Tailwind CSS offers a utility-first framework that simplifies the process of building custom user interfaces with pre-defined classes for rapid styling. Its mobile-first design approach and responsive utilities allow you to create flexible layouts that adapt seamlessly across devices. Discover how Tailwind CSS can transform your web development workflow by continuing to read the full article.
Table of Comparison
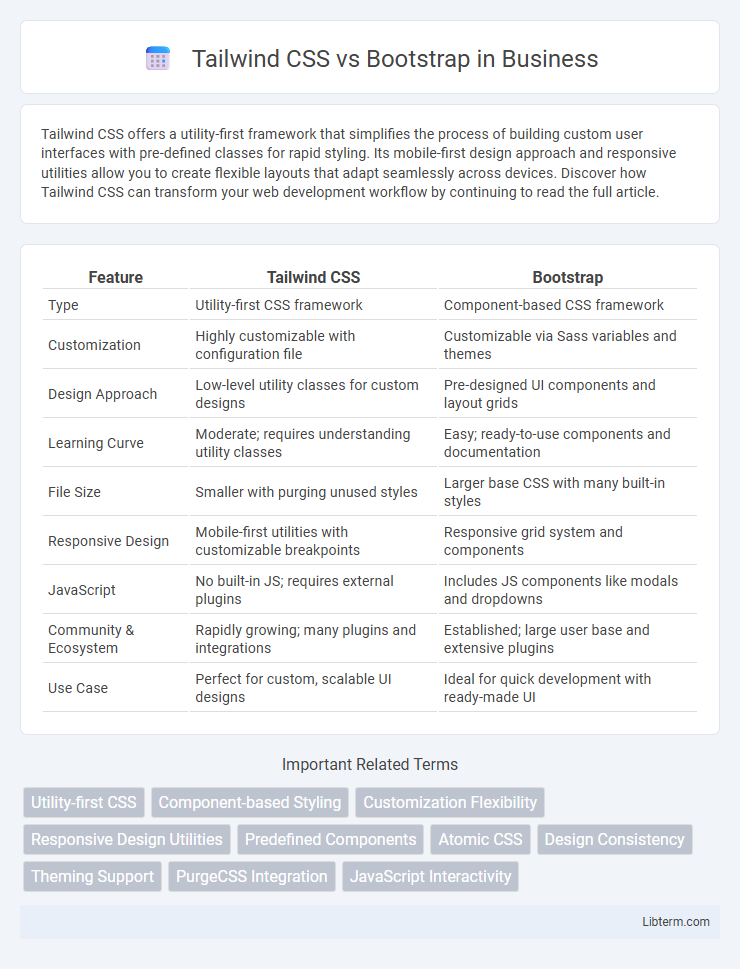
| Feature | Tailwind CSS | Bootstrap |
|---|---|---|
| Type | Utility-first CSS framework | Component-based CSS framework |
| Customization | Highly customizable with configuration file | Customizable via Sass variables and themes |
| Design Approach | Low-level utility classes for custom designs | Pre-designed UI components and layout grids |
| Learning Curve | Moderate; requires understanding utility classes | Easy; ready-to-use components and documentation |
| File Size | Smaller with purging unused styles | Larger base CSS with many built-in styles |
| Responsive Design | Mobile-first utilities with customizable breakpoints | Responsive grid system and components |
| JavaScript | No built-in JS; requires external plugins | Includes JS components like modals and dropdowns |
| Community & Ecosystem | Rapidly growing; many plugins and integrations | Established; large user base and extensive plugins |
| Use Case | Perfect for custom, scalable UI designs | Ideal for quick development with ready-made UI |
Introduction to Tailwind CSS and Bootstrap
Tailwind CSS is a utility-first CSS framework that provides low-level, atomic classes enabling developers to build custom designs without leaving HTML, promoting rapid and flexible styling. Bootstrap is a widely-used front-end framework offering a comprehensive set of pre-designed components and responsive grid systems to streamline interface development. Both frameworks aim to improve development efficiency, yet Tailwind emphasizes design customization through utility classes, while Bootstrap focuses on ready-to-use UI components.
Core Philosophy and Design Principles
Tailwind CSS emphasizes utility-first design by providing low-level, atomic classes that enable developers to build custom interfaces without predefined components, promoting maximum flexibility and minimal CSS bloat. Bootstrap adopts a component-based approach with a robust set of pre-styled UI elements, focusing on rapid prototyping and consistency across projects through a standardized design system. Tailwind encourages design system creation through configuration and customization, while Bootstrap relies on a default, opinionated theme aimed at uniformity and ease of use.
Ease of Use and Learning Curve
Tailwind CSS offers a utility-first approach that allows developers to rapidly style elements using predefined classes, which can reduce the need to write custom CSS and speed up the design process. Bootstrap provides a comprehensive component library with ready-made UI elements, making it easier for beginners to build responsive layouts without deep CSS knowledge. While Bootstrap's predefined components simplify initial learning, Tailwind's flexibility requires more upfront understanding of its utility classes but offers greater customization once mastered.
Customization and Theming Capabilities
Tailwind CSS offers unmatched customization with its utility-first approach, allowing developers to create unique designs by composing small, reusable classes without overriding default styles. Bootstrap provides a robust theming system with predefined components and variables, but customization often requires overriding CSS or using Sass variables, which can be less flexible. For projects emphasizing granular control and bespoke themes, Tailwind CSS enables faster, more maintainable theming compared to Bootstrap's more structured design framework.
Component Libraries and Ecosystem Support
Tailwind CSS offers an extensive ecosystem of utility-first component libraries such as Headless UI and Tailwind UI, providing highly customizable and accessible UI elements that integrate seamlessly with its atomic styling approach. Bootstrap features a comprehensive, well-established component library with pre-styled, responsive components that enable rapid prototyping and consistent design patterns across projects. Both frameworks have strong community support and third-party integrations, but Tailwind's ecosystem emphasizes flexibility and design system scalability, while Bootstrap prioritizes ease of use and out-of-the-box UI consistency.
Performance and File Size Comparison
Tailwind CSS offers a utility-first approach that generates smaller CSS file sizes by including only the classes you use, resulting in faster load times and improved performance compared to Bootstrap's comprehensive component library. Bootstrap's pre-built components and extensive default styles can lead to larger CSS bundles, which may impact initial page rendering speed. By leveraging PurgeCSS and JIT compilation, Tailwind's optimized output significantly reduces unused CSS, enhancing overall application efficiency.
Responsiveness and Grid Systems
Tailwind CSS offers a highly customizable, utility-first approach to responsiveness, allowing developers to control breakpoints and grid layouts with granular precision through predefined classes. Bootstrap provides a robust, mobile-first 12-column grid system with predefined responsive utilities that simplify layout design across devices. Tailwind's flexibility suits developers seeking bespoke designs, while Bootstrap's integrated components and grid system streamline rapid, consistent responsive development.
Community Support and Documentation
Tailwind CSS boasts a rapidly growing community with extensive official documentation, interactive playgrounds, and a rich ecosystem of plugins that enhance customization. Bootstrap remains highly popular with a vast, mature community offering comprehensive documentation, numerous tutorials, and third-party themes for rapid development. Both frameworks provide strong community support, but Tailwind's modern utility-first approach attracts developers seeking flexibility, while Bootstrap's extensive user base ensures abundant resources and troubleshooting help.
Use Cases and Industry Adoption
Tailwind CSS excels in projects requiring highly customized designs with utility-first classes, favored by developers in startups and tech companies for its flexibility and scalability. Bootstrap is widely adopted in enterprise and legacy systems due to its comprehensive pre-built components and grid system, enabling faster development for standard, responsive layouts. Industry adoption trends show Tailwind gaining traction among frontend developers prioritizing performance and design control, while Bootstrap remains dominant in conservative industries like finance and healthcare where consistent UI frameworks are critical.
Conclusion: Which Framework Should You Choose?
Tailwind CSS offers unmatched customization and a utility-first approach, making it ideal for developers prioritizing design flexibility and performance optimization. Bootstrap provides a robust set of pre-styled components and a grid system, suitable for rapid prototyping and consistent UI across large projects. Choosing between Tailwind CSS and Bootstrap depends on your project's complexity, design requirements, and development speed preferences.
Tailwind CSS Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com