Brand diversification expands your business by introducing new products or entering different markets, enhancing growth opportunities and reducing risks from market fluctuations. Effective strategies incorporate market research, understanding customer needs, and leveraging existing brand reputation to ensure successful expansions. Discover practical tips and examples in the rest of this article to guide your brand diversification journey.
Table of Comparison
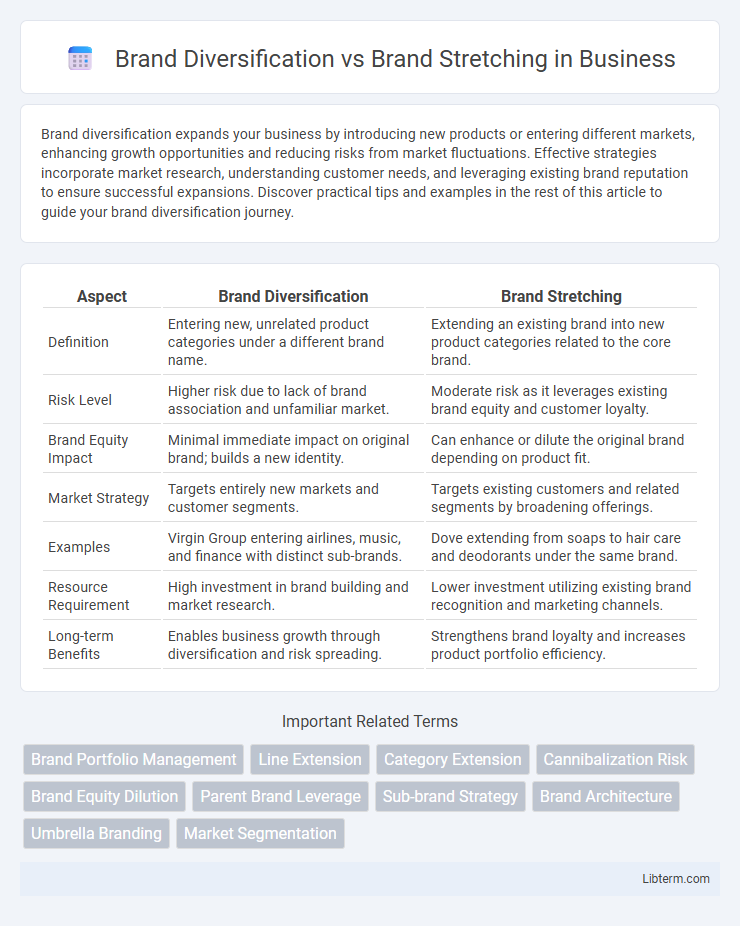
| Aspect | Brand Diversification | Brand Stretching |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Entering new, unrelated product categories under a different brand name. | Extending an existing brand into new product categories related to the core brand. |
| Risk Level | Higher risk due to lack of brand association and unfamiliar market. | Moderate risk as it leverages existing brand equity and customer loyalty. |
| Brand Equity Impact | Minimal immediate impact on original brand; builds a new identity. | Can enhance or dilute the original brand depending on product fit. |
| Market Strategy | Targets entirely new markets and customer segments. | Targets existing customers and related segments by broadening offerings. |
| Examples | Virgin Group entering airlines, music, and finance with distinct sub-brands. | Dove extending from soaps to hair care and deodorants under the same brand. |
| Resource Requirement | High investment in brand building and market research. | Lower investment utilizing existing brand recognition and marketing channels. |
| Long-term Benefits | Enables business growth through diversification and risk spreading. | Strengthens brand loyalty and increases product portfolio efficiency. |
Understanding Brand Diversification
Brand diversification involves creating or acquiring new brands to enter different markets or product categories, minimizing risk by spreading business interests across unrelated sectors. It enhances market reach and customer segments by leveraging distinct brand identities that cater to specific consumer needs without diluting the original brand equity. Companies use brand diversification to achieve sustainable growth, balance revenue streams, and adapt to changing market dynamics effectively.
Defining Brand Stretching
Brand stretching refers to leveraging an established brand name to enter a different product category, aiming to capitalize on existing brand equity and consumer trust. This strategy differs from brand diversification, which involves creating entirely new brands or sub-brands for various product lines to target distinct market segments. Successful brand stretching requires careful alignment between the original brand's identity and the new product category to prevent brand dilution and maintain credibility.
Key Differences Between Brand Diversification and Stretching
Brand diversification involves expanding a company's portfolio by introducing new brands in different product categories to target distinct markets, whereas brand stretching leverages an existing brand name to launch products in new categories. Diversification reduces risk by spreading investments across unrelated markets, while stretching capitalizes on brand equity to quickly gain consumer acceptance in adjacent or unrelated segments. Brand diversification typically requires separate marketing strategies for each brand, whereas brand stretching relies on the strength and recognition of the parent brand for cross-category success.
Advantages of Brand Diversification
Brand diversification enhances market presence by allowing companies to enter multiple product categories, reducing dependency on a single market and mitigating risks associated with market fluctuations. It fosters innovation and caters to diverse consumer needs, driving revenue growth through varied income streams. This strategy also strengthens brand equity by building a broad portfolio that appeals to different customer segments, increasing overall brand resilience.
Benefits of Brand Stretching
Brand stretching enables companies to leverage existing brand equity to enter new product categories, reducing marketing costs and enhancing consumer trust. It facilitates faster market acceptance and increases revenue streams by capitalizing on established brand recognition. This strategy also allows businesses to test innovative products with lower risk due to the credibility of the parent brand.
Risks Associated with Both Strategies
Brand diversification carries the risk of overextending resources and diluting the core brand identity, potentially confusing customers and weakening overall brand equity. Brand stretching can lead to consumer skepticism if the new product category lacks relevance or credibility, damaging the brand's trust and reputation. Both strategies risk cannibalizing existing markets and failing to meet consumer expectations, which can result in financial losses and reduced brand loyalty.
Real-World Examples: Successes and Failures
Brand diversification often leads to success when companies like Apple expand into new product categories, such as wearables and services, leveraging strong brand equity to capture new markets. In contrast, brand stretching can fail when brands like Colgate attempt to enter unrelated sectors like frozen food, diluting brand identity and confusing consumers. Successful examples highlight strategic alignment with core brand values, while failures emphasize the risks of overextending beyond consumer expectations.
Factors to Consider Before Choosing a Strategy
When choosing between brand diversification and brand stretching, companies must evaluate market compatibility, consumer perception, and resource allocation. Brand diversification requires entering distinct markets leveraging separate identities, which demands significant investment and risk assessment. Brand stretching depends on the strength and relevance of the existing brand equity to avoid brand dilution and maintain customer trust.
How to Execute Effective Brand Stretching or Diversification
Effective brand stretching requires thorough market research to ensure alignment between the new product category and the core brand values, minimizing consumer confusion. Successful brand diversification involves leveraging existing brand equity while creating distinct brand identities to cater to different target audiences. Consistent messaging, quality control, and strategic marketing campaigns are crucial to maintain brand integrity and build customer trust across diversified offerings.
Future Trends in Brand Expansion Strategies
Brand diversification and brand stretching will increasingly leverage digital technologies and data analytics to tailor personalized consumer experiences and identify emerging market segments. Future trends emphasize sustainable and ethical brand extensions that resonate with socially conscious customers while minimizing brand dilution risks. Companies will prioritize agile brand architectures to quickly adapt to shifting consumer preferences and global market dynamics.
Brand Diversification Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com