A joint venture is a strategic business arrangement where two or more parties pool resources to achieve a specific goal while sharing risks and rewards. This collaboration enhances innovation, market access, and operational efficiencies by leveraging each partner's strengths. Discover how a joint venture can unlock new opportunities and drive growth for your business in the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
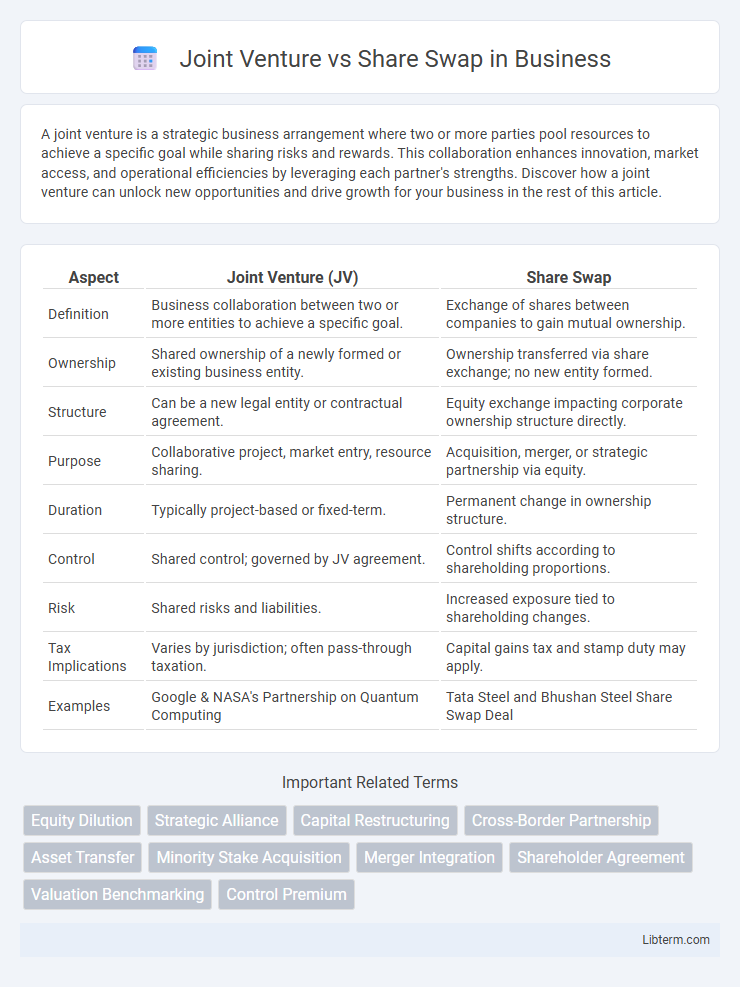
| Aspect | Joint Venture (JV) | Share Swap |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Business collaboration between two or more entities to achieve a specific goal. | Exchange of shares between companies to gain mutual ownership. |
| Ownership | Shared ownership of a newly formed or existing business entity. | Ownership transferred via share exchange; no new entity formed. |
| Structure | Can be a new legal entity or contractual agreement. | Equity exchange impacting corporate ownership structure directly. |
| Purpose | Collaborative project, market entry, resource sharing. | Acquisition, merger, or strategic partnership via equity. |
| Duration | Typically project-based or fixed-term. | Permanent change in ownership structure. |
| Control | Shared control; governed by JV agreement. | Control shifts according to shareholding proportions. |
| Risk | Shared risks and liabilities. | Increased exposure tied to shareholding changes. |
| Tax Implications | Varies by jurisdiction; often pass-through taxation. | Capital gains tax and stamp duty may apply. |
| Examples | Google & NASA's Partnership on Quantum Computing | Tata Steel and Bhushan Steel Share Swap Deal |
Understanding Joint Ventures: Definition and Purpose
A joint venture (JV) is a strategic business arrangement where two or more parties pool resources, expertise, and capital to achieve specific objectives while remaining independent entities. Its primary purpose is to leverage complementary strengths, share risks, and access new markets or technologies without a full merger or acquisition. Unlike share swaps, which involve exchanging equity stakes to restructure ownership, joint ventures create a separate legal entity focused on collaborative projects.
What Is a Share Swap? Explained
A share swap is a financial transaction where one company exchanges its shares for the shares of another company, enabling mergers or acquisitions without immediate cash payments. This method is commonly used in joint ventures to align the interests of involved parties by granting equity stakes rather than direct capital investments. Share swaps facilitate strategic partnerships and business expansion by combining resources and expertise through equity ownership.
Key Differences Between Joint Ventures and Share Swaps
Joint ventures involve two or more companies pooling resources to create a new business entity where profits, losses, and control are shared, whereas share swaps are transactions where shareholders exchange shares of one company for shares in another without forming a separate entity. Joint ventures typically focus on collaborative projects with joint management, while share swaps often facilitate mergers or acquisitions, altering ownership structures without operational integration. The key difference lies in the operational collaboration of joint ventures versus the ownership restructuring of share swaps.
Legal Structures and Requirements
Joint ventures require a formal agreement defining the partnership's scope, profit-sharing, and governance, often necessitating registration as a new legal entity under corporate or partnership law. Share swaps involve exchanging equity interests between companies, typically governed by securities regulations and corporate laws to ensure proper valuation, disclosure, and shareholder approval. Both structures demand compliance with jurisdiction-specific statutory requirements, regulatory filings, and adherence to corporate governance standards to validate the transaction and protect stakeholder rights.
Financial Implications: Joint Venture vs Share Swap
Joint ventures involve pooling resources and sharing profits, liabilities, and capital expenditures, which can impact cash flow and earnings volatility for both parties. Share swaps typically result in changes to ownership percentages without immediate cash flow effects but can dilute existing shareholders and alter control dynamics. Financial implications vary as joint ventures require ongoing capital commitment and profit sharing, whereas share swaps influence share valuation and equity structure more directly.
Strategic Benefits for Businesses
Joint ventures enable businesses to pool resources, share risks, and access new markets, fostering innovation and competitive advantage through collaborative expertise. Share swaps facilitate strategic ownership alignment, allowing companies to consolidate control, optimize capital structure, and enhance shareholder value without immediate cash outflows. Both methods drive growth and expansion by leveraging complementary strengths and creating synergies tailored to specific business objectives.
Risks and Challenges Involved
Joint ventures involve shared control and resource pooling, exposing partners to risks such as cultural clashes, management conflicts, and uneven commitment levels, which can lead to operational inefficiencies. Share swaps, often involving equity exchanges between companies, pose challenges like valuation discrepancies, dilution of ownership, and regulatory compliance issues, potentially affecting shareholder value. Both arrangements require thorough due diligence and clear contractual agreements to mitigate risks associated with integration and strategic alignment.
Tax Considerations in Both Structures
Tax considerations in joint ventures often involve income splitting, potential double taxation, and the treatment of profits and losses at the entity level, affecting overall tax liability. In share swaps, tax implications center on capital gains realization, deferment opportunities, and the possibility of tax-free reorganizations under specific legal frameworks. Understanding the tax treatment of asset transfers, dividend distributions, and ownership changes is crucial to optimizing tax efficiency in both joint venture and share swap structures.
Real-World Examples and Case Studies
In the real estate sector, the joint venture between Brookfield Property Partners and CIM Group exemplifies how shared expertise drives large-scale urban developments, while Tata Steel's share swap with Bhushan Steel highlighted strategic asset consolidation to optimize production capacity. Joint ventures often facilitate combining complementary strengths and resources in projects like infrastructure or technology, as seen in the collaboration between Sony and Ericsson. Conversely, share swaps allow companies to realign ownership structures and achieve synergies without immediate cash flow, demonstrated by Vodafone's share swap with Idea Cellular to strengthen their telecom presence in India.
Choosing the Right Option: Factors to Consider
Selecting between a joint venture and a share swap depends on the strategic goals, control preferences, and financial implications for the companies involved. Joint ventures offer collaborative project-specific advantages with shared risks, while share swaps facilitate equity ownership and long-term integration without immediate cash transactions. Key considerations include alignment of business objectives, valuation accuracy, regulatory compliance, and the desired level of operational control in the partnership.
Joint Venture Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com