Duty of confidentiality requires professionals to protect sensitive information entrusted to them, ensuring it is not disclosed without proper authorization. This ethical obligation builds trust between parties and safeguards privacy, which is critical in fields such as law, medicine, and business. Explore the rest of the article to understand how this duty impacts your responsibilities and legal implications.
Table of Comparison
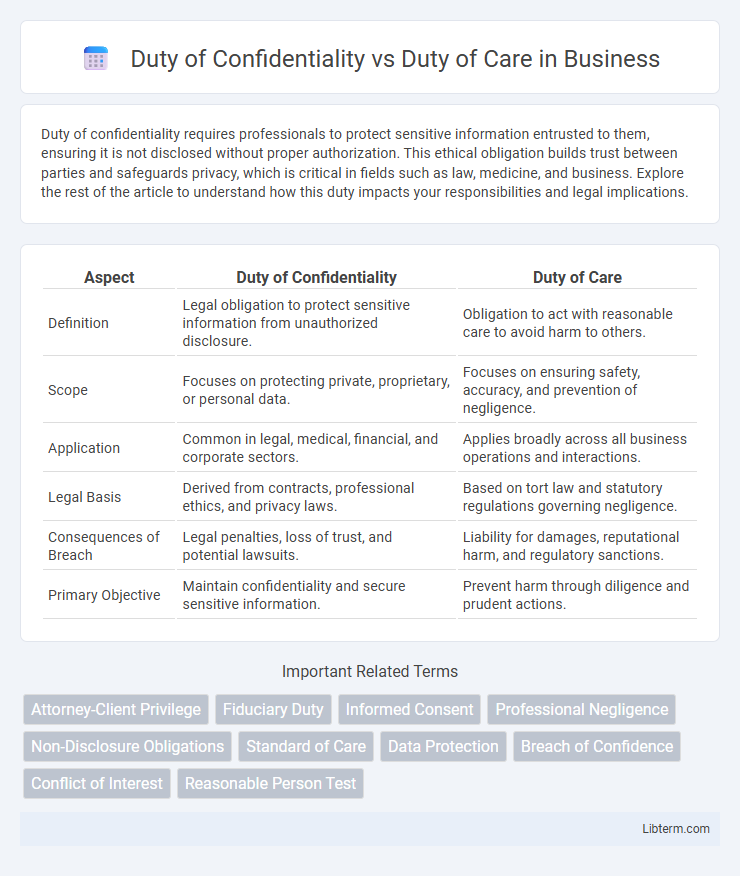
| Aspect | Duty of Confidentiality | Duty of Care |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Legal obligation to protect sensitive information from unauthorized disclosure. | Obligation to act with reasonable care to avoid harm to others. |
| Scope | Focuses on protecting private, proprietary, or personal data. | Focuses on ensuring safety, accuracy, and prevention of negligence. |
| Application | Common in legal, medical, financial, and corporate sectors. | Applies broadly across all business operations and interactions. |
| Legal Basis | Derived from contracts, professional ethics, and privacy laws. | Based on tort law and statutory regulations governing negligence. |
| Consequences of Breach | Legal penalties, loss of trust, and potential lawsuits. | Liability for damages, reputational harm, and regulatory sanctions. |
| Primary Objective | Maintain confidentiality and secure sensitive information. | Prevent harm through diligence and prudent actions. |
Understanding the Duty of Confidentiality
The Duty of Confidentiality requires professionals to protect sensitive information entrusted to them, ensuring it is not disclosed without proper authorization. This duty is fundamental in maintaining trust between parties, particularly in legal, medical, and financial contexts. Understanding its scope involves recognizing the limits on sharing information, which differ from the broader Duty of Care that emphasizes overall responsibility to act in another's best interest.
Defining the Duty of Care
The Duty of Care is a legal obligation requiring individuals or entities to exercise reasonable caution to prevent harm to others, primarily in professional or contractual relationships. It mandates adherence to established standards and protocols to avoid negligence that could result in injury or loss. The Duty of Care contrasts with the Duty of Confidentiality, which specifically pertains to protecting sensitive information from unauthorized disclosure.
Key Differences Between Duty of Confidentiality and Duty of Care
Duty of Confidentiality obligates professionals to protect sensitive information shared by clients from unauthorized disclosure, ensuring privacy and trust. Duty of Care requires individuals to act with reasonable caution and prudence to avoid causing harm or injury to others in foreseeable situations. The key difference lies in Duty of Confidentiality focusing on information protection, while Duty of Care centers on preventing physical or financial harm through responsible conduct.
Legal Foundations of Confidentiality
The Duty of Confidentiality is grounded in legal principles such as solicitor-client privilege, medical ethics, and data protection laws like GDPR, ensuring sensitive information remains protected from unauthorized disclosure. The Duty of Care mandates that professionals act with reasonable competence and diligence to prevent harm to clients or patients, often supported by statutory obligations and common law precedents. Both duties intersect legally, with confidentiality protections reinforcing the standard of care required in professional and fiduciary relationships.
Legal Foundations of Care
The Duty of Confidentiality is legally grounded in privacy laws and ethical standards requiring professionals to protect sensitive client information from unauthorized disclosure. The Duty of Care, established through negligence law, mandates that professionals provide services with reasonable skill, prudence, and caution to prevent harm to clients. Courts enforce both duties to uphold trust and accountability in professional relationships, emphasizing legal responsibilities in care provision.
Real-World Examples: Confidentiality Breaches
Duty of Confidentiality requires professionals to protect sensitive client information, as illustrated by data leaks in healthcare where patient records are exposed due to insufficient safeguards. Duty of Care mandates that professionals act with reasonable caution to prevent harm, demonstrated by financial advisors facing lawsuits after negligent advice leads to client losses. Real-world confidentiality breaches, such as unauthorized sharing of trade secrets in corporate settings, highlight the intersection where failure in confidentiality can simultaneously constitute a breach of duty of care.
Case Studies: Breaches in Duty of Care
Case studies of breaches in Duty of Care reveal critical lapses where professionals failed to meet legal and ethical obligations, resulting in harm or loss to clients or patients. Examples include medical malpractice cases where negligence led to injury, and legal negligence where inadequate advice caused financial damage. These breaches illustrate the importance of maintaining strict adherence to the Duty of Care to prevent liability and ensure trust in professional relationships.
Balancing Confidentiality and Care in Professional Settings
Balancing the duty of confidentiality with the duty of care in professional settings requires careful navigation to protect client privacy while addressing their well-being. Professionals must ensure that sensitive information remains secure unless disclosure is necessary to prevent harm or comply with legal obligations. Effective practices include informed consent, clear communication about confidentiality limits, and adherence to ethical guidelines set by regulatory bodies.
Consequences of Breaching Each Duty
Breaching the Duty of Confidentiality can lead to severe legal penalties, including lawsuits for damages, loss of professional licenses, and reputational harm due to unauthorized disclosure of sensitive information. Violating the Duty of Care often results in negligence claims, financial liabilities, and potential criminal charges when harm to individuals or entities occurs from failure to meet established standards. Both breaches undermine trust and may trigger regulatory investigations, but confidentiality breaches primarily affect information security, while care breaches impact overall safety and welfare.
Best Practices for Upholding Both Duties
Maintaining the duty of confidentiality and duty of care requires strict adherence to secure information management protocols and continuous professional training to ensure ethical handling of sensitive data. Best practices include implementing encrypted communication channels, conducting regular audits to detect potential breaches, and fostering a culture of transparency and accountability within organizations. Clear documentation of decisions and actions strengthens legal compliance and helps balance patient or client trust with professional responsibility.
Duty of Confidentiality Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com