Vertical integration enhances control over the supply chain by combining multiple stages of production within a single company, resulting in reduced costs and improved efficiency. This strategy allows businesses to better manage quality, streamline operations, and respond swiftly to market changes. Discover how vertical integration can transform Your company's competitive edge by reading the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
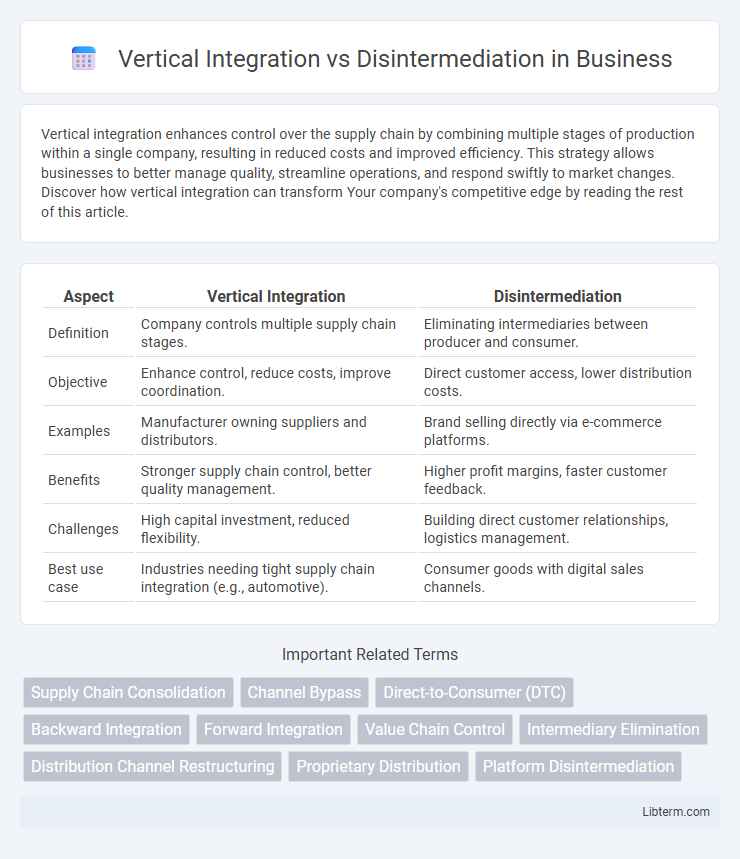
| Aspect | Vertical Integration | Disintermediation |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Company controls multiple supply chain stages. | Eliminating intermediaries between producer and consumer. |
| Objective | Enhance control, reduce costs, improve coordination. | Direct customer access, lower distribution costs. |
| Examples | Manufacturer owning suppliers and distributors. | Brand selling directly via e-commerce platforms. |
| Benefits | Stronger supply chain control, better quality management. | Higher profit margins, faster customer feedback. |
| Challenges | High capital investment, reduced flexibility. | Building direct customer relationships, logistics management. |
| Best use case | Industries needing tight supply chain integration (e.g., automotive). | Consumer goods with digital sales channels. |
Understanding Vertical Integration
Vertical integration refers to a company's ownership and control over multiple stages of its supply chain, from raw materials to final product distribution, enhancing operational efficiency and reducing dependency on external suppliers. This strategy allows businesses to improve quality control, streamline production processes, and capture greater profit margins by internalizing activities traditionally performed by third parties. Vertical integration contrasts with disintermediation, where companies remove intermediaries to deal directly with customers, prioritizing streamlined sales channels over supply chain ownership.
Defining Disintermediation
Disintermediation refers to the removal of intermediaries in the supply chain, allowing producers to sell directly to consumers, thereby reducing costs and improving efficiency. This strategy contrasts with vertical integration, where a company controls multiple stages of production or distribution internally. Disintermediation leverages digital platforms and technology to streamline operations and enhance customer interactions.
Key Differences Between Vertical Integration and Disintermediation
Vertical integration involves a company expanding its control over multiple stages of production or distribution within its supply chain, while disintermediation eliminates intermediaries to connect producers directly with consumers. Vertical integration typically increases operational control and reduces dependency on suppliers, enhancing efficiency through internal resource coordination. Disintermediation focuses on cutting costs and streamlining transactions by removing middlemen, often driven by digital platforms that enable direct sales and communication.
Historical Evolution of Business Structures
Vertical integration emerged prominently during the late 19th and early 20th centuries as companies like Carnegie Steel sought to control all production stages, optimizing efficiency and reducing costs. Disintermediation gained traction with the rise of digital technology in the late 20th century, enabling businesses to bypass traditional intermediaries and directly connect with consumers. The historical evolution from vertical integration to disintermediation reflects shifting priorities from consolidation of supply chains to leveraging technology for direct market access.
Strategic Benefits of Vertical Integration
Vertical integration enhances supply chain control, reducing costs and improving quality by streamlining production and distribution processes. Companies gain competitive advantages through increased market power, better coordination, and faster response to market changes. This strategic approach strengthens brand loyalty and drives innovation by aligning all stages of the value chain under one management.
Advantages of Disintermediation in Modern Markets
Disintermediation reduces costs by eliminating intermediaries, allowing companies to connect directly with customers and increase profit margins. It enhances transparency and speed in transactions, improving customer experience and satisfaction in fast-paced modern markets. Direct access to consumer data enables businesses to tailor products and marketing strategies effectively, fostering innovation and competitive advantage.
Risks and Challenges of Each Approach
Vertical integration faces risks such as high capital investment, reduced flexibility, and potential inefficiencies from managing diverse operations internally. Disintermediation challenges include loss of expert intermediaries, increased complexity in direct customer management, and heightened exposure to market fluctuations. Both approaches require strategic risk assessment to balance control benefits against operational and financial vulnerabilities.
Real-World Case Studies
Vertical integration in companies like Apple demonstrates control over supply chains and product distribution, enhancing efficiency and brand consistency. Disintermediation is evident in platforms like Airbnb, which eliminate traditional intermediaries in hospitality, directly connecting service providers with customers. These strategic approaches significantly affect market dynamics, operational costs, and customer experience across industries.
Impact on Supply Chain Efficiency
Vertical integration streamlines supply chain efficiency by consolidating production stages, reducing dependency on external suppliers, and enhancing coordination and control over inventory and logistics. Disintermediation eliminates intermediaries, directly connecting manufacturers with consumers, which accelerates product flow, reduces costs, and improves responsiveness to market demand. Both strategies optimize supply chain performance but differ in their approach to control and distribution channels.
Choosing the Right Strategy for Your Business
Choosing the right strategy between vertical integration and disintermediation depends on your business goals, operational capabilities, and market dynamics. Vertical integration enhances control over the supply chain and can reduce costs by consolidating production stages, while disintermediation removes intermediaries to improve profit margins and strengthen direct customer relationships. Assessing factors such as resource availability, industry competition, and customer demand patterns is crucial for selecting the most effective approach to optimize efficiency and growth.
Vertical Integration Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com