Revenue represents the total income generated by a business from its core operations, typically through sales of goods or services. It serves as a crucial indicator of a company's financial health and growth potential. Explore the rest of the article to understand how revenue impacts your business strategy and financial decisions.
Table of Comparison
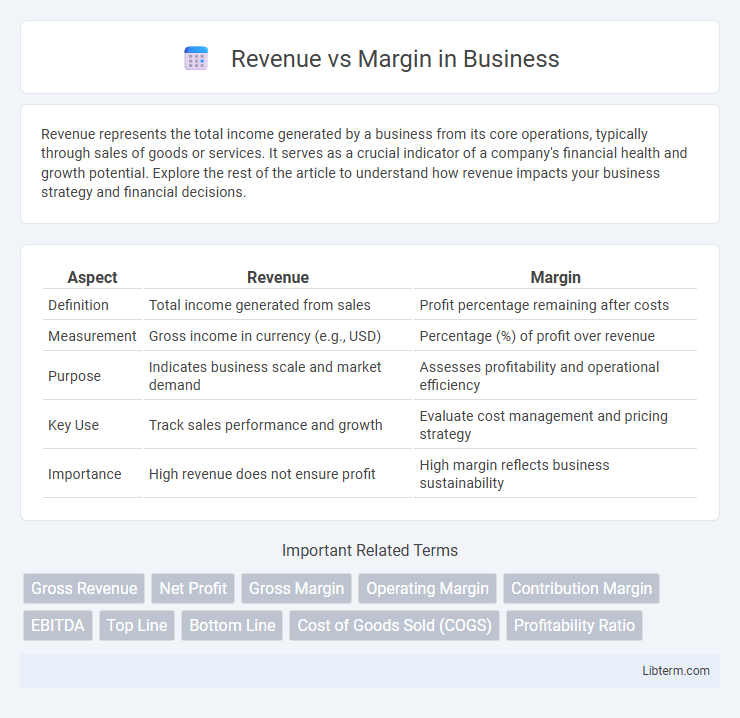
| Aspect | Revenue | Margin |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Total income generated from sales | Profit percentage remaining after costs |
| Measurement | Gross income in currency (e.g., USD) | Percentage (%) of profit over revenue |
| Purpose | Indicates business scale and market demand | Assesses profitability and operational efficiency |
| Key Use | Track sales performance and growth | Evaluate cost management and pricing strategy |
| Importance | High revenue does not ensure profit | High margin reflects business sustainability |
Introduction to Revenue vs Margin
Revenue represents the total income generated from sales before any expenses are deducted, serving as a key indicator of a company's market reach and demand for its products or services. Margin, often expressed as a percentage, measures the profitability by showing the difference between revenue and costs, highlighting operational efficiency and cost management. Understanding the relationship between revenue and margin is crucial for assessing financial health and making informed business decisions.
Defining Revenue: What It Means for Businesses
Revenue represents the total income generated from sales of goods or services before any expenses are deducted, reflecting a business's ability to attract customers and generate demand. It serves as a critical indicator of market reach and operational scale, influencing cash flow and investment potential. Understanding revenue provides insight into overall business performance and growth trajectory, distinct from profit margins that measure cost efficiency and profitability.
Understanding Margin: Types and Importance
Margin represents the percentage of revenue retained as profit after accounting for costs, with key types including gross margin, operating margin, and net margin. Gross margin measures profitability from core production activities, operating margin factors in operating expenses, and net margin reflects overall profitability after taxes and interest. Understanding these margins is crucial for evaluating financial health, pricing strategies, and operational efficiency in business management.
Key Differences Between Revenue and Margin
Revenue represents the total income generated from sales before any expenses are deducted, serving as the top line in financial statements. Margin, often expressed as gross profit margin or net profit margin, indicates the percentage of revenue that remains after covering costs, highlighting profitability. While revenue measures overall business activity, margin provides insight into cost efficiency and financial health.
Why Margin Matters More Than Revenue
Margin matters more than revenue because it directly reflects profitability, showing how much profit a company retains from its sales after covering costs. High revenue can be misleading if margins are low, as expenses might consume most income, leading to minimal or no profit. Focusing on margin ensures sustainable growth and financial health by emphasizing efficient cost management and value creation.
Common Misconceptions About Revenue and Margin
Revenue represents the total income generated from sales before any expenses, while margin reflects the profitability after costs are deducted. A common misconception is that high revenue guarantees high profit margin, but businesses can have substantial revenue with low or negative margins due to high operating costs. Understanding the distinction between gross margin, operating margin, and net margin is crucial for accurately assessing a company's financial health and operational efficiency.
How to Improve Business Margins
Improving business margins requires focusing on cost control, pricing strategies, and operational efficiency. Reducing variable and fixed expenses while optimizing supply chain management directly increases gross and net profit margins. Implementing value-based pricing and enhancing product differentiation can further maximize revenue without proportionally increasing costs.
Revenue Growth vs Margin Expansion: Strategic Choices
Revenue growth drives top-line expansion by increasing sales volume or price points, fueling market share gains and broader customer reach. Margin expansion enhances profitability through cost reduction, operational efficiency, and improved pricing power, maximizing value from existing revenue streams. Strategic choices depend on business goals, market conditions, and competitive landscape, balancing aggressive revenue pursuits with sustainable margin improvements.
Industry Examples: Revenue vs Margin in Practice
In the retail industry, companies like Walmart generate massive revenue through high sales volume but maintain thin profit margins to stay competitive. Conversely, luxury brands such as Hermes prioritize high margins by selling premium products with significant markups despite lower overall revenue. Technology firms like Apple balance substantial revenue with strong margins by leveraging innovation and brand loyalty to command premium pricing.
Conclusion: Balancing Revenue and Margin for Success
Achieving success requires a strategic balance between revenue generation and maintaining healthy profit margins. Prioritizing revenue without regard to margin can lead to unsustainable growth, while focusing solely on margin may limit market share expansion. Businesses must optimize pricing, cost control, and sales volume to ensure long-term profitability and competitive advantage.
Revenue Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com