over a defined period, often four years with a one-year cliff, ensuring gradual ownership accumulation. Phantom equity grants mimic this structure but provide cash or stock value during liquidity events without transferring actual shares, offering flexibility in private companies. Liquidity events like IPOs or acquisitions trigger the realization of stock options or phantom equity, but phantom equity holders receive payouts based on company valuation without needing to exercise options.
Impact on Company Ownership and Dilution
Stock options grant employees actual equity, resulting in ownership dilution as new shares are issued upon exercise, directly affecting company ownership percentages. Phantom equity provides value linked to company stock without issuing real shares, preserving ownership structure and avoiding dilution. Companies favor phantom equity when maintaining control and minimizing shareholder dilution is a priority.
Best Use Cases for Each Incentive
Stock options are best suited for startups aiming to attract and retain employees by offering potential ownership that aligns with company growth and future valuation increases. Phantom equity works well for established private companies that want to provide equity-like benefits without diluting ownership or dealing with complex equity issuance. Use stock options when employee motivation through actual equity stake is crucial, while phantom equity fits scenarios requiring cash-based rewards tied to company performance without granting real shares.
Choosing the Right Equity Plan for Your Organization
Evaluating Stock Options versus Phantom Equity requires understanding your organization's valuation method, employee incentives, and liquidity preferences. Stock options offer actual equity ownership with potential capital gains, ideal for startups aiming to align employee interests with company growth. Phantom equity provides cash-based rewards mimicking stock value, suitable for firms seeking to avoid equity dilution while motivating employees through long-term performance.
Stock Options Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com