Shared services streamline organizational processes by consolidating support functions such as HR, IT, and finance into a centralized unit to improve efficiency and reduce costs. This approach enhances service quality through standardized procedures and leverages economies of scale, enabling your business to focus more on core activities. Discover how implementing shared services can transform your operations by reading the full article.
Table of Comparison
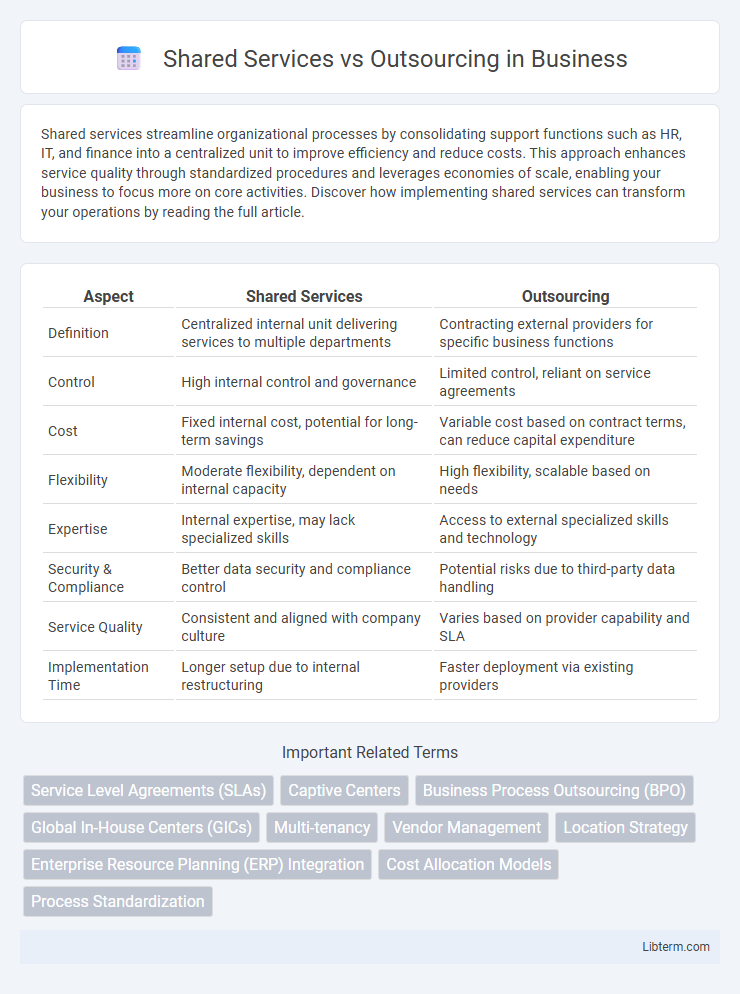
| Aspect | Shared Services | Outsourcing |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Centralized internal unit delivering services to multiple departments | Contracting external providers for specific business functions |
| Control | High internal control and governance | Limited control, reliant on service agreements |
| Cost | Fixed internal cost, potential for long-term savings | Variable cost based on contract terms, can reduce capital expenditure |
| Flexibility | Moderate flexibility, dependent on internal capacity | High flexibility, scalable based on needs |
| Expertise | Internal expertise, may lack specialized skills | Access to external specialized skills and technology |
| Security & Compliance | Better data security and compliance control | Potential risks due to third-party data handling |
| Service Quality | Consistent and aligned with company culture | Varies based on provider capability and SLA |
| Implementation Time | Longer setup due to internal restructuring | Faster deployment via existing providers |
Introduction to Shared Services and Outsourcing
Shared services centralize internal business functions like HR, IT, and finance within an organization, enhancing efficiency through standardized processes and cost reduction. Outsourcing involves contracting external vendors to manage specific services or operations, enabling access to specialized expertise and scalability. Both strategies aim to optimize resource allocation but differ in control, cost structure, and organizational impact.
Key Definitions: What Are Shared Services and Outsourcing?
Shared services refer to the centralized internal provision of business functions, such as finance, IT, or human resources, within an organization to multiple departments or units, aiming to improve efficiency and reduce costs. Outsourcing involves contracting third-party providers to perform specific business processes or services, allowing companies to leverage external expertise and focus on core activities. Key distinctions include ownership, control, and integration, where shared services remain in-house while outsourcing relies on external vendors.
Core Differences Between Shared Services and Outsourcing
Shared Services centralize internal business functions within an organization to improve efficiency and reduce costs, while Outsourcing involves contracting external third-party providers to handle specific tasks or processes. Shared Services retain greater control and alignment with company culture, whereas Outsourcing offers access to specialized expertise and scalability but may involve less direct oversight. The choice depends on strategic priorities such as cost management, control, and resource flexibility.
Advantages of Shared Services
Shared Services offer centralized management of internal business functions, leading to improved operational efficiency and consistent quality control. By leveraging economies of scale within the organization, Shared Services reduce costs and enhance service delivery responsiveness compared to Outsourcing. This model ensures better alignment with company culture and strategic objectives, minimizing risks related to data security and vendor dependence.
Benefits of Outsourcing
Outsourcing offers significant cost savings by leveraging lower labor expenses and reducing overhead related to infrastructure and technology. It enables businesses to access specialized expertise and advanced technologies without investing heavily in recruitment or training. Enhanced scalability and flexibility in operations allow companies to quickly adjust resources based on demand, improving overall efficiency and responsiveness.
Challenges of Implementing Shared Services
Implementing shared services often faces challenges such as resistance to change from employees accustomed to decentralized processes and difficulties in standardizing diverse operational systems across business units. Integrating various legacy technologies and aligning metrics to ensure consistent service levels across departments can hinder efficiency gains and cost savings. Managing governance structures to maintain accountability while fostering collaboration across multiple stakeholders further complicates the effective rollout of shared services models.
Potential Risks of Outsourcing
Outsourcing introduces potential risks such as loss of control over core business processes and exposure to data security breaches. Dependence on third-party vendors may lead to inconsistent service quality and operational disruptions. Contract management complexities and communication barriers further exacerbate the challenges of maintaining seamless business operations.
Cost Comparison: Shared Services vs Outsourcing
Shared services typically provide cost savings by centralizing internal processes, reducing duplication, and leveraging economies of scale within the organization, which often results in lower overhead expenses compared to outsourcing. Outsourcing may offer cost advantages through access to lower labor rates and specialized expertise but can include hidden fees, contract management costs, and potential quality variability. Analyzing total cost of ownership reveals shared services usually have higher upfront investments but deliver long-term cost efficiency, whereas outsourcing offers more variable costs with potential risks impacting overall savings.
Choosing the Right Model for Your Organization
Choosing the right model between shared services and outsourcing depends on your organization's goals for cost efficiency, control, and scalability. Shared services offer greater control and standardization by centralizing functions within the company, while outsourcing provides access to specialized expertise and flexibility often at lower operational costs. Analyzing factors such as internal capabilities, desired service levels, and long-term strategic priorities ensures alignment with organizational objectives and maximizes value.
Future Trends in Shared Services and Outsourcing
Future trends in shared services emphasize automation, artificial intelligence, and data analytics to enhance operational efficiency and decision-making. Outsourcing is evolving with increased focus on strategic partnerships, nearshoring, and integrating advanced technologies like robotic process automation and cloud computing. Both models are converging towards hybrid approaches, leveraging digital transformation to optimize cost savings, agility, and innovation in business processes.
Shared Services Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com