Business-to-Employee (B2E) strategies focus on enhancing employee engagement, productivity, and satisfaction through targeted communication and technology solutions within an organization. These initiatives often include internal portals, training programs, and personalized services designed to meet Your professional needs. Explore the rest of this article to discover how B2E approaches can transform your workplace experience.
Table of Comparison
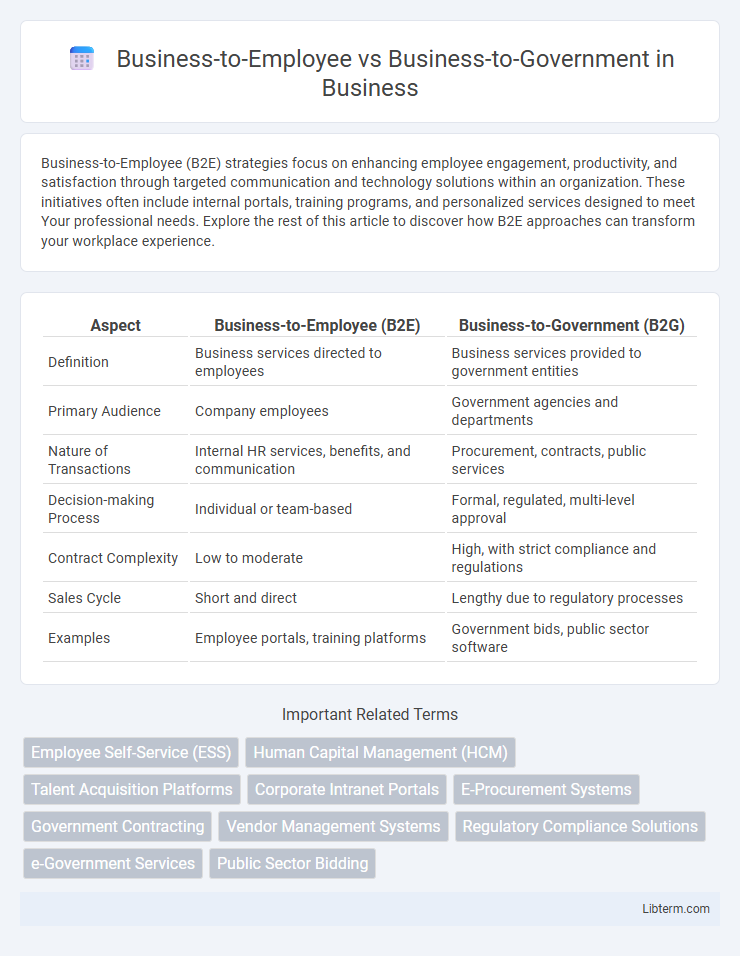
| Aspect | Business-to-Employee (B2E) | Business-to-Government (B2G) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Business services directed to employees | Business services provided to government entities |
| Primary Audience | Company employees | Government agencies and departments |
| Nature of Transactions | Internal HR services, benefits, and communication | Procurement, contracts, public services |
| Decision-making Process | Individual or team-based | Formal, regulated, multi-level approval |
| Contract Complexity | Low to moderate | High, with strict compliance and regulations |
| Sales Cycle | Short and direct | Lengthy due to regulatory processes |
| Examples | Employee portals, training platforms | Government bids, public sector software |
Understanding Business-to-Employee (B2E) and Business-to-Government (B2G) Models
Business-to-Employee (B2E) models emphasize internal organizational interactions, enhancing employee engagement and productivity through tailored services, intranets, and HR portals. Business-to-Government (B2G) models focus on transactions between businesses and government agencies, involving compliance, public procurement, and regulatory communications. Understanding these models highlights B2E's role in workforce optimization and B2G's importance in navigating government contracts and statutory requirements.
Core Objectives of B2E vs B2G Strategies
Business-to-Employee (B2E) strategies focus on enhancing employee engagement, productivity, and satisfaction through internal services and digital tools tailored for workforce needs. Business-to-Government (B2G) strategies prioritize compliance, transparent procurement processes, and regulatory alignment to establish strong partnerships with public sector entities. While B2E centers on optimizing human resource value and company culture, B2G targets efficient contract management and adherence to government policies.
Key Stakeholders in B2E and B2G Relationships
Key stakeholders in Business-to-Employee (B2E) relationships primarily include company employees, HR departments, and internal communication teams, focusing on enhancing employee engagement and productivity. In contrast, Business-to-Government (B2G) stakeholders encompass government agencies, regulatory bodies, and compliance officers, emphasizing adherence to regulations, contract management, and public sector procurement processes. Understanding these distinct groups is crucial for tailoring communication and operational strategies effectively within each relationship type.
Differences in Procurement and Engagement Processes
Business-to-Employee (B2E) procurement focuses on streamlining internal processes to enhance employee services, often involving digital platforms for ease of access and personalized solutions. In contrast, Business-to-Government (B2G) procurement is characterized by strict regulatory compliance, transparent bidding procedures, and lengthy contract evaluations to meet public sector standards. Engagement in B2E emphasizes user experience and satisfaction within a company, whereas B2G demands formal interactions, adherence to legal frameworks, and accountability to public stakeholders.
Technology Integration: B2E vs B2G Approaches
Business-to-Employee (B2E) technology integration centers on enhancing internal workflows, utilizing platforms like intranets, employee self-service portals, and collaboration tools to boost productivity and engagement. In contrast, Business-to-Government (B2G) solutions prioritize compliance, secure data exchange, and interoperability with government systems through standardized APIs, e-procurement platforms, and regulatory reporting software. Effective B2E approaches leverage cloud-based enterprise resource planning (ERP) and Human Resource Management Systems (HRMS), while B2G strategies focus on government-specific technologies such as electronic tendering systems and digital identity verification frameworks.
Regulatory and Compliance Considerations
Business-to-Employee (B2E) models prioritize compliance with labor laws, data privacy regulations, and internal policies to protect employee information and ensure fair workplace practices. Business-to-Government (B2G) transactions involve stringent adherence to government procurement rules, regulatory frameworks, and transparency standards, often requiring certifications and audits. Understanding sector-specific regulatory requirements is critical for organizations to avoid penalties and build trust in both B2E and B2G environments.
Benefits and Challenges of B2E Strategies
Business-to-Employee (B2E) strategies enhance internal communication, boost employee engagement, and streamline HR processes through personalized digital platforms. These initiatives face challenges such as ensuring data security, maintaining employee privacy, and fostering user adoption across diverse workforce demographics. In contrast, Business-to-Government (B2G) interactions prioritize regulatory compliance, transparent procurement processes, and relationship management, but encounter hurdles including complex bureaucratic protocols, lengthy contract cycles, and stringent reporting requirements.
Advantages and Obstacles in B2G Partnerships
Business-to-Government (B2G) partnerships offer significant advantages such as access to large, stable contracts and opportunities for long-term collaboration with public sector entities, driving consistent revenue streams. However, B2G engagements face obstacles including complex regulatory compliance, extended procurement cycles, and stringent bidding processes that require specialized expertise. In contrast, Business-to-Employee (B2E) strategies enhance workforce productivity and employee engagement through tailored solutions but often encounter challenges in scalability and integrating diverse employee needs within organizational frameworks.
Measuring Success in B2E and B2G Initiatives
Measuring success in Business-to-Employee (B2E) initiatives often revolves around employee engagement metrics, productivity improvements, and satisfaction surveys that reflect workforce commitment and retention rates. In contrast, Business-to-Government (B2G) success hinges on compliance with regulatory requirements, contract acquisition rates, and the efficiency of public service delivery as demonstrated through key performance indicators (KPIs) aligned with government standards. Both B2E and B2G sectors require tailored analytics to evaluate return on investment (ROI) and alignment with organizational goals for sustainable growth.
Future Trends and Innovations in B2E and B2G Models
Emerging technologies such as AI-driven analytics and blockchain are reshaping Business-to-Employee (B2E) platforms by enhancing personalized employee experiences and streamlining HR processes. In Business-to-Government (B2G) models, innovations like smart contracts and secure digital identity solutions are driving more transparent, efficient public service delivery and regulatory compliance. Both sectors increasingly leverage cloud-based ecosystems and Internet of Things (IoT) integration to foster real-time data exchange and automation, paving the way for more agile and responsive organizational frameworks.
Business-to-Employee Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com