A merger is a strategic business move where two companies combine to form a single entity, enhancing market share and operational efficiency. This process often involves complex negotiations, regulatory approvals, and integration of resources to maximize value. Explore the rest of the article to understand how a merger can impact your business growth and competitive advantage.
Table of Comparison
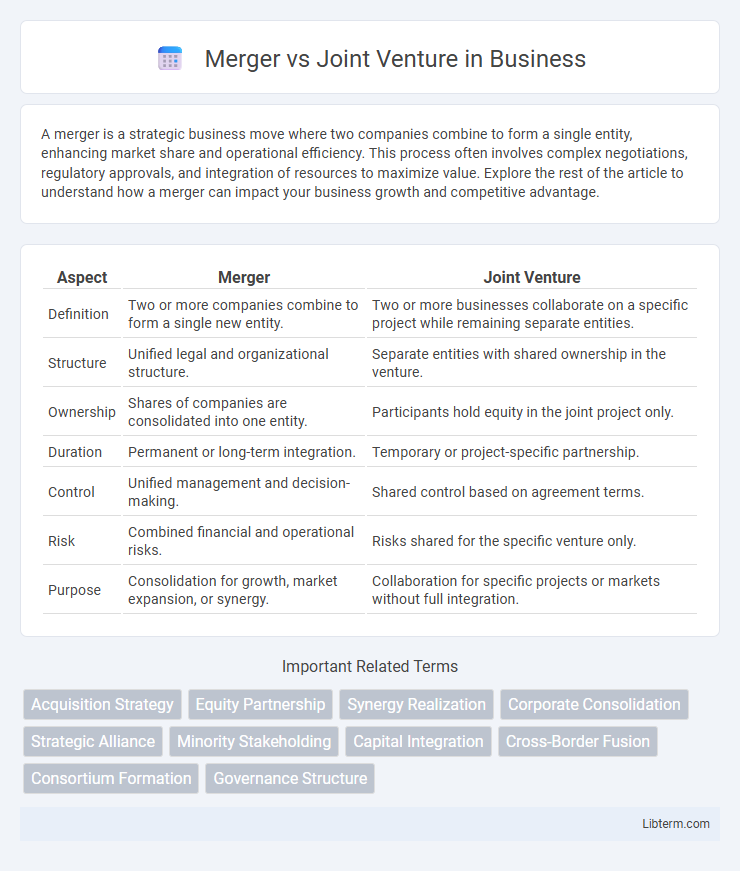
| Aspect | Merger | Joint Venture |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Two or more companies combine to form a single new entity. | Two or more businesses collaborate on a specific project while remaining separate entities. |
| Structure | Unified legal and organizational structure. | Separate entities with shared ownership in the venture. |
| Ownership | Shares of companies are consolidated into one entity. | Participants hold equity in the joint project only. |
| Duration | Permanent or long-term integration. | Temporary or project-specific partnership. |
| Control | Unified management and decision-making. | Shared control based on agreement terms. |
| Risk | Combined financial and operational risks. | Risks shared for the specific venture only. |
| Purpose | Consolidation for growth, market expansion, or synergy. | Collaboration for specific projects or markets without full integration. |
Introduction to Mergers and Joint Ventures
Mergers involve the combination of two companies into a single legal entity to achieve synergies, enhanced market share, and operational efficiencies. Joint ventures create a strategic alliance where two or more parties collaborate while remaining independent entities, sharing resources, risks, and profits for a specific project or business activity. Both structures facilitate growth and competitive advantage but differ significantly in integration and control mechanisms.
Definition of Merger
A merger is a legal consolidation where two or more companies combine to form a single new entity, with one company often surviving and the others ceasing to exist. This process unifies assets, liabilities, and operations under a single corporate structure, enabling increased market share and operational efficiency. Mergers differ from joint ventures, which involve collaboration without full integration or ownership consolidation.
Definition of Joint Venture
A joint venture is a strategic alliance where two or more parties agree to pool their resources for a specific project or business activity while maintaining their separate identities. Unlike a merger, which combines companies into a single entity, a joint venture creates a new, jointly-owned enterprise with shared risks and rewards. This arrangement enables partners to leverage complementary strengths without full integration or loss of autonomy.
Key Differences Between Merger and Joint Venture
A merger combines two companies into a single entity, resulting in unified ownership, management, and resources, while a joint venture is a collaborative agreement where two or more businesses retain their separate identities but work together on a specific project or business activity. Mergers typically lead to permanent integration and shared liabilities, whereas joint ventures are often temporary partnerships with defined scopes and limited liability exposure. Ownership transfer and corporate restructuring occur in mergers, contrasting with joint ventures' contractual alliances that maintain independent control of the partnering firms.
Advantages of Mergers
Mergers offer significant advantages such as increased market share, enhanced operational efficiency through resource consolidation, and improved financial strength that facilitates better access to capital. Combining assets and expertise enables companies to achieve economies of scale and reduce competition in their industry. This strategic move often results in stronger brand presence and greater innovation capacity compared to joint ventures.
Advantages of Joint Ventures
Joint ventures enable companies to combine resources and expertise while maintaining their individual identities, fostering innovation and flexibility in project execution. They offer shared financial risk and access to new markets without the complexities of full mergers, making them ideal for strategic alliances and short- to medium-term objectives. Enhanced collaboration in joint ventures often leads to faster market entry and localized operational advantages.
Disadvantages of Mergers
Mergers often face significant challenges such as cultural clashes between organizations, leading to employee dissatisfaction and reduced productivity. High integration costs and complex regulatory approvals can delay the process, creating financial strain. Furthermore, loss of managerial control and potential layoffs may result in decreased morale and operational disruptions.
Disadvantages of Joint Ventures
Joint ventures often face challenges such as cultural clashes between partnering companies, leading to misaligned goals and operational inefficiencies. Limited control over management decisions can hinder swift execution and strategic alignment, impacting business performance. Shared liabilities and potential conflicts over profit distribution create financial risks that might outweigh the benefits of collaboration.
Factors to Consider When Choosing Between Merger and Joint Venture
When choosing between a merger and a joint venture, consider factors such as control levels, financial commitment, and long-term strategic goals. Mergers involve full integration of companies and often require significant financial and operational commitment, while joint ventures allow collaboration with shared risks and resources without full consolidation. Evaluate cultural compatibility, regulatory implications, and desired duration of the partnership to determine the optimal structure.
Conclusion: Which Is Right for Your Business?
Choosing between a merger and a joint venture depends on your business goals, risk tolerance, and desired level of control. A merger offers full integration and long-term synergy by combining two entities into one, ideal for companies aiming for complete operational unification. In contrast, a joint venture allows for shared resources and expertise without losing independence, making it suitable for businesses seeking collaboration on specific projects or entering new markets with limited commitment.
Merger Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com