Philanthropy plays a crucial role in addressing social challenges by funding education, healthcare, and community development. Effective giving strategies ensure that your contributions create lasting impact and empower beneficiaries. Explore the rest of the article to discover how your philanthropy can drive meaningful change.
Table of Comparison
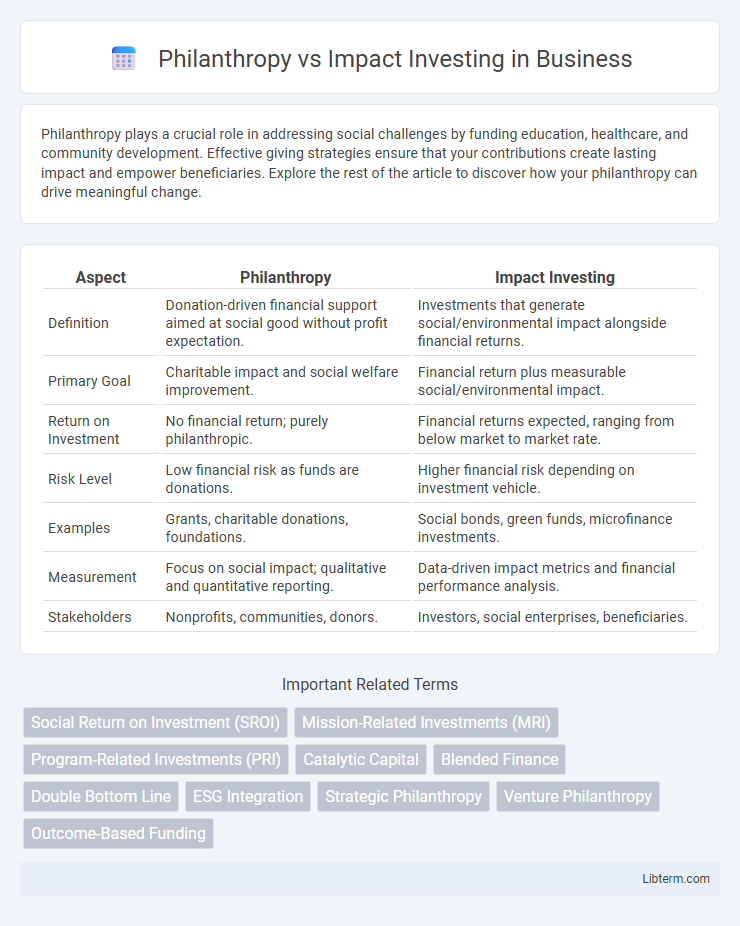
| Aspect | Philanthropy | Impact Investing |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Donation-driven financial support aimed at social good without profit expectation. | Investments that generate social/environmental impact alongside financial returns. |
| Primary Goal | Charitable impact and social welfare improvement. | Financial return plus measurable social/environmental impact. |
| Return on Investment | No financial return; purely philanthropic. | Financial returns expected, ranging from below market to market rate. |
| Risk Level | Low financial risk as funds are donations. | Higher financial risk depending on investment vehicle. |
| Examples | Grants, charitable donations, foundations. | Social bonds, green funds, microfinance investments. |
| Measurement | Focus on social impact; qualitative and quantitative reporting. | Data-driven impact metrics and financial performance analysis. |
| Stakeholders | Nonprofits, communities, donors. | Investors, social enterprises, beneficiaries. |
Understanding Philanthropy: Definition and Goals
Philanthropy involves voluntarily donating resources such as money, time, or expertise to promote social welfare without seeking financial returns. Its primary goals include addressing immediate social needs, supporting charitable organizations, and advancing causes like education, health, and poverty alleviation. Unlike impact investing, philanthropy prioritizes maximizing social impact over generating measurable financial gains.
What is Impact Investing? Key Principles
Impact investing involves deploying capital to generate measurable social or environmental benefits alongside financial returns. Key principles include strategic intent to create positive change, intentionality in targeting specific social or environmental outcomes, and rigorous measurement to assess impact performance. Investors prioritize alignment of investment goals with sustainable development objectives and transparent reporting to ensure accountability.
Core Differences Between Philanthropy and Impact Investing
Philanthropy primarily involves donating funds or resources without expecting a financial return, focusing on social or environmental causes through grants and charitable contributions. Impact investing seeks measurable social or environmental benefits alongside financial returns by investing in businesses, organizations, or funds. The core difference lies in philanthropy's grant-based, non-reciprocal nature versus impact investing's market-driven approach aimed at sustainable impact and financial gains.
Measuring Success: Social Impact vs Financial Return
Philanthropy primarily measures success through social impact metrics such as community well-being, educational improvements, and poverty reduction, focusing on long-term positive change without emphasis on financial gains. Impact investing evaluates both social impact and financial return, using quantifiable indicators like return on investment (ROI) alongside social outcomes such as job creation, environmental sustainability, or health improvements. While philanthropy prioritizes altruistic goals and societal benefits, impact investing integrates financial performance with measurable social impact to attract investors seeking dual returns.
Funding Mechanisms and Financial Structures Compared
Philanthropy primarily utilizes grant-based funding mechanisms that do not require financial returns, focusing on charitable donations and foundation grants to support social causes. Impact investing employs investment vehicles such as equity, debt, or blended finance structures, aiming to generate measurable social or environmental outcomes alongside financial returns. While philanthropy relies on endowments, donations, and fundraising campaigns, impact investing leverages capital market instruments to attract investors seeking both impact and sustainable profits.
Types of Organizations Involved in Each Approach
Philanthropy primarily involves nonprofit organizations, charitable foundations, and individual donors focused on grant-making to support social causes without expecting financial returns. Impact investing engages a broader range of organizations, including social enterprises, mission-driven businesses, impact funds, and venture capital firms seeking both measurable social impact and financial returns. Many hybrid models and benefit corporations (B Corps) operate at the intersection, combining philanthropic goals with investment strategies to maximize social and economic outcomes.
Role of Accountability and Transparency
Philanthropy emphasizes accountability through donor reporting and transparency in fund allocation to ensure trust and ethical use of resources. Impact investing integrates financial returns with measurable social and environmental outcomes, requiring rigorous transparency frameworks and performance metrics. Both approaches depend on clear reporting standards to maintain stakeholder confidence and demonstrate real-world effectiveness.
Real-World Examples: Case Studies in Action
Philanthropy in practice includes examples like the Bill & Melinda Gates Foundation's efforts to combat infectious diseases through grants, targeting immediate social benefits without financial returns. Impact investing is exemplified by funds like the Acumen Fund, which deploys capital into sustainable businesses addressing poverty while generating financial returns. These approaches differ in structure but share a goal of social change, demonstrated by measurable outcomes such as increased access to healthcare or improved economic opportunities in underserved communities.
Challenges and Criticisms of Each Model
Philanthropy often faces criticism for lacking measurable returns and scalability, making long-term impact assessment challenging. Impact investing encounters difficulties in balancing financial returns with social outcomes, leading to potential conflicts between profit motives and mission goals. Both models struggle with transparency issues and the risk of unintended consequences that can undermine their effectiveness.
Choosing the Right Approach: Factors to Consider
Choosing the right approach between philanthropy and impact investing depends on factors such as desired financial returns, risk tolerance, and long-term social impact goals. Philanthropy typically involves grants or donations without expecting financial returns, ideal for addressing urgent social needs and supporting nonprofits. Impact investing targets measurable social and environmental outcomes alongside financial gains, suitable for investors seeking sustainable solutions with scalable impact.
Philanthropy Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com